Introduction
Overview of Veltam-F and Its Therapeutic Class
Veltam-F is a fixed-dose combination therapy designed for the management of benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH). It integrates two distinct pharmacological classes: an alpha-1 adrenergic receptor blocker (Tamsulosin) and a 5-alpha-reductase inhibitor (Finasteride). By addressing both dynamic and static components of BPH, Veltam-F provides a dual mechanism for symptom relief and long-term disease modification.
Brief History and Development of Combination Therapy for Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH)
The evolution of treatment for BPH has spanned several decades. Initially, therapies focused solely on symptom alleviation with alpha-blockers. Later, 5-alpha-reductase inhibitors were introduced to modify disease progression. The recognition that monotherapy could not address both symptom severity and long-term outcomes led to the development of combination regimens, culminating in formulations such as Veltam-F.
Difference Between Monotherapy and Combination Therapy
Monotherapy with either Tamsulosin or Finasteride provides partial benefit. Tamsulosin improves urinary flow but does not reduce prostate size, while Finasteride decreases prostate volume but requires months to achieve noticeable improvement. Combination therapy integrates these benefits:
- Tamsulosin alone: Immediate relief from urinary symptoms but limited long-term disease modification.
- Finasteride alone: Reduction in disease progression but slower onset of symptom relief.
- Veltam-F combination: Rapid symptomatic relief with long-term structural benefits.
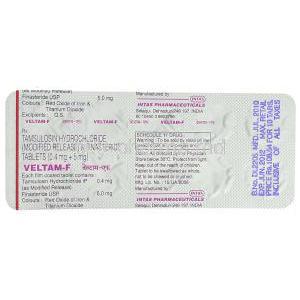
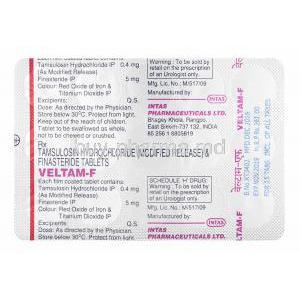
Composition and Active Ingredients
Tamsulosin: Pharmacological Classification
Tamsulosin is classified as an alpha-1 adrenergic receptor antagonist. It selectively targets receptors located in the prostate and bladder neck, thereby reducing smooth muscle tone without significant systemic hypotension.
Finasteride: Pharmacological Classification
Finasteride belongs to the class of 5-alpha-reductase inhibitors. It blocks the enzymatic conversion of testosterone to dihydrotestosterone (DHT), the principal androgen responsible for prostatic enlargement.
Inactive Excipients and Formulation Details
In addition to its active ingredients, Veltam-F contains excipients that ensure stability, bioavailability, and ease of administration. These include microcrystalline cellulose, lactose monohydrate, magnesium stearate, and other pharmaceutical binders. The formulation is designed for once-daily oral intake.
Alfuzosin vs Tamsulosin
tamsulosin has a higher specificity for alpha-1A receptors, leading to fewer blood pressure-related side effects, while alfuzosin may have a better tolerability profile with fewer ejaculatory side effects and is sometimes a better option for patients with a sulfa allergy
Finasteride vs tamsulosin
Both medications help with urinary symptoms of BPH, such as a weak urine stream. Finasteride works by reducing the size of the prostate, which relieves pressure on the urethra (the tube that empties the bladder). Tamsulosin works by relaxing muscles in the prostate and bladder, improving urine flow.
Silodosin vs tamsulosin
Silodosin is more selective for the alpha-1A receptor, potentially causing less orthostatic hypotension, while tamsulosin blocks alpha-1A and alpha-1D receptors. Silodosin also has a higher risk of retrograde ejaculation, whereas tamsulosin carries a higher risk of headaches and dizziness.
Terazosin vs tamsulosin
Terazosin is taken once daily at bedtime, while tamsulosin should be taken 30 minutes after the same meal each day. Both medications are available as a lower-cost generic. Common side effects of terazosin include dizziness and weakness, while tamsulosin can cause headaches, dizziness, and abnormal ejaculation.
Doxazosin vs tamsulosin
Tamsulosin is considered a first-choice treatment for BPH, whereas doxazosin is not a first-choice for high blood pressure. Both medications can cause dizziness and low blood pressure, but tamsulosin is less likely to cause a sudden drop in blood pressure upon standing.
Dutasteride vs finasteride
both are similar in how well they work for reducing BPH symptoms. Finasteride starts working more quickly, but dutasteride generally shrinks the prostate more.
Finasteride and minoxidil
Finasteride and minoxidil are common, but different, treatments for hair loss (androgenetic alopecia) that work through different mechanisms. Finasteride, typically an oral medication, blocks dihydrotestosterone (DHT), the hormone responsible for shrinking hair follicles. Minoxidil, a topical solution or foam, acts as a vasodilator, increasing blood flow to the scalp and providing nutrients and oxygen to hair follicles to stimulate growth.
How Veltam-F Works
Mechanism of Action of Tamsulosin
Tamsulosin reduces adrenergic stimulation in prostatic tissue and bladder outlet. This relaxation of smooth muscle improves urinary flow, diminishes urgency, and decreases residual urine volume. Patients often notice relief within days of initiation.
Mechanism of Action of Finasteride
Finasteride lowers circulating and intraprostatic DHT levels, leading to gradual shrinkage of the prostate gland. This structural reduction mitigates obstruction and lowers the risk of acute urinary retention or the need for surgical procedures.
Combined Effect in Alleviating Symptoms
The synergy of Tamsulosin and Finasteride ensures both rapid and sustained therapeutic benefit:
- Immediate symptom relief from smooth muscle relaxation.
- Progressive reduction in prostate size and long-term risk reduction.
- Overall improvement in patient-reported symptom scores and quality of life.
Approved Medical Uses
Treatment of Moderate to Severe Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH)
Veltam-F is indicated for men experiencing significant lower urinary tract symptoms due to BPH. It is prescribed when monotherapy is insufficient or when both symptom relief and disease progression control are required.
Prevention of Acute Urinary Retention and Need for Surgical Intervention
By lowering the likelihood of urinary retention, Veltam-F reduces the chances of catheterization or surgical intervention. Long-term use is associated with reduced incidence of transurethral resection of the prostate (TURP) and other invasive procedures.
Improvement in Urinary Flow Rate and Symptom Scores
Clinical trials demonstrate significant increases in maximum urinary flow rate (Qmax) and reductions in International Prostate Symptom Scores (IPSS) compared with monotherapy regimens.
Off-Label Uses
Potential Role in Chronic Urinary Retention
Though not formally approved, Veltam-F may be used in select cases of chronic urinary retention to prevent recurrence following catheter removal.
Management of Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms Beyond BPH
Some clinicians extend its use to other lower urinary tract dysfunctions, such as bladder outlet obstruction not solely attributable to prostate enlargement.
Investigational Use in Reducing Prostate Cancer Risk
Finasteride has been studied for its role in chemoprevention of prostate cancer. While results are mixed, ongoing investigations suggest a potential risk-modifying effect in select populations.
Dosage and Administration
Standard Dosage Recommendations for Adult Men
The typical dose consists of one capsule daily, containing the fixed combination of Tamsulosin 0.4 mg and Finasteride 5 mg. This regimen is designed for long-term use under medical supervision.
Method of Administration
Veltam-F should be taken orally, usually after the same meal each day to optimize absorption and minimize gastrointestinal discomfort. The capsule must be swallowed whole without crushing or chewing.
Duration of Treatment and Expectations for Clinical Improvement
Symptomatic relief from Tamsulosin may be observed within days. Structural benefits from Finasteride require continuous therapy, often several months, to manifest fully. Sustained adherence is critical to achieving both short- and long-term outcomes.
Dosage Adjustments in Renal or Hepatic Impairment
Patients with mild to moderate renal or hepatic dysfunction generally require no adjustment, but close monitoring is recommended. In severe impairment, caution is advised due to altered pharmacokinetics and potential accumulation.
Side Effects
Common Side Effects
Veltam-F, like other pharmacological agents, may produce certain adverse effects. Many of these are mild and tend to diminish with continued therapy. However, awareness is essential to ensure timely management.
- Dizziness and Headache: Resulting from vascular relaxation and central nervous system effects.
- Nasal Congestion: A consequence of alpha-1 blockade in nasal mucosa, often transient.
- Sexual Dysfunction: Manifestations include ejaculation disorders, reduced libido, and erectile difficulties, largely linked to the finasteride component.
- Gastrointestinal Disturbances: Nausea, diarrhea, and occasional abdominal discomfort are reported in sensitive individuals.
Serious Side Effects
Though less frequent, severe adverse reactions warrant clinical intervention. Immediate medical attention is advised if such events occur.
- Orthostatic Hypotension and Fainting: Abrupt drops in blood pressure upon standing may cause syncope and falls.
- Gynecomastia and Breast Tenderness: Hormonal alterations from finasteride can lead to breast enlargement or sensitivity.
- Rare Allergic Reactions: Cutaneous rashes, urticaria, and angioedema of the face or throat can develop in rare cases.
Drug Interactions
Interactions with Other Alpha-Blockers and Antihypertensive Medications
Concurrent use with additional alpha-blockers or antihypertensives can magnify hypotensive effects, raising the risk of dizziness, fainting, and postural instability.
CYP3A4 and CYP2D6 Inhibitors Affecting Tamsulosin Metabolism
Tamsulosin is extensively metabolized by hepatic cytochrome enzymes. Potent CYP3A4 inhibitors (e.g., ketoconazole) and CYP2D6 inhibitors (e.g., paroxetine) can elevate plasma concentrations, enhancing both therapeutic and adverse effects.
Interactions with Hormonal Therapies and Finasteride-Related Drug Interactions
Finasteride may alter serum prostate-specific antigen (PSA) values, complicating prostate cancer screening. It may also interact with hormonal therapies, particularly those modifying androgenic activity.
Warnings and Important Precautions
Risk of Intraoperative Floppy Iris Syndrome (IFIS) During Cataract Surgery
Patients scheduled for ophthalmic surgery should inform surgeons about Tamsulosin use, as it predisposes to IFIS, complicating the surgical field.
Monitoring for Prostate Cancer Before and During Therapy
Finasteride reduces PSA levels by approximately 50%, potentially masking early signs of malignancy. Regular digital rectal examination and PSA monitoring are indispensable.
Effects on Sexual Function and Psychological Well-Being
Persistent sexual side effects may influence mental health, contributing to anxiety or depressive states in some patients.
Long-Term Use Considerations
Chronic administration requires vigilance for cumulative adverse effects, particularly metabolic and endocrine disturbances.
Contraindications
Known Hypersensitivity
Individuals with a history of allergic reaction to Tamsulosin, Finasteride, or excipients should avoid use.
Contraindication in Women and Children
Due to teratogenicity and lack of clinical safety data, Veltam-F is contraindicated in females and pediatric populations.
Severe Hepatic Impairment
Patients with advanced liver dysfunction may experience impaired metabolism, rendering therapy unsafe.
Careful Administration
Patients with Orthostatic Hypotension or Cardiovascular Disorders
Those with preexisting cardiovascular instability require dose caution and monitoring for hypotensive episodes.
Patients with Impaired Liver or Kidney Function
Renal and hepatic impairment necessitate periodic evaluation of drug clearance and adjustment in dosing frequency.
Patients Undergoing Cataract or Glaucoma Surgery
Surgical teams should be alerted to ongoing treatment, as intraoperative complications may arise.
Administration in Special Populations
Elderly Patients
Older adults exhibit heightened sensitivity to postural hypotension. Lower starting doses and gradual titration may be required.
Pregnant Women and Nursing Mothers
Finasteride is teratogenic to male fetuses. Contact with broken or crushed tablets should be strictly avoided by women of childbearing potential. Breastfeeding mothers are also contraindicated due to potential transmission in milk.
Children and Adolescents
Safety and efficacy data are absent for pediatric populations, and use is not recommended.
Overdosage and Emergency Management
Symptoms of Overdose
Excessive ingestion may present as severe hypotension, tachycardia, profound dizziness, and potential cardiovascular collapse.
Immediate Management
Initial interventions include supportive measures: patient stabilization, intravenous fluids, and monitoring of vital signs.
No Specific Antidote
Treatment remains symptomatic. There is no established antidote for Tamsulosin or Finasteride overdose.
Storage and Handling Precautions
Recommended Storage Conditions
Tablets should be stored in a cool, dry environment, protected from excessive heat and direct sunlight. Ideal storage temperature is below 25°C.
Safe Handling Due to Finasteride’s Teratogenic Potential
Women, particularly those who are pregnant or may become pregnant, should not handle crushed or broken capsules to avoid dermal absorption of finasteride.
Shelf-Life and Disposal Instructions
Use only within the manufacturer’s recommended shelf-life. Expired medication should be discarded responsibly, avoiding environmental contamination.
Veltam-F, Tamsulosin / Finasteride FAQ
- What is Veltam-F used for?
- What are the side effects of Veltam?
- How long can we take Veltam?
- Why is tamsulosin given with finasteride?
- How long should a man take tamsulosin?
- Does finasteride permanently shrink the prostate?
- Can you take tamsulosin finasteride once a day?
- What is the best time to take tamsulosin and finasteride?
- Does finasteride affect blood pressure?
- What is the major side effect of tamsulosin?
- What happens when you stop taking tamsulosin?
- Can tamsulosin make you pee more at night?
- Can tamsulosin cause erectile dysfunction?
- What are the serious side effects of finasteride?
- Is finasteride a steroid?
- Can you take finasteride with amlodipine?
- Does finasteride affect memory?
What is Veltam-F used for?
The Veltam F Tablet MR is a medication designed to treat a condition known as hyperplasia or BPH for short. This condition occurs when the prostate gland becomes enlarged.
What are the side effects of Veltam?
- Hypotension
- Dizziness
- Drowsiness
- Low Libido
- Sleeping difficulties
How long can we take Veltam?
As prescribed by your doctor
Why is tamsulosin given with finasteride?
To enhance its efficacy and postpone BPH progression
How long should a man take tamsulosin?
Long-term
Does finasteride permanently shrink the prostate?
Yes
Can you take tamsulosin finasteride once a day?
Yes
What is the best time to take tamsulosin and finasteride?
30 minutes before meal
Does finasteride affect blood pressure?
Yes
What is the major side effect of tamsulosin?
- Dizziness
- Problems with ejaculating
What happens when you stop taking tamsulosin?
If you stop taking tamsulosin all of a sudden, your symptoms can come back or get worse.
Can tamsulosin make you pee more at night?
Yes
Can tamsulosin cause erectile dysfunction?
Yes
What are the serious side effects of finasteride?
- Breast changes
- Rashes
- Itching
- Edema
Is finasteride a steroid?
No
Can you take finasteride with amlodipine?
Finasteride may decrease the antihypertensive activities of Amlodipine.
Does finasteride affect memory?
Yes