Introduction to Atorlip (Atorvastatin)
Overview of Atorlip and Its Therapeutic Class
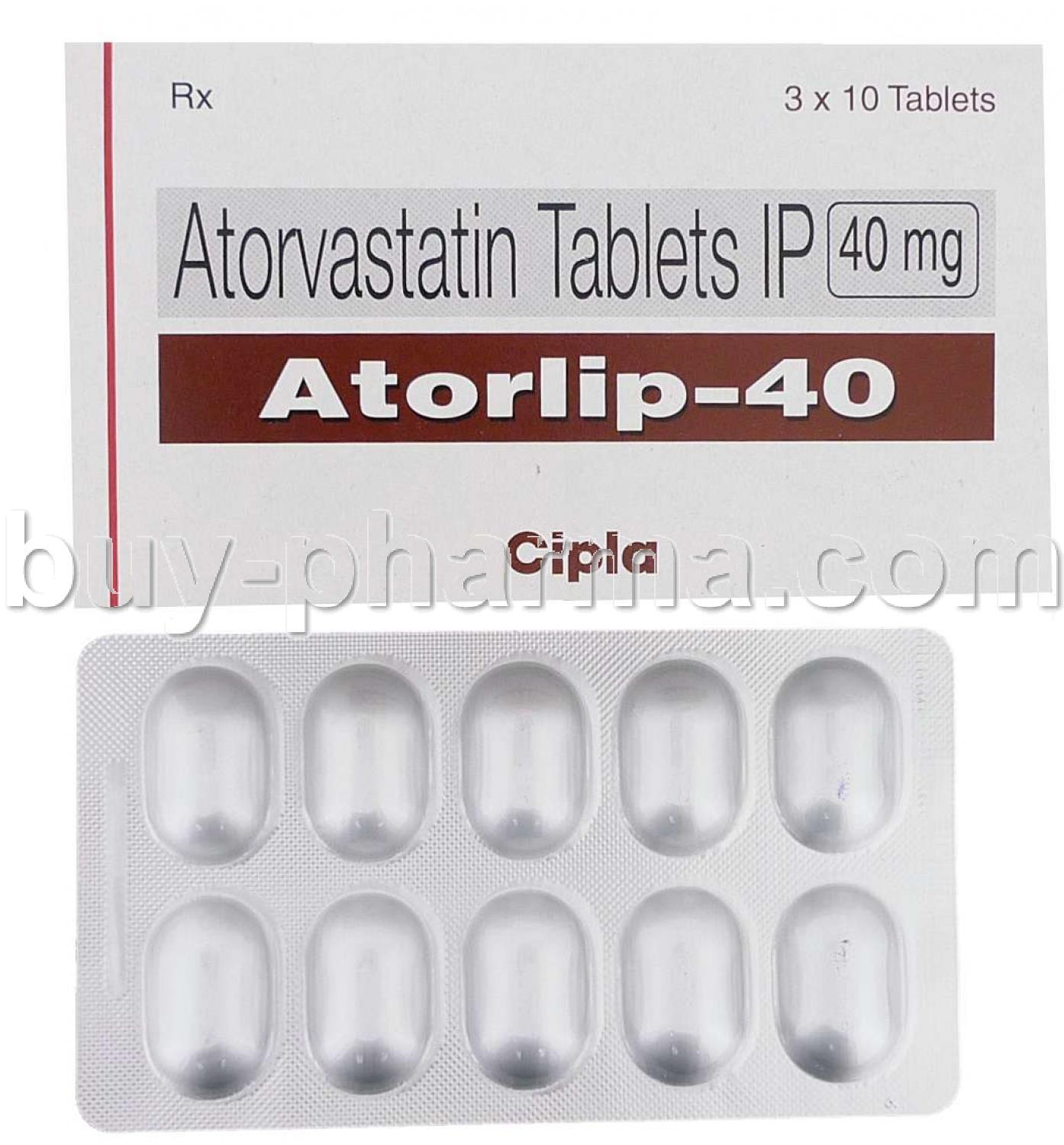
Atorlip is a widely prescribed lipid-lowering agent belonging to the statin class, specifically known as HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors. It is primarily indicated for the management of hyperlipidemia and cardiovascular risk reduction.
Origin and Approval History
Atorvastatin, the active compound in Atorlip, received FDA approval in the late 1990s. Since then, it has become a global standard in cholesterol management due to its high efficacy and favorable safety profile.
Manufacturer Information and Availability
Atorlip is manufactured by Cipla, a reputable pharmaceutical company known for its quality generics. The medication is widely available in various international markets in multiple dosage strengths.
Medical Uses of Atorlip (Atorvastatin)
2.1 Primary Indications
- Reduces elevated total and LDL cholesterol levels in patients with primary hypercholesterolemia.
- Used in the management of mixed dyslipidemia, improving HDL while reducing triglycerides.
- Prevents myocardial infarction, stroke, and angina in patients with multiple risk factors such as diabetes or hypertension.
- Indicated in both homozygous and heterozygous familial hypercholesterolemia to prevent early cardiovascular disease.
2.2 Off-Label Uses of Atorlip
- As an adjunct in polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) to address lipid abnormalities.
- Explored in neurodegenerative conditions such as Alzheimer's for its potential neuroprotective effects.
- Investigated for its anti-inflammatory effects in systemic autoimmune conditions like rheumatoid arthritis.
- Potential utility in managing non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) through metabolic modulation.
How Atorlip (Atorvastatin) Works: Mechanism of Action
- Inhibits the HMG-CoA reductase enzyme, a rate-limiting step in cholesterol biosynthesis.
- Decreases hepatic cholesterol production, thereby stimulating LDL receptor expression.
- Promotes enhanced clearance of circulating LDL cholesterol from the bloodstream.
- Reduces serum triglyceride levels and modestly elevates HDL cholesterol.
- Exerts pleiotropic benefits including anti-inflammatory effects and plaque stabilization.
Dosage and Administration Guidelines for Atorlip
4.1 Standard Adult Dosage
- Initial dose commonly starts at 10–20 mg once daily.
- High-risk patients may begin with 40 mg daily.
- Maximum dose is 80 mg/day, titrated based on lipid goals and tolerance.
4.2 Dosage Adjustments
- Lower starting doses in patients with hepatic impairment are advised.
- Adjustments may be necessary when co-administered with CYP3A4 inhibitors.
- In elderly patients, lower doses with gradual escalation are recommended.
4.3 Administration Instructions
- Administered once daily, with or without meals.
- If a dose is missed, take it as soon as remembered unless it’s near the time for the next dose.
- Do not crush or chew; swallow tablets whole with water.
Composition and Formulation of Atorlip
- Active Ingredient: Atorvastatin calcium
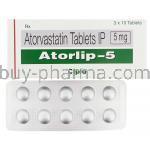
- Available Strengths: 5 mg, 10 mg, 20 mg, 40 mg, and 80 mg tablets
- Excipients: May include lactose monohydrate, calcium carbonate, sodium starch glycolate
- Tablet Appearance: Round or oval-shaped, film-coated tablets marked with dosage strength
Storage and Stability Information
- Store at controlled room temperature, ideally between 20°C to 25°C (68°F to 77°F).
- Protect from moisture, direct sunlight, and excessive heat.
- Ensure tablets remain in original packaging until use to maintain stability.
Drug Interactions with Atorlip
7.1 Major Drug Interactions
- Co-administration with strong CYP3A4 inhibitors (e.g., ketoconazole, clarithromycin) can increase atorvastatin levels significantly.
- Concomitant use with fibrates or niacin heightens the risk of myopathy.
- May enhance the anticoagulant effect of warfarin—monitor INR levels closely.
7.2 Moderate to Minor Interactions
- Grapefruit juice inhibits atorvastatin metabolism, leading to higher systemic exposure.
- Can alter hormonal levels when taken with oral contraceptives.
- Cyclosporine may increase atorvastatin plasma levels—monitor closely.
Warnings and Contraindications
8.1 Black Box Warnings (if applicable)
No official black box warning; however, hepatic dysfunction remains a significant clinical concern requiring vigilant monitoring.
8.2 Contraindications
- History of hypersensitivity to atorvastatin or its constituents.
- Patients with active liver disease or persistently elevated hepatic enzymes without explanation.
- Contraindicated in pregnancy due to potential harm to the fetus (Category X).
- Breastfeeding mothers should not use atorvastatin as it may be excreted in human milk.
Common and Serious Side Effects of Atorlip
9.1 Common Side Effects
- Muscle pain (myalgia), cramps, or weakness.
- Gastrointestinal issues such as diarrhea, flatulence, or abdominal discomfort.
- Transient elevations in liver transaminases.
- Neurological complaints including headache and sleep disturbances like insomnia.
9.2 Serious Adverse Effects
- Rhabdomyolysis: severe muscle breakdown leading to kidney failure.
- Hepatic failure or drug-induced hepatitis in rare cases.
- Possible cognitive side effects including memory lapses or mental confusion.
- Severe allergic reactions including anaphylaxis, angioedema, or rash.
Important Precautions Before Starting Atorlip
- Liver Function Test (LFT) Baseline Monitoring: Prior to initiating Atorlip therapy, baseline hepatic enzyme levels (ALT, AST) should be measured. Elevated enzymes may signal pre-existing liver dysfunction, warranting caution or deferral of treatment.
- Muscle Symptom Assessment and Creatine Kinase (CK) Levels: Patients with a history of statin-induced myopathy or unexplained muscle aches should undergo baseline CK testing. Monitoring is essential for early detection of rhabdomyolysis.
- Alcohol Intake Limitation: Excessive alcohol consumption may potentiate hepatic injury. Patients should be advised to minimize or avoid alcohol to reduce hepatotoxicity risks during therapy.
- Monitoring Glucose Levels in Diabetic Patients: Atorlip may modestly raise blood glucose levels. Diabetic individuals should undergo periodic glucose monitoring to maintain optimal glycemic control.
- Periodic Lipid Panel Evaluation: Lipid profiles should be rechecked at regular intervals (typically 4–12 weeks after initiation and periodically thereafter) to assess therapeutic response and guide dose adjustments.
Careful Administration in Special Populations
11.1 Administration to Elderly Patients
- Increased Susceptibility to Side Effects: Elderly individuals may exhibit heightened sensitivity to Atorlip, particularly regarding muscle-related adverse effects and hepatic tolerance.
- Monitoring of Renal and Hepatic Function: Age-related decline in organ function necessitates close monitoring of renal and liver parameters to mitigate the risk of drug accumulation and toxicity.
- Consideration of Polypharmacy and Fall Risk: Due to the prevalence of concurrent medications and comorbidities, the risk of drug-drug interactions and falls related to statin-induced muscle weakness must be carefully evaluated.
11.2 Administration During Pregnancy and Lactation
- Category X: Contraindicated in Pregnancy: Atorlip is classified as pregnancy category X due to its teratogenic potential. It is strictly contraindicated in women who are pregnant or planning to conceive.
- Risk of Fetal Harm and Developmental Abnormalities: Inhibition of cholesterol biosynthesis during gestation can impair fetal development, leading to structural malformations and growth delays.
- Presence in Breast Milk and Breastfeeding Recommendation: Atorvastatin may be excreted in breast milk. Lactating women are advised to discontinue either nursing or the drug, depending on the clinical necessity.
11.3 Administration to Children and Adolescents
- Approved Pediatric Indications: Atorlip is approved for children aged 10 years and older with heterozygous familial hypercholesterolemia when lifestyle modification fails to adequately control lipid levels.
- Age-Specific Dosage Guidelines: Pediatric dosing should be initiated at the lowest effective dose, typically starting at 10 mg/day, with cautious titration based on LDL reduction and tolerance.
- Safety and Efficacy in Younger Populations: Clinical studies support efficacy in reducing LDL cholesterol in pediatric populations, although long-term safety data are still evolving. Growth and sexual maturation should be monitored.
Overdosage and Emergency Management
- Symptoms of Overdose: Manifestations may include pronounced myalgia, confusion, dizziness, and elevated serum creatine kinase and liver enzyme levels. Cardiovascular symptoms are rare but possible.
- Recommended Management: Treatment is supportive and symptomatic. Monitor LFTs and CK levels regularly. Initiate IV hydration to protect renal function if rhabdomyolysis is suspected.
- Use of Activated Charcoal or Gastric Lavage: In cases of recent ingestion, gastrointestinal decontamination may be considered, although its effectiveness decreases over time.
- Dialysis Inefficacy: Atorvastatin is highly protein-bound, rendering dialysis ineffective for drug clearance in overdose scenarios.
Handling Precautions and Patient Education
- Safe Handling and Storage by Caregivers: Store Atorlip in its original packaging away from moisture and heat. Keep out of reach of children and pets to prevent accidental ingestion.
- Importance of Adherence and Regular Follow-Up: Patients should be educated on the importance of taking the medication as prescribed and not discontinuing therapy without consulting their physician.
- Counseling on Diet and Lifestyle Changes Alongside Therapy: Emphasize that Atorlip is an adjunct, not a replacement, for a heart-healthy diet, regular exercise, and smoking cessation.
- Recognizing Signs of Serious Side Effects for Timely Reporting: Encourage immediate medical consultation if the patient experiences unexplained muscle pain, yellowing of the skin or eyes, dark urine, or severe fatigue.
Atorlip, Atorvastatin FAQ
- Are Atorlip and Atorvastatin the same?
- When is the best time to take Atorlip?
- What is the biggest side effect of Atorvastatin?
- Does Atorlip 10 mg have side effects?
- Why is atorvastatin not used at night?
- Is atorvastatin a blood thinner?
- How long is it safe to take atorvastatin?
- Which organ does atorvastatin affect?
- Is atorvastatin safe for kidneys?
- Is atorvastatin a safe medicine?
- How long after taking atorvastatin do you get side effects?
- How to take an atorlip?
- What is the most serious side effect of atorvastatin?
- When to avoid atorvastatin?
- What is the use of Atorlip medicine?
- Which company makes Atorlip?
- What foods should be avoided when taking atorvastatin?
- Does atorvastatin lower blood pressure?
- Do you lose weight with atorvastatin?
- Can atorvastatin make you tired?
- Can atorvastatin cause hair loss?
- Who cannot take atorvastatin?
- Can atorvastatin affect the eyes?
- Can atorvastatin affect teeth?
- What are the benefits of Atorlip?
- What are the positive effects of atorvastatin?
Are Atorlip and Atorvastatin the same?
Yes
When is the best time to take Atorlip?
Anytime
What is the biggest side effect of Atorvastatin?
Nausea, headache, nosebleeds, sore throat, constipation, farting
Does Atorlip 10 mg have side effects?
Nausea, headache, nosebleeds, sore throat, constipation, farting
Why is atorvastatin not used at night?
Cholesterol production in our bodies tends to hit its peak at night. So taking a statin with a lasting effect before bed might be the way to go since it'll be working its magic when cholesterol production is at its highest.
Is atorvastatin a blood thinner?
No
How long is it safe to take atorvastatin?
As long as symptoms lasts
Which organ does atorvastatin affect?
Liver and kidney
Is atorvastatin safe for kidneys?
Yes
Is atorvastatin a safe medicine?
Yes
How long after taking atorvastatin do you get side effects?
Statin-related muscle pain is pretty rare. When it does occur, it tends to happen on the first few months.
How to take an atorlip?
Anytime of the day
What is the most serious side effect of atorvastatin?
Habdomyolysis
When to avoid atorvastatin?
When you have decompensated cirrhosis or acute (sudden) liver failure
What is the use of Atorlip medicine?
It is used to control elevated blood cholesterol levels.
Which company makes Atorlip?
Cipla Ltd
What foods should be avoided when taking atorvastatin?
Grapefruit
Does atorvastatin lower blood pressure?
Yes
Do you lose weight with atorvastatin?
No
Can atorvastatin make you tired?
Yes
Can atorvastatin cause hair loss?
Yes
Who cannot take atorvastatin?
- People with liver or kidney problem
- Pregnant or trying
- Have lung disease
- Previous stroke
Can atorvastatin affect the eyes?
Yes
Can atorvastatin affect teeth?
No
What are the benefits of Atorlip?
It is used to lower cholesterol.
What are the positive effects of atorvastatin?
Lowering cholesterol levels and preventing heart attack