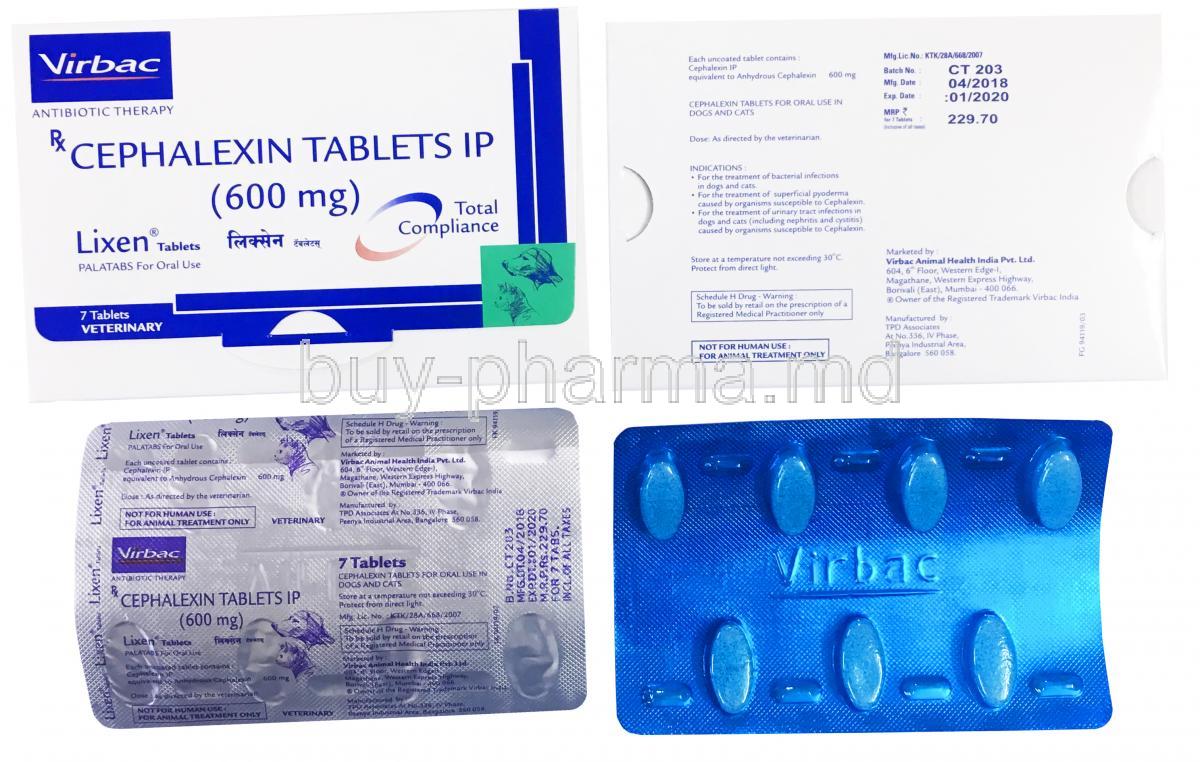
1. Introduction to Lixen (Cephalexin Monohydrate)
Lixen, formulated with the active ingredient Cephalexin Monohydrate, belongs to the first-generation class of cephalosporin antibiotics. This well-established antimicrobial agent is predominantly prescribed for the treatment of various bacterial infections. Cephalexin is renowned for its broad application in primary care and infectious disease management due to its excellent efficacy and favorable safety profile.
Originally approved in the late 1960s, Cephalexin has maintained a long-standing presence in both hospital and outpatient settings. It is included on the World Health Organization’s List of Essential Medicines. In global pharmaceutical markets, Lixen is available as both a branded and generic medication under various trade names, allowing broad access across regions.
Therapeutically, Lixen is distributed in multiple oral dosage forms including capsules, tablets, and oral suspensions. Available strengths typically range from 125 mg to 1000 mg, accommodating patients across age groups and infection severity.
2. Composition and Pharmacological Profile
The principal active ingredient in Lixen is Cephalexin Monohydrate, a beta-lactam antibiotic that exhibits bactericidal activity. It is designed for systemic action following oral administration and is structurally classified under the cephalosporin subgroup of beta-lactam antibiotics.
- Dosage forms: 125 mg/5 mL and 250 mg/5 mL oral suspensions, 250 mg and 500 mg capsules or tablets
- Excipients: May include microcrystalline cellulose, magnesium stearate, and coloring agents depending on the formulation
Cephalexin’s chemical structure shares a β-lactam ring, integral to its function, and resembles penicillin derivatives, yet offers enhanced stability and reduced allergic cross-reactivity in some cases.
3. How Lixen Works: Mechanism of Action
Cephalexin operates by targeting bacterial cell wall synthesis. It binds to specific penicillin-binding proteins (PBPs), inhibiting the transpeptidation step of peptidoglycan cross-linking, a crucial process in bacterial cell wall integrity. The result is osmotic instability and eventual bacterial lysis.
- Spectrum: Effective primarily against Gram-positive cocci (e.g., Streptococcus spp., Staphylococcus aureus) and select Gram-negative bacilli (e.g., E. coli)
- Bactericidal effect: Lixen acts by killing bacteria rather than merely suppressing their growth
- Pharmacodynamics: Demonstrates time-dependent killing, making proper dosing intervals essential
4. Approved Medical Uses of Lixen
Lixen is indicated for the treatment of a variety of infections caused by susceptible organisms. Its efficacy in uncomplicated and moderate infections makes it a first-line agent in numerous clinical scenarios:
- Upper respiratory tract infections: Pharyngitis, tonsillitis due to Streptococcus pyogenes
- Lower respiratory tract infections: Acute bronchitis and mild pneumonia
- Skin and soft tissue infections: Impetigo, folliculitis, cellulitis, infected wounds
- Urinary tract infections: Acute cystitis and uncomplicated UTIs in adults and children
- Otitis media: Especially effective in pediatric patients
- Bone infections: Osteomyelitis caused by susceptible staphylococci and streptococci
5. Off-Label Uses and Emerging Applications
While Lixen is primarily used for approved infections, clinical experience and evolving guidelines have supported several off-label applications:
- Dental prophylaxis: Alternative to amoxicillin in patients with penicillin allergy prior to dental procedures
- Recurrent UTIs: Used in low-dose suppressive therapy protocols
- Diverticulitis: Occasionally used in combination with metronidazole for mild, uncomplicated cases
- Acne vulgaris: Particularly when caused by Gram-positive bacteria like P. acnes
- Veterinary use: Commonly prescribed for dogs and cats with respiratory, skin, and urinary infections
6. Dosage and Administration Guidelines
The dosage of Lixen is contingent on the infection type, severity, and patient-specific factors such as age and renal function.
- Adults: 250–500 mg every 6 hours, with a maximum of 4 grams per day
- Children: 25–50 mg/kg/day divided into multiple doses
- Renal impairment: Dosage interval must be extended based on creatinine clearance levels
- Duration: 7 to 14 days, depending on infection
Lixen may be taken with or without food. However, administering with food can help minimize gastrointestinal discomfort. In case of a missed dose, patients should take it as soon as remembered unless it's close to the next scheduled dose.
7. Common and Serious Side Effects of Lixen
Like all medications, Lixen can cause side effects. Most are mild and self-limiting, but serious reactions can occur in rare instances.
- Common effects: Diarrhea, nausea, vomiting, dyspepsia
- Allergic responses: Rash, urticaria, pruritus, and rarely, anaphylaxis
- Severe reactions: Stevens-Johnson Syndrome, toxic epidermal necrolysis, interstitial nephritis
- Gastrointestinal: Risk of antibiotic-associated colitis due to Clostridium difficile
Monitoring for rash, unusual fatigue, or gastrointestinal bleeding is advised. Patients should report any adverse events to their healthcare provider promptly.
8. Drug Interactions and Potential Conflicts
Lixen can interact with various drugs, potentially altering its efficacy or increasing the risk of adverse effects.
- Probenecid: Reduces renal excretion of cephalexin, increasing plasma levels
- Bacteriostatic antibiotics: May reduce the bactericidal effect of Lixen
- Oral contraceptives: Cephalexin may reduce hormonal contraceptive efficacy
- Diagnostic tests: May yield false-positive results for urinary glucose (Benedict’s or Fehling’s solution)
9. Contraindications and Situations to Avoid Use
Lixen should be avoided in patients with specific medical histories or sensitivities:
- Hypersensitivity: Known allergy to cephalosporins or other beta-lactam antibiotics
- Severe allergic reactions: History of anaphylaxis or severe cutaneous reactions to antibiotics
- Metabolic conditions: Formulations containing lactose are contraindicated in patients with hereditary galactose intolerance or lactase deficiency
Caution is advised when prescribing to individuals with prior severe penicillin allergy due to possible cross-reactivity.
10. Important Precautions Before and During Use
Before initiating therapy with Lixen (Cephalexin Monohydrate), several precautionary considerations must be addressed to ensure optimal treatment outcomes and to mitigate avoidable risks.
- Penicillin Allergy History: Due to structural similarities between cephalosporins and penicillins, there is a known risk of cross-reactivity. Patients with a documented history of severe penicillin allergy, such as anaphylaxis or Stevens-Johnson Syndrome, should be prescribed Lixen with extreme caution or offered alternative treatments.
- Preexisting Gastrointestinal Conditions: Individuals with a history of gastrointestinal diseases, especially colitis (including Clostridium difficile-associated diarrhea), should be closely monitored, as antibiotic use may exacerbate these conditions.
- Renal Function Evaluation: Cephalexin is primarily eliminated via the kidneys. A baseline assessment of renal function is recommended before initiating treatment, particularly in elderly patients or those with known renal impairment.
- Prolonged Use and Superinfection: Extended courses of therapy may result in overgrowth of non-susceptible organisms, including fungi or resistant bacteria. Monitoring for signs of superinfection is essential, and treatment should be adjusted accordingly if secondary infections arise.
11. Careful Administration in Special Populations
11.1 Use in Elderly Patients
Older adults often exhibit decreased physiological reserve, including reduced renal clearance, which affects drug metabolism and excretion. Careful administration of Lixen in this group is critical.
- Renal Function Monitoring: Creatinine clearance should be estimated before initiating treatment and monitored periodically during prolonged courses of therapy.
- Nephrotoxicity Risk: Though Cephalexin has a relatively low nephrotoxic profile, elderly patients may be more vulnerable to renal stress, especially when combined with other nephrotoxic agents.
- Dose Accumulation: Impaired elimination may lead to plasma drug accumulation and heighten the risk of adverse effects, necessitating dose adjustments.
11.2 Use in Pregnant and Breastfeeding Women
Cephalexin is categorized as Pregnancy Category B by the FDA, suggesting a favorable safety profile based on animal reproduction studies, although well-controlled studies in humans are lacking.
- Pregnancy Safety: No evidence of fetal harm has been demonstrated in animal studies. Cephalexin is commonly used when antibiotics are indicated during pregnancy.
- Breastfeeding Considerations: The drug is excreted in small quantities in breast milk. While generally considered safe, infants should be monitored for gastrointestinal disturbances or allergic reactions.
- Risk-Benefit Analysis: The decision to use Lixen during pregnancy or lactation should be guided by a clinical risk-benefit assessment, balancing infection severity against fetal or neonatal exposure.
11.3 Use in Pediatric Populations
Lixen is frequently prescribed in pediatric medicine, with established efficacy and safety when dosed appropriately.
- Clinical Use in Children: Cephalexin is indicated for a range of infections in children, including otitis media, pharyngitis, and urinary tract infections.
- Age- and Weight-Based Dosing: Pediatric dosing typically ranges from 25–50 mg/kg/day, divided into multiple doses. Adjustments must be carefully calculated to avoid under- or overdosing.
- Neonatal Use: Routine administration in neonates is not generally recommended due to immature renal function and limited pharmacokinetic data in this age group.
12. Overdose and Emergency Management
An overdose of Lixen, while uncommon, can result in significant clinical manifestations requiring urgent intervention.
- Clinical Symptoms: Signs of overdose may include intense nausea, persistent vomiting, epigastric distress, diarrhea, and in some cases, hematuria (blood in the urine).
- Immediate Response: Gastric lavage or induced emesis may be considered in cases of recent ingestion. Supportive therapy—hydration, electrolyte correction, and symptomatic relief—is typically sufficient.
- Hemodialysis: In patients with renal dysfunction or severe toxicity, hemodialysis may facilitate the elimination of Cephalexin and should be considered when indicated.
13. Handling and Storage Recommendations
Proper storage and handling of Lixen ensure the stability and efficacy of the medication throughout its shelf life.
- Storage Conditions: Capsules and tablets should be stored at controlled room temperature, typically between 15°C and 30°C. Reconstituted oral suspension must be refrigerated and used within 14 days.
- Shelf Life: Each formulation includes an expiration date provided by the manufacturer. Products should not be used past this date due to potential degradation.
- Disposal: Unused or expired medication should be disposed of in accordance with local pharmaceutical waste guidelines. Flushing or discarding in household trash is discouraged.
14. Handling Precautions for Safe Use
To maintain therapeutic efficacy and prevent unintended outcomes, proper handling and usage practices must be followed.
- Reconstitution of Suspension: The oral suspension should be reconstituted with the exact amount of water specified on the label. The bottle must be shaken well before each dose.
- Child Safety: All formulations should be kept in child-resistant containers and stored out of reach of children to prevent accidental ingestion.
- Antibiotic Stewardship: Cephalexin should only be used for bacterial infections as prescribed. Unnecessary or incorrect usage contributes to the development of antibiotic resistance.