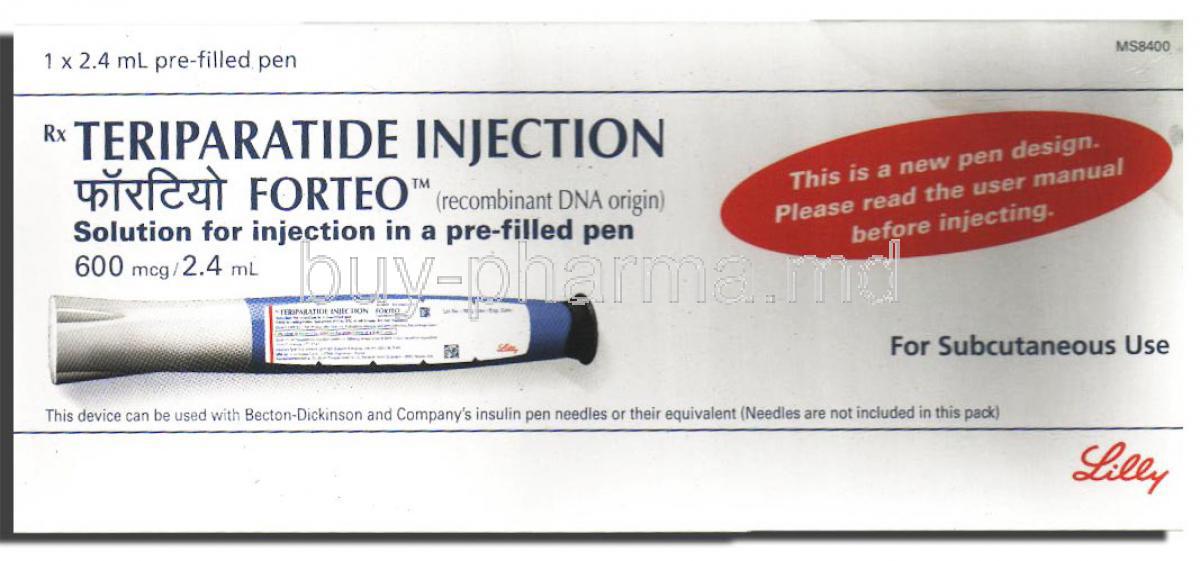
Forteo, Teriparatide Injectoin
- Introduction to Forteo (Teriparatide Injection)
- How Forteo (Teriparatide Injection) Works
- Forteo uses
- Off-Label Uses of Forteo (Teriparatide Injection)
- Dosage and Administration of Forteo (Teriparatide Injection)
- Composition and Formulation of Forteo (Teriparatide Injection)
- Storage and Stability of Forteo (Teriparatide Injection)
- Forteo side effects
- Serious and Rare Side Effects of Forteo (Teriparatide Injection)
- Drug Interactions with Forteo (Teriparatide Injection)
- Warnings and Precautions When Using Forteo (Teriparatide Injection)
- Contraindications for Forteo (Teriparatide Injection) Use
- Forteo Administration and Monitoring
- Important Precautions for Forteo (Teriparatide Injection) Use
- Administration of Forteo (Teriparatide Injection) in the Elderly
- Administration of Forteo (Teriparatide Injection) to Pregnant and Nursing Women
- Administration of Forteo (Teriparatide Injection) to Pediatric Patients
- Overdosage of Forteo (Teriparatide Injection)
- Safe Handling Precautions for Forteo (Teriparatide Injection)
Introduction to Forteo (Teriparatide Injection)
Overview of Forteo
Forte, containing teriparatide as the main ingredient, is a biologic treatment created to address osteoporosis by promoting bone growth. This injectable drug has changed the way high fracture risk patients are cared for significantly in various age groups.
Historical Development and FDA Approval Timeline
Teriparatide emerged from groundbreaking studies on parathyroid hormone analogues. Received FDA authorization in 2002. It has become a treatment for managing osteoporosis over time thanks to ongoing monitoring and research confirming its effectiveness and safety record.
Importance of Forteo in Osteoporosis Treatment
Unlike traditional antiresorptive treatments that merely slow bone loss, Forteo actively promotes new bone synthesis, enhancing bone quality and structural integrity. It is especially critical for individuals with severe osteoporosis or those who have failed previous treatments.
How Forteo (Teriparatide Injection) Works
Forteo mechanism of action
Forteois is designed to work with parathyroid hormone by encouraging bone-building activity and supporting the creation of fresh bone material. This periodic stimulation encourages bone development of breakdown.
Pharmacodynamics and Pharmacokinetics
- Onset of Action: Increases in bone formation markers observed within weeks.
- Absorption: Rapidly absorbed subcutaneously, reaching peak concentrations in 30 minutes.
- Elimination: Cleared via hepatic metabolism with a half-life of approximately 1 hour.
Comparison with Other Osteoporosis Treatments
While bisphosphonates and selective estrogen receptor modulators inhibit bone resorption, Forteo uniquely builds new bone, offering a potent alternative for high-risk patients. Its anabolic action fills a crucial gap in osteoporosis therapy algorithms.
Forteo uses
Forteo for osteoporosis in Postmenopausal Women at High Fracture Risk
Osteoporosis in Men with Primary or Hypogonadal Osteoporosis at High Fracture Risk
Glucocorticoid-Induced Osteoporosis
Treatment of Osteoporosis Associated with Long-Term Corticosteroid Use
Forte strengthens the bones of patients who need to take corticosteroids for conditions, helping to minimize any negative effects on their skeletal system caused by these medications.
Off-Label Uses of Forteo (Teriparatide Injection)
Fracture Healing Acceleration
Osteogenesis Imperfecta Management
Chronic Hypoparathyroidism
Atypical Femoral Fracture Recovery Support
Bone Graft Enhancement in Orthopedic Surgeries
Dosage and Administration of Forteo (Teriparatide Injection)
Forteo dosage
The recommended amount of Forteo to take is 20 micrograms given under the skin once a day.
Administration Technique: Subcutaneous Injection
- Administer into the thigh or abdominal wall using the prefilled pen device.
- Rotate injection sites to minimize local reactions and lipodystrophy.
Forteo injection sites
It's essential to rotate injection sites to maintain skin health and ensure that medications are absorbed effectively.
Forteo duration of therapy
Due to potential risks, the total lifetime exposure to Forteo is limited to 24 months. Subsequent treatment plans should be discussed with a healthcare provider.
Composition and Formulation of Forteo (Teriparatide Injection)
Active Ingredients: Teriparatide
Each vial of Forteo contains teriparatide, a version of the human parathyroid hormone (also known as bioactive PTH or hPTH in medical terminology).
Inactive Ingredients and Excipients
Crafted with additives, like acid and sodium acetates, along with mannitol and m-cresol to maintain the stability and cleanliness of the product.
Presentation Forms: Prefilled Pens and Delivery Systems
Forteois is conveniently packaged in a pen for use, with 28 daily doses to make injections simpler and enhance compliance.
Tymlos vs forteo
Forteois a lower dosage of medication, at 20mcg, as opposed to 80 mcg in Tymlos. Some people may experience a reaction to the preservative in Tymlos that you won't encounter with Forteo.
Forteo vs prolia
Forteois is a version of the hormone that aids in bone formation and requires daily injections. On the other hand, Prolia is a type of monoclonal antibody that hinders bone deterioration by targeting a protein involved in breaking down bones. It is given through injections every six months.
Evenity vs forteo
You should take Evenity for a month for a year, while Forteo should be taken daily for up to two years, and remember to take Evenity with your intake of calcium and vitamin D supplements.
Fosamax vs forteo
Both Fosamax and Forteo work differently to improve bone health; Fosamax helps slow down bone breakdown, and Forteo assists in building bone tissue.
Forteo vs nolvadex
Forteois is a medication administered via injection to address osteoporosis; whereas Nolvadex is a pill taken orally for the treatment of hormone receptor HR+) breast cancer.
Forteo vs reclast
Forte is a medication that helps build bone strength by promoting bone formation. In contrast, Reclast is a type of medication that works to prevent bone deterioration by slowing down the process of bone resorption. Forte is typically taken through injections, while Reclast is administered yearly via intravenous infusion.
Storage and Stability of Forteo (Teriparatide Injection)
Forteo storage
Store Forteo under refrigeration at 2°C to 8°C (36°F to 46°F) at all times, even during use. Avoid exposure to freezing temperatures.
Shelf Life and Expiry Considerations
Each pen has a limited shelf life once opened and should be discarded after 28 days of first use, even if medication remains.
Instructions for Storage After First Use
Remember to put the pen in the refrigerator after every injection and keep it safe from light by storing it with the cap on when not being used.
Forteo side effects
Nausea, Dizziness, and Leg Cramps
Injection Site Reactions
- Redness, swelling, and mild pain at the injection site are typical but usually self-limited.
- Proper technique and site rotation help minimize these occurrences.
Headache and Muscle Pain
Patients may experience mild to moderate headaches or generalized musculoskeletal discomfort, which is generally responsive to conservative measures.

Hypercalcemia-Related Symptoms
As Forteo can transiently elevate serum calcium levels, some patients may experience symptoms such as fatigue, constipation, or weakness. Routine monitoring is recommended to detect and manage hypercalcemia promptly.
Serious and Rare Side Effects of Forteo (Teriparatide Injection)
Osteosarcoma Risk and Black Box Warning
Forteo carries a black box warning for an increased risk of osteosarcoma, a rare but aggressive form of bone cancer. Although observed primarily in rat studies, this potential risk necessitates cautious patient selection and vigilant monitoring.

Orthostatic Hypotension
Transient episodes of orthostatic hypotension may occur, particularly after initial doses. Patients are advised to sit or lie down if symptoms such as dizziness, lightheadedness, or fainting sensations emerge.
Severe Allergic Reactions
In some cases rarely do patients encounter extreme sensitivity reactions, like anaphylaxis or swelling of the skin known as angioedema or hives called urticaria. It is essential to stop and seek help when severe allergic reactions occur.
Urolithiasis (Kidney Stones)
Forte induced high calcium levels can increase the risk of kidney stones in people so it's important to stay hydrated and regularly check your urine calcium levels to prevent this issue.
Drug Interactions with Forteo (Teriparatide Injection)
Interactions with Digoxin
Teriparatide may alter serum calcium levels, potentiating the effects of digoxin and increasing the risk of digoxin toxicity. Close monitoring of digoxin levels and cardiac function is advisable during concomitant therapy.
Potential Impact When Combined with Antiresorptive Therapies
Co-administration with antiresorptive agents, such as bisphosphonates, may attenuate Forteo's anabolic effect. Sequential, rather than concurrent, use is generally preferred to optimize bone health outcomes.
Considerations with Calcium Supplements and Diuretics
Concurrent use of calcium supplements or thiazide diuretics requires caution, as both can exacerbate hypercalcemia when combined with Forteo therapy. Dose adjustments or careful timing may be necessary.
Warnings and Precautions When Using Forteo (Teriparatide Injection)
Risk Factors for Osteosarcoma
- Previous skeletal radiation therapy
- Paget's disease of bone
- Unexplained elevations in serum alkaline phosphatase
Patients presenting with these risk factors should avoid Forteo therapy unless the benefits overwhelmingly outweigh the risks.
Monitoring Serum Calcium Levels
Regular monitoring of calcium levels in the bloodstream is essential during the stages of treatment to ensure management and avoid potential complications associated with elevated calcium levels that may require adjustments to dosage or even discontinuation of treatment if necessary.
Safety Precautions During Initial Dosing Period
To reduce the chance of orthostatic hypotension occurring, patients are recommended to take their medication while sitting or lying down and then rest for a few minutes after the injection.
Contraindications for Forteo (Teriparatide Injection) Use
Hypersensitivity to Teriparatide or Any Component
People who are allergic to teriparatide or any ingredients in the Forteo formulation should not use this medication.
History of Bone Malignancies
Patients with a history of bone cancers or skeletal metastases should not use Forteo, as it may stimulate tumor growth.
Metabolic Bone Diseases Other Than Osteoporosis
Conditions such as hyperparathyroidism or Paget's disease present contraindications due to potential exacerbation under teriparatideâs anabolic influence.
Hypercalcemia and Unexplained Elevated Alkaline Phosphatase
Pre-existing hypercalcemia or unexplained increases in alkaline phosphatase levels require thorough evaluation prior to initiating therapy.
Forteo Administration and Monitoring
Necessity for Baseline Bone Density Tests
Dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry (DEXA) scans should be performed before commencing therapy to establish a treatment baseline and monitor progress over time.
Monitoring Serum Calcium and Uric Acid Levels
- Periodic serum calcium assessments during therapy
- Uric acid monitoring, particularly in patients with a history of gout or renal stones
Periodic Reevaluation of Therapy Necessity
Regular clinical evaluations are essential to assess therapeutic efficacy and to determine whether ongoing Forteo use remains appropriate.
Important Precautions for Forteo (Teriparatide Injection) Use
Avoidance of Concurrent Use with Other Bone Anabolic Agents
Using anabolic agents simultaneously can worsen effects without providing extra treatment benefits, so it's best to avoid this approach unless managed by a specialist.

Limitation of Total Treatment Duration (24 Months Lifetime Maximum)
To reduce the risk of developing osteosarcoma over time, patients are advised not to use Forteo for more than 24 months in their lifetime.
Education on Orthostatic Hypotension Risk
Patients must be educated on recognizing and managing orthostatic hypotension symptoms to prevent injury from potential falls or fainting episodes.
Administration of Forteo (Teriparatide Injection) in the Elderly
Efficacy Considerations in Patients Over 65 Years
Studies conducted in settings have shown effectiveness among elderly individuals; however, it is essential to monitor side effects diligently.

Increased Monitoring for Falls and Fracture Risk
Elderly individuals are more prone to falls, so it's crucial to focus attention not only on home safety but also on keeping an eye for any negative impacts that may arise.
Dosing Consistency and Cognitive Support Needs
Supporting patients may involve helping them remember when to take their medications and providing assistance with cognitive skills to ensure they take their doses properly and safely.
Administration of Forteo (Teriparatide Injection) to Pregnant and Nursing Women
Teratogenicity Studies and Pregnancy Category Information
Studies on animals have shown effects on fetuses, leading to the classification of Forteo as Pregnancy Category C, advising caution in its use unless deemed essential for treatment purposes.
Recommendations for Use in Women of Childbearing Potential
Women who can get pregnant should make sure to use birth control while receiving treatment and stop taking the medication soon as they find out they are pregnant.
Contraindications During Breastfeeding
Forteo should not be used during breastfeeding, as it is unknown whether teriparatide is excreted into human milk and what effect it may have on the nursing infant.
Administration of Forteo (Teriparatide Injection) to Pediatric Patients
Limited Data on Safety and Efficacy in Children
The safety and effectiveness of Forteo have not been established in pediatric populations, and its use is generally discouraged in individuals with open epiphyses.
Research on Off-Label Use in Severe Osteoporosis in Pediatric Populations
Investigational use has occurred in severely osteoporotic children, such as those with genetic bone disorders, but remains experimental and tightly regulated.
Risk-Benefit Assessment in Young Patients
Any pediatric use requires a meticulous evaluation of potential benefits versus long-term skeletal risks, undertaken only by experienced specialists.
Overdosage of Forteo (Teriparatide Injection)
Symptoms of Overdose (Severe Hypercalcemia)
Excessive dosing can lead to profound hypercalcemia, manifesting as nausea, vomiting, weakness, mental status changes, and cardiac arrhythmias.
Immediate Management and Supportive Care
In suspected overdose cases, immediate cessation of Forteo, aggressive hydration, and medical interventions to lower serum calcium levels are indicated.
Emergency Protocols for Suspected Overdose
Patients experiencing symptoms suggestive of overdose should seek emergency medical care without delay, with electrolyte panels and cardiac monitoring prioritized upon presentation.
Safe Handling Precautions for Forteo (Teriparatide Injection)
Instructions for Proper Pen Use
- Always attach a new, sterile needle before each injection.
- Store the pen with the cap on to protect the medication from light.
- Follow proper priming procedures before initial use.
Disposal Procedures for Used Pens
Used pens and needles should be disposed of in FDA-cleared sharps disposal containers to prevent accidental injuries and environmental contamination.
Safety Measures to Prevent Accidental Exposure
Keep Forteo pens out of reach of children and pets. Never share pens between patients to avoid cross-contamination or inadvertent exposure to infectious diseases.
Forteo, Teriparatide Injectoin FAQ
- Are there any side effects from Forteo?
- Where is the best place to inject Forteo?
- What is the benefit of Forteo injection?
- Does Forteo affect your kidneys?
- When is the best time to inject Forteo?
- Who should not use Forteo?
- What is a natural alternative to Forteo?
- What happens if you stop taking Forteo?
- Who is a candidate for FORTEO?
- How many years can you take Forteo?
- What happens when you stop teriparatide?
- Do you need to take calcium with Forteo?
- Can Forteo cause kidney problems?
- Can I take Forteo every other day?
- What is the success rate of Forteo?
- Does Forteo need to be refrigerated?
- Are there any side effects from Forteo?
- Does Forteo affect your kidneys?
- Who should not use Forteo?
- What is a natural alternative to Forteo?
- Can Forteo cause kidney problems?
Are there any side effects from Forteo?
Common side effects of Forteo are usually mild. This can include discomfort, an upset stomach, and occasional dizziness.
Where is the best place to inject Forteo?
Thigh or abdomen (lower stomach area)
What is the benefit of Forteo injection?
Treatment of osteoporosis
Does Forteo affect your kidneys?
Taking Forteo might lead to a rise in calcium levels in your urine, which could potentially elevate the chances of developing bladder or kidney stones.
When is the best time to inject Forteo?
Any time of the day
Who should not use Forteo?
Bone cancer or a medical history involving it; elevated levels of phosphatase (an enzyme, in bones); the presence of metabolic bone diseases, such as Paget's disease; or if the epiphyses are still open (indicating ongoing bone growth).
What is a natural alternative to Forteo?
Ensuring your bones stay healthy as you age requires getting calcium from green veggies and dairy products and vitamin D from salmon while balancing calorie intake is crucial.
What happens if you stop taking Forteo?
Osteoporosis may worsen
Who is a candidate for FORTEO?
Postmenopausal women and men diagnosed with osteoporosis are at a higher risk of experiencing bone fractures
How many years can you take Forteo?
2 years
What happens when you stop teriparatide?
Postmenopausal women lose bone mass
Do you need to take calcium with Forteo?
If your doctor suggests taking calcium and vitamin D supplements alongside Forteo medication.
Can Forteo cause kidney problems?
Taking Forteo may lead to an increase in your blood calcium levels, which could increase the likelihood of kidney stones forming in your body.
Can I take Forteo every other day?
Everyday
What is the success rate of Forteo?
96 out of every 100 individuals who received Forteo experienced a boost in bone density. Additionally, 44% had an increase of 10% bone density.
Does Forteo need to be refrigerated?
Yes
Are there any side effects from Forteo?
Typical side effects of Forteo are usually minor. It may include joint discomfort, stomach upset, and occasional dizziness.
Does Forteo affect your kidneys?
Taking Forteo might result in calcium levels in your urine, potentially raising the chance of developing bladder or kidney stones.
Who should not use Forteo?
History of bone cancer or high levels of phosphatase (an enzyme, in bones), metabolic bone disease, like Paget's disease of the bone, or open epiphyses (indicating bones that are still growing).
What is a natural alternative to Forteo?
Ensuring bones involves getting calcium and vitamin D from sources, like leafy greens and salmon, while also considering protein intake, from dairy products as you age, and managing calorie intake carefully.
Can Forteo cause kidney problems?
Taking Forteo may increase the levels of calcium in your blood, which could increase your risk of developing kidney stones.