Biosev, Sevelamer
- Introduction
- Composition and Formulations
- Sevelamer Mechanism of Action
- Sevelamer Uses
- Off-Label Uses
- Sevelamer Dosage and Administration
- Administration in Special Populations
- Sevelamer Side Effects
- Warnings and Precautions
- Sevelamer Contraindications
- Drug and Food Interactions
- Careful Administration and Monitoring
- Overdose
- Handling and Storage Precautions
- Professional Recommendations
Introduction
Overview of Biosev (Sevelamer)
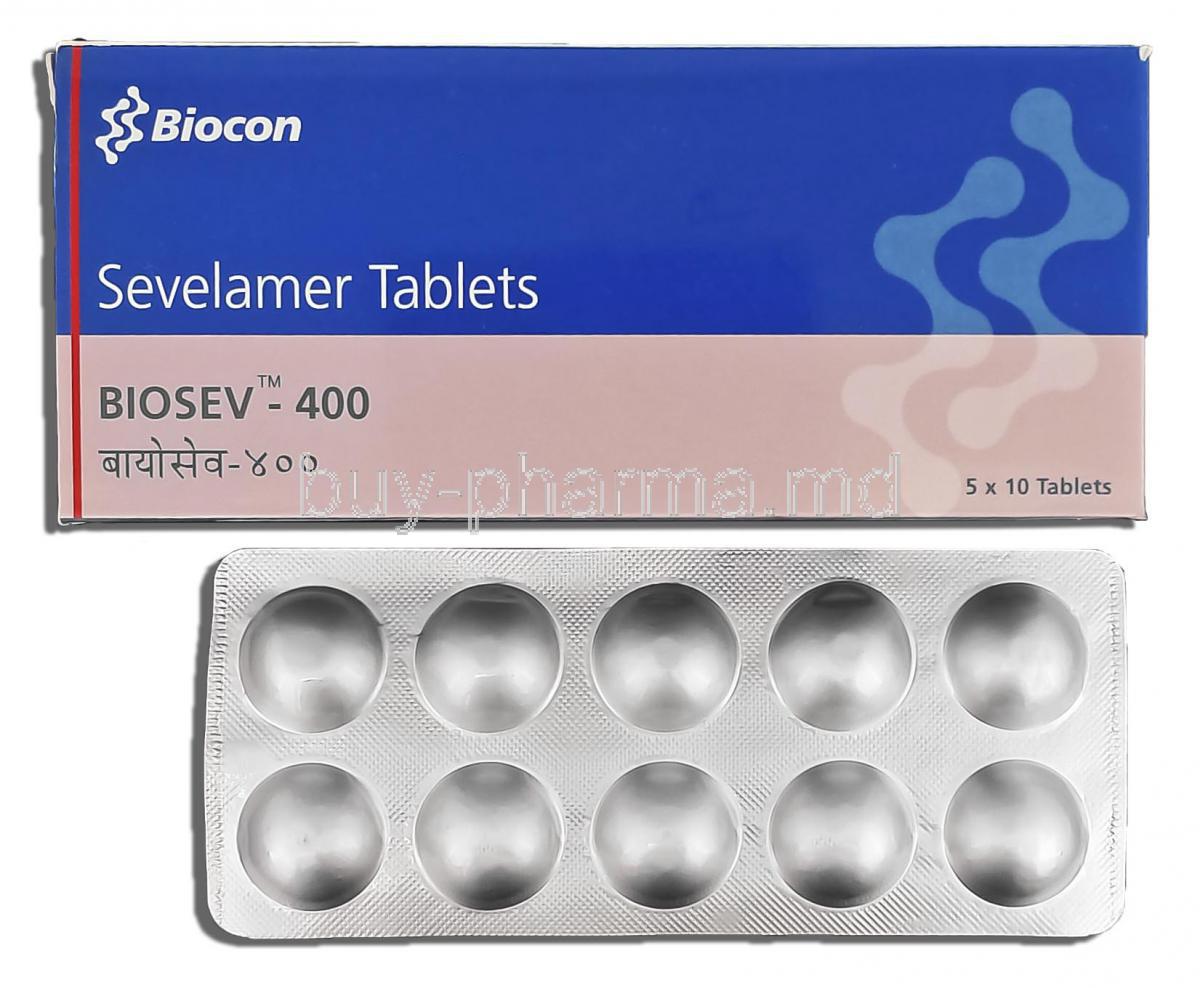
Biosev, known by its generic name Sevelamer, is a non-absorbed phosphate binder widely prescribed for individuals experiencing elevated serum phosphate levels. This therapeutic agent plays a central role in managing complications associated with chronic kidney disease, particularly in patients undergoing dialysis. Unlike calcium-based binders, Sevelamer does not contribute to calcium overload, which makes it a preferred option in long-term therapy.
Therapeutic classification and background
Sevelamer belongs to the class of polymer-based phosphate binders. It is an ion-exchange resin that acts locally within the gastrointestinal tract. Introduced as an alternative to calcium-based therapies, its development marked a significant advance in reducing the risk of vascular calcification while controlling hyperphosphatemia. The drug has become an essential part of nephrology practice worldwide.
Clinical importance in chronic kidney disease and dialysis patients
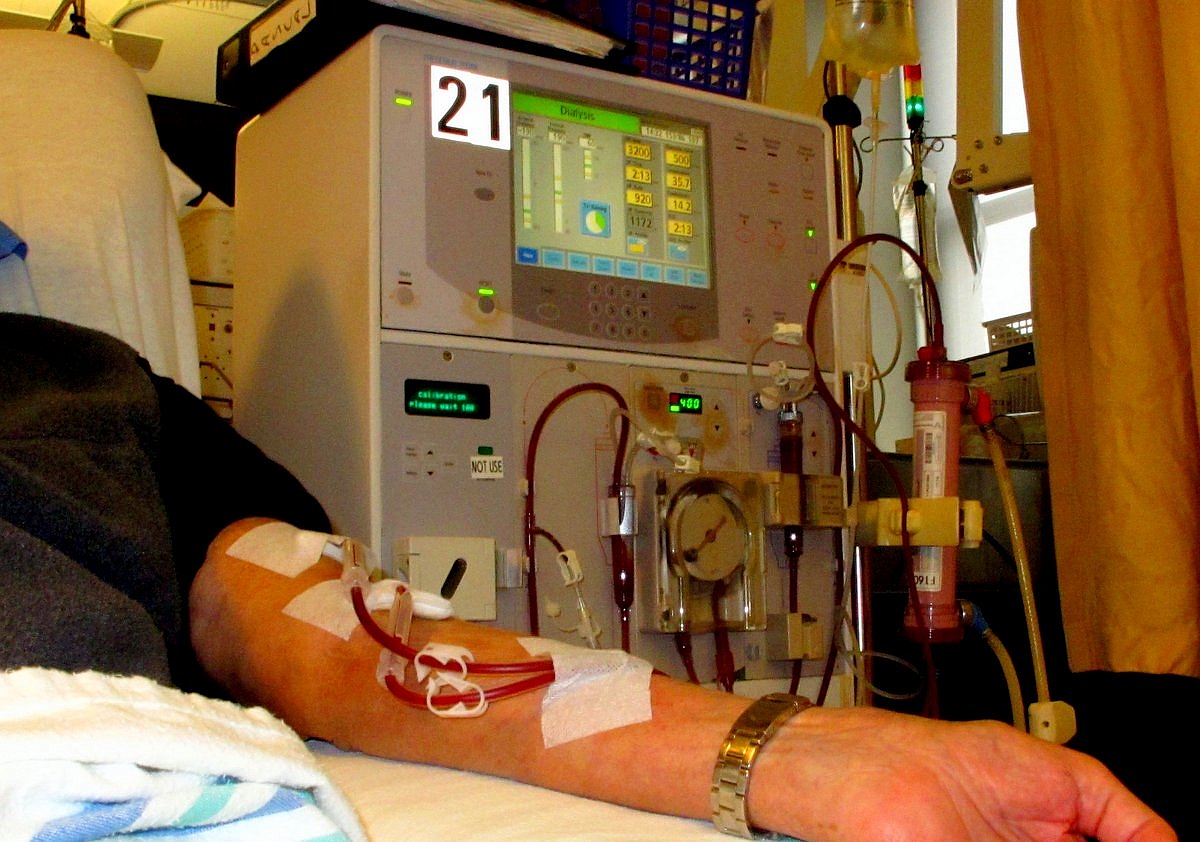
Patients with chronic kidney disease (CKD), especially those receiving hemodialysis or peritoneal dialysis, often suffer from impaired phosphate excretion. Elevated phosphate levels can lead to secondary hyperparathyroidism, renal osteodystrophy, and increased cardiovascular risk. Biosev assists in mitigating these complications by binding dietary phosphate before it is absorbed, thereby supporting long-term survival and quality of life.
Composition and Formulations
Active ingredient: Sevelamer hydrochloride / carbonate
The primary active pharmaceutical substance is Sevelamer, which is available in two salt forms: hydrochloride and carbonate. Both act through similar mechanisms, though the carbonate form may offer advantages in terms of acid-base balance.
Sevelamer drug class
Sevelamer belongs to a group of medications known as phosphate binders.
Available dosage forms
- Film-coated tablets designed for oral administration
- Powder formulations intended for suspension in water or suitable liquids
Excipients and their role
In addition to the active component, formulations contain excipients that stabilize the medication, aid in disintegration, and enhance patient compliance. These may include microcrystalline cellulose, coloring agents, and stabilizers.
Velphoro vs sevelamer
Velphoro (sucroferric oxyhydroxide) and Sevelamer carbonate are both phosphate binders used to lower blood phosphate levels in people with chronic kidney disease (CKD) on dialysis. Velphoro is 2.6x more potent than 1 tablet of sevelamer.
Phoslo vs sevelamer
PhosLo (calcium acetate) and Sevelamer are both phosphate binders utilized to control elevated phosphate levels in chronic kidney disease; however, Sevelamer is a calcium-free alternative, unlike PhosLo, which may result in increased calcium levels. Sevelamer has the potential to decrease vascular calcification and may provide a survival advantage for certain hemodialysis patients, while PhosLo can be more effective and is frequently a more economical choice when hypercalcemia (high calcium) is not an issue.
Sevelamer Mechanism of Action
How Sevelamer binds dietary phosphate
Sevelamer functions as a non-absorbed, cross-linked polymer. Within the intestinal lumen, it binds phosphate ions electrostatically, preventing their absorption into the bloodstream. The complex is subsequently excreted via feces.
Reduction of phosphate absorption and impact
By diminishing phosphate absorption, Biosev lowers serum phosphate levels and reduces the risk of mineral and bone disorders associated with chronic kidney disease. The therapeutic effect is cumulative, requiring consistent administration with meals.
Additional effects
Beyond phosphate control, Sevelamer demonstrates bile acid-binding properties, which can reduce low-density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol. This lipid-lowering effect contributes to improved cardiovascular profiles in long-term dialysis patients.
Sevelamer Uses
Management of hyperphosphatemia in dialysis patients
The primary indication of Biosev is the management of hyperphosphatemia in individuals undergoing hemodialysis or peritoneal dialysis. It provides effective phosphate control without exacerbating hypercalcemia.
Use in CKD patients not on dialysis
Biosev is also indicated for patients with chronic kidney disease not yet requiring dialysis but experiencing hyperphosphatemia. Early phosphate control helps in slowing disease progression.
Prevention of renal osteodystrophy and secondary hyperparathyroidism
Off-Label Uses
Management of hyperphosphatemia in pediatric patients
Use in calciphylaxis
Potential LDL cholesterol reduction
Investigational applications
Exploratory research is ongoing into potential roles of Sevelamer in metabolic disorders and cardiovascular conditions related to phosphate imbalance and oxidative stress.
Sevelamer Dosage and Administration
Sevelamer Dose for Adults
The initial dose typically depends on baseline serum phosphate levels. Adults—At first, 800 to 1600 milligrams (mg) (1 to 2 tablets) three times a day with meals, depending on your blood phosphorus level.
Dose adjustments
Dosage is titrated every two to four weeks until optimal serum phosphate levels are achieved. Regular monitoring ensures effectiveness and safety.
Administration with meals
Biosev must be taken with meals to ensure maximum binding of dietary phosphate. Skipping or delaying intake may reduce efficacy.

Specific instructions for dosage forms
- Tablets: Swallow whole with water. Do not crush or chew.
- Powder: Dissolve in water and consume immediately to avoid degradation.

Administration in Special Populations
Elderly patients
Older adults may require careful monitoring due to polypharmacy and comorbid conditions. Regular assessment of gastrointestinal tolerance is recommended.
Pregnant women
Animal studies are limited, and data on human pregnancy are insufficient. Biosev should be prescribed only when benefits outweigh potential risks.

Nursing mothers
Sevelamer is not systemically absorbed, and transfer into breast milk is unlikely. However, clinical discretion is advised.
Children
Pediatric data are limited, though use has been documented. Dosing requires individualized assessment, and compliance may be challenging in young children.
Sevelamer Side Effects
Common side effects
- Nausea and vomiting
- Constipation or diarrhea
- Abdominal pain

Less common adverse effects
Dyspepsia, bloating, flatulence, and in rare cases, intestinal obstruction, have been reported in long-term use.
Long-term risks
Because Biosev can reduce absorption of fat-soluble vitamins and folic acid, monitoring and supplementation may be necessary in prolonged therapy.
Warnings and Precautions
Risk of gastrointestinal obstruction
Patients with existing gastrointestinal motility disorders are at greater risk of obstruction or perforation. Careful patient selection is necessary.
Monitoring vitamin levels
Long-term therapy may necessitate supplementation of vitamins A, D, E, K, and folic acid to avoid deficiency.
Potential for metabolic acidosis
Sevelamer hydrochloride has been associated with acidosis in susceptible individuals. Monitoring of bicarbonate levels is recommended.
Importance of regular phosphate monitoring
Frequent laboratory evaluation ensures therapeutic success and prevents complications such as bone disease or cardiovascular calcification.
Sevelamer Contraindications
Known hypersensitivity to sevelamer or formulation components
Biosev (Sevelamer) should not be administered in individuals with a documented hypersensitivity to the active substance or any excipients in the formulation. Allergic manifestations may include rash, pruritus, or in rare cases, systemic reactions. A thorough medical history is essential before initiating treatment.
Bowel obstruction or history of severe gastrointestinal motility disorders
Patients with existing bowel obstruction, or those with a history of severe gastrointestinal motility disorders such as ileus or chronic constipation, should avoid Sevelamer. The polymeric structure of the drug may exacerbate intestinal stasis, increasing the risk of obstruction and perforation.
Drug and Food Interactions
Interactions with ciprofloxacin and reduced bioavailability
Sevelamer binds to ciprofloxacin in the gastrointestinal tract, significantly reducing its bioavailability. This can diminish the antimicrobial effect of ciprofloxacin. Patients requiring both agents should take ciprofloxacin at least two hours before or six hours after Sevelamer.
Potential interactions with immunosuppressants
- Ciclosporin: potential reduction in systemic levels
- Tacrolimus: possible alteration in absorption dynamics
- Mycophenolate: reduced plasma concentrations in some patients
Close therapeutic drug monitoring is strongly advised for patients receiving these immunosuppressants concurrently with Sevelamer.
Considerations with fat-soluble vitamins and folic acid absorption
Prolonged therapy may impair absorption of vitamins A, D, E, K, and folic acid. Patients on long-term treatment should undergo periodic nutritional assessments, with supplementation provided where necessary.
Timing of administration with other oral medications
Sevelamer may interfere with the absorption of various oral agents. A separation of dosing times is recommended, typically administering other medications at least one hour before or three hours after Sevelamer.
Careful Administration and Monitoring
Patients with swallowing disorders or gastrointestinal motility issues
For individuals with dysphagia, or those prone to gastrointestinal motility problems, tablet formulations may pose risks. Powder formulations suspended in water are often preferable in such cases.
Monitoring for vitamin deficiencies and supplementation
Chronic use may necessitate supplementation of:
- Vitamin D for bone mineral health
- Vitamin K to support coagulation
- Folic acid for erythropoietic function
Routine laboratory assessments should guide supplementation strategies.
Adjusting therapy based on phosphate control and tolerance
Dosing must be titrated according to serum phosphate levels, gastrointestinal tolerability, and overall therapeutic response. Clinical judgment ensures both efficacy and safety of long-term treatment.
Overdose
Symptoms of sevelamer overdose
Excessive intake may lead to severe gastrointestinal symptoms such as:
- Persistent constipation
- Abdominal pain
- Intestinal obstruction
Supportive management and discontinuation
Treatment is supportive, focusing on discontinuation of the drug, hydration, and medical interventions to relieve obstruction. Surgical consultation may be required in severe cases.
No specific antidote
Currently, no antidote exists for Sevelamer overdose. Clinical management remains symptomatic and supportive.
Handling and Storage Precautions
Recommended storage conditions
Store Sevelamer at controlled room temperature, protected from moisture and excessive heat. Avoid storing near direct sunlight or in humid environments such as bathrooms.
Safe handling of powder formulations
Powder should be dissolved in water immediately before ingestion. Care should be taken to prevent inhalation of dust particles, particularly in sensitive individuals.
Instructions for patients and caregivers
Patients and caregivers should be instructed to:
- Keep medication in its original packaging until use
- Ensure accurate dosing with each administration
- Dispose of unused or expired medication safely
Professional Recommendations
Importance of individualized therapy
Sevelamer therapy should be tailored to each patient's phosphate burden, dietary habits, and comorbid conditions. A one-size-fits-all approach is discouraged.
Regular laboratory monitoring
Monitoring is vital and should include:
- Serum phosphate levels for therapeutic efficacy
- Calcium and parathyroid hormone (PTH) for mineral balance
- Lipid profiles to assess secondary cardiovascular benefits
Dietary counseling as part of management
Optimal results are achieved when Sevelamer therapy is combined with dietary modifications. Patients should receive counseling on limiting phosphate-rich foods and adhering to individualized nutrition plans.
Biosev, Sevelamer FAQ
- What is Biosev C 400 mg used for?
- What is the drug sevelamer used for?
- What is the reason for taking sevelamer with food?
- When should sevelamer be given?
- What is the mechanism of action of sevelamer?
- What are the common sevelamer side effects?
- How effective is sevelamer?
- How quickly does sevelamer start working?
- Does sevelamer make you sleepy?
- Does sevelamer cause gas?
- What should I avoid while taking sevelamer?
- What is the maximum dosing of sevelamer?
- When to stop taking sevelamer?
- Is sevelamer toxic to the liver?
- What are the serious side effects of sevelamer carbonate?
- What are the benefits of drinking sevelamer?
- Does sevelamer cause weight gain?
- Does sevelamer work if not eating?
- Are there alternatives to sevelamer?
- Can sevelamer increase calcium?
- Does sevelamer affect blood sugar?
- Does sevelamer affect potassium?
- What are the benefits of sevelamer?
- How long after eating can you take sevelamer?
- Is sevelamer covered by Medicare?
- Why do dialysis patients need sevelamer?
- What is the difference between sevelamer and sevelamer?
What is Biosev C 400 mg used for?
Biosev C 400mg Tablet is designed to regulate elevated phosphate levels in the bloodstream, particularly for individuals with chronic kidney disease undergoing dialysis. It aids in managing phosphate accumulation, promoting healthy bones, and preventing issues such as bone pain, itching, and complications associated with the heart and blood vessels.
What is the drug sevelamer used for?
Sevelamer is utilized to manage elevated phosphorus levels in individuals with chronic kidney disease who are undergoing dialysis (a medical procedure that purifies the blood when the kidneys are not functioning correctly).
What is the reason for taking sevelamer with food?
So that it can bind the phosphorus in the food
When should sevelamer be given?
3 times daily with meals
What is the mechanism of action of sevelamer?
Sevelamer helps prevent hyperphosphatemia by binding to dietary phosphate in the gut, thereby stopping its absorption and reducing serum parathyroid hormone levels. It is not absorbed after oral administration, though absorption studies have not been conducted in patients with renal disease.
What are the common sevelamer side effects?
- Indigestion
- Bloating
- Nausea
- Vomiting
- Abdominal discomfort
- Diarrhea
How effective is sevelamer?
A total of 75% of patients with stage 4 and 70% of patients with stage 5 chronic kidney disease reached the target serum phosphorus by the end of treatment.
How quickly does sevelamer start working?
Immediately
Does sevelamer make you sleepy?
Yes
Does sevelamer cause gas?
Yes
What should I avoid while taking sevelamer?
Sevelamer might affect how certain vitamins, including A, D, E, and K, are absorbed.
What is the maximum dosing of sevelamer?
14 grams in CKD patients on dialysis
When to stop taking sevelamer?
- if you experience any difficulties with swallowing.
- Severe Constipation. Sevelamer may lead to severe constipation
Is sevelamer toxic to the liver?
No
What are the serious side effects of sevelamer carbonate?
- Allergic reactions—skin rash, itching, hives, swelling of the face, lips, tongue, or throat.
- Bowel blockage—stomach cramping, inability to have a bowel movement or pass gas, loss of appetite, vomiting.
What are the benefits of drinking sevelamer?
Sevelamer is prescribed to reduce elevated blood phosphorus (phosphate) levels in patients undergoing dialysis because of advanced kidney disease. While dialysis can remove some phosphate from the bloodstream, it often falls short of effectively maintaining balanced phosphate levels.
Does sevelamer cause weight gain?
No
Does sevelamer work if not eating?
No
Are there alternatives to sevelamer?
Sucroferric oxyhydroxide
Can sevelamer increase calcium?
Yes
Does sevelamer affect blood sugar?
No
Does sevelamer affect potassium?
Reduces potassium levels
What are the benefits of sevelamer?
Enhanced lipid profiles and possibly reduced all-cause mortality
How long after eating can you take sevelamer?
30 minutes
Is sevelamer covered by Medicare?
Yes
Why do dialysis patients need sevelamer?
Sevelamer is utilized to manage elevated phosphorus levels in individuals with chronic kidney disease who are undergoing dialysis (a medical procedure that filters the blood when the kidneys are not functioning effectively).
What is the difference between sevelamer and sevelamer?
Sevelamer carbonate does not lower serum bicarbonate levels