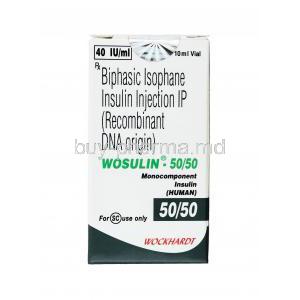
Univia-Mix Biphasic Isophane Insulin
- Introduction to Univia-Mix Biphasic Isophane Insulin
- Medical and Off-Label Uses of Univia-Mix Biphasic Isophane Insulin
- Mechanism of Action: How Univia-Mix Biphasic Isophane Insulin Works
- Dosage and Administration Guidelines
- Composition and Available Strengths
- Potential Side Effects of Univia-Mix Biphasic Isophane Insulin
- Important Warnings and Safety Considerations
- Contraindications for Use of Univia-Mix Biphasic Isophane Insulin
- Drug Interactions and Impact on Blood Glucose Control
- Special Considerations for Careful Administration
- Important Precautions and Risk Management
- Overdose and Emergency Management
- Storage and Stability of Univia-Mix Biphasic Isophane Insulin
- Handling Precautions and Patient Safety Measures
Introduction to Univia-Mix Biphasic Isophane Insulin
Medical and Off-Label Uses of Univia-Mix Biphasic Isophane Insulin
2.1 Approved Therapeutic Uses
2.2 Off-Label and Investigational Uses
Mechanism of Action: How Univia-Mix Biphasic Isophane Insulin Works
Dosage and Administration Guidelines
4.1 General Dosage Recommendations
4.2 Administration Instructions
Composition and Available Strengths
Potential Side Effects of Univia-Mix Biphasic Isophane Insulin
6.1 Common Side Effects
6.2 Less Common and Serious Side Effects
Important Warnings and Safety Considerations
Contraindications for Use of Univia-Mix Biphasic Isophane Insulin
Drug Interactions and Impact on Blood Glucose Control
Special Considerations for Careful Administration
10.1 Administration in Elderly Patients
10.2 Use in Pregnant and Breastfeeding Women
10.3 Use in Pediatric Patients
Important Precautions and Risk Management
Overdose and Emergency Management
Storage and Stability of Univia-Mix Biphasic Isophane Insulin
Handling Precautions and Patient Safety Measures
Univia-Mix Biphasic Isophane Insulin FAQ
- What is biphasic isophane insulin used for?
- What are mixed or biphasic insulins?
- When should I take biphasic insulin?
- Do you give isophane insulin before or after food?
- How to use biphasic Isophane Insulin injection?
- What type of insulin is biphasic isophane?
- What is the difference between regular insulin and isophane insulin?
- What is biphasic isophane insulin 50 50?
- What is the meaning of isophane?
- Which patients would best suit biphasic insulin?
- What are the benefits of biphasic isophane insulin?
- What is the duration of action of biphasic isophane insulin?
- Is biphasic insulin long-acting?
What is biphasic isophane insulin used for?
Combining Biphasic Isophane Insulin with insulin creates a treatment that includes both short-lasting types of insulin, for managing type 1 and type 2 diabetes in adults and children by regulating blood sugar levels effectively.
What are mixed or biphasic insulins?
A biphasic insulin formulation combines short-lasting insulin with a long-lasting insulin, in set ratios.
When should I take biphasic insulin?
You typically need to administer insulin twice daily: once before breakfast and then again before your evening meal.
Do you give isophane insulin before or after food?
You can opt to receive the injection 15 minutes before a meal or right after eating.
How to use biphasic Isophane Insulin injection?
After receiving an injection, it's recommended to have a meal or snack with carbohydrates within 30 minutes.The dosage of insulin varies based on the patient's needs, typically falling between 1 and 1 IU/kg/day.
What type of insulin is biphasic isophane?
Insulin isophane is a type of insulin made in a lab through modification, designed to act as an intermediate insulin with a longer duration of action.
What is the difference between regular insulin and isophane insulin?
Insulin isophane is considered intermediate-duration insulin, while regular insulin is known as short-duration insulin.
What is biphasic isophane insulin 50 50?
The Biphasic Isophane Insulin consists of a blend of insulin and Isophane (also known as NPH insulin).
What is the meaning of isophane?
The ratio of protamine to insulin is the same as in a solution created by combining amounts of a solution where all the protamine settles out and a solution where all the insulin settles out.
Which patients would best suit biphasic insulin?
Biphasic insulins are one of the key treatment options for patients with postprandial hyperglycaemia.
What are the benefits of biphasic isophane insulin?
It aids in the absorption of sugar in muscles and fat cells, which leads to a reduction in liver sugar production and helps blood sugar levels after meal intake while reducing the risk of diabetes related complications.
What is the duration of action of biphasic isophane insulin?
The effects can last for up to 24 hours, with the peak impact occurring between 6 and 8 hours after taking action.
Is biphasic insulin long-acting?
A biphasic insulin combines a fast or short-term insulin with a moderate duration insulin in ratios.