Introduction to Tiova Rotacapsule
Tiova Rotacapsule contains Tiotropium Bromide, a potent anticholinergic bronchodilator specifically designed to enhance respiratory function. It belongs to the class of long-acting muscarinic antagonists (LAMA), providing sustained relief from airflow obstruction. By targeting overactive cholinergic pathways in the lungs, this medication reduces bronchospasm and improves overall lung capacity. Marketed under various brand names, Tiotropium is widely available across global regions, particularly prescribed in chronic respiratory conditions.
Composition and Formulation
The principal active ingredient in Tiova Rotacapsule is Tiotropium Bromide. Each capsule is precisely formulated to deliver an optimal dose, ensuring uniform therapeutic effects. Available strengths typically include 18 mcg per capsule, optimized for once-daily inhalation therapy. In addition to the active agent, the capsules contain carefully selected excipients that stabilize the formulation. The drug is administered using a Rotahaler, a specialized device that enables the fine powder to reach deep into the respiratory tract for maximum efficacy.
Mechanism of Action: How Tiotropium Works
Tiotropium acts as a long-acting muscarinic antagonist (LAMA). It selectively blocks muscarinic receptors (M3 subtype) located on smooth muscle in the bronchial airways. This antagonism leads to relaxation of the bronchial muscles, reduced contraction, and improved airflow. By decreasing parasympathetic tone, Tiotropium prevents sustained bronchoconstriction. Its prolonged binding affinity provides therapeutic coverage for 24 hours, enabling convenient once-daily administration. Patients experience reduced dyspnea, fewer exacerbations, and enhanced exercise tolerance.
Approved Medical Uses
Tiova Rotacapsule is primarily indicated for the long-term management of chronic respiratory disorders. Approved uses include:
- Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD): Improves airflow limitation and enhances quality of life in patients with persistent respiratory compromise.
- Maintenance therapy for chronic bronchitis: Reduces mucus hypersecretion and mitigates airway inflammation.
- Emphysema-related obstruction: Restores ventilation efficiency by alleviating trapped air in the alveoli.
- Prevention of COPD exacerbations: Decreases the frequency and severity of acute flare-ups requiring hospitalization.
Off-Label Uses
Beyond established indications, Tiotropium demonstrates utility in off-label contexts. Emerging evidence supports its use in:
- Asthma management: Particularly in patients unresponsive to corticosteroids or long-acting beta-agonists.
- Bronchiectasis: Helps reduce recurrent infections and airway obstruction.
- Pulmonary fibrosis-associated symptoms: May provide adjunctive relief from breathlessness.
- Exercise-induced bronchospasm: Investigational use to minimize airway narrowing during exertion.
Dosage and Administration
The recommended adult dosage is typically one 18 mcg capsule inhaled once daily. Capsules must be used exclusively with the Rotahaler device to ensure precise delivery. Proper inhalation technique is vital: insert the capsule, pierce it within the chamber, and inhale the released powder deeply. If a dose is missed, it should be taken as soon as remembered unless the next scheduled dose is imminent. Consistent, daily administration is essential for sustained therapeutic effect and prevention of symptom recurrence.
Special Administration Considerations
- Elderly patients: Generally well tolerated, though increased susceptibility to anticholinergic effects necessitates close monitoring.
- Pregnant women: Limited human data exist; administration should only proceed when benefits outweigh fetal risks.
- Nursing mothers: Excretion into breast milk is possible; caution is advised to prevent infant exposure.
- Children and adolescents: Safety and efficacy have not been fully established; routine use is not recommended under 18 years.
Side Effects
Common Side Effects
- Dry mouth and throat irritation
- Cough or mild hoarseness
- Transient dizziness
- Constipation and occasional urinary retention
Less Common but Important Side Effects
- Blurred vision and potential worsening of glaucoma
- Palpitations or tachycardia
- Allergic skin reactions including rash and urticaria
Serious Adverse Effects
- Paradoxical bronchospasm: Unexpected airway tightening after inhalation
- Severe hypersensitivity responses: Angioedema, anaphylaxis, and other systemic allergic reactions
Drug Interactions
Tiotropium Bromide may interact with various pharmacological agents, potentially intensifying anticholinergic effects or altering therapeutic outcomes. Understanding these interactions is crucial for safe and effective therapy.
- Other anticholinergics: Concomitant use with medications such as ipratropium or glycopyrrolate can magnify side effects including dry mouth, urinary retention, and blurred vision.
- Beta-agonists and corticosteroids: While often co-prescribed for COPD management, the combination requires monitoring, as additive cardiovascular strain or paradoxical airway reactions may occur.
- Systemic antihistamines and antidepressants: Drugs with anticholinergic activity, such as tricyclic antidepressants or certain antihistamines, may exacerbate drowsiness, constipation, and ocular complications.
- Alcohol and smoking: Excessive alcohol can heighten dizziness or sedation, while tobacco smoking reduces pulmonary function, diminishing the clinical benefit of inhaled therapy.
Warnings and Important Precautions
Several safety concerns necessitate vigilance during treatment:
- Risk of acute narrow-angle glaucoma: Ocular exposure to the powder may precipitate acute angle-closure crises with eye pain, visual halos, and redness.
- Urinary retention: Patients with prostatic hyperplasia or bladder neck obstruction are particularly vulnerable to urinary difficulties.
- Cardiovascular risks: Individuals with arrhythmias, ischemic heart disease, or uncontrolled hypertension should be carefully monitored due to potential tachycardia and palpitations.
- Avoiding ocular exposure: Inhalation should be performed with precision to prevent medication contact with the eyes.
- Renal impairment: Reduced clearance in renal dysfunction may heighten systemic effects, warranting dose caution and periodic monitoring.
Contraindications
Tiotropium must not be administered in the following situations:
- Hypersensitivity: Patients with known allergies to Tiotropium, Atropine, or their derivatives should avoid this medication.
- Severe allergic reactions to formulation components: History of anaphylaxis or angioedema linked to excipients is a contraindication.
- Acute bronchospasm: Tiotropium is unsuitable for acute rescue therapy; it does not provide immediate relief of sudden breathing difficulties.
Careful Administration
Certain patient groups require heightened caution:
- Cardiovascular disorders: Regular cardiac assessment is advised in those with arrhythmias or recent myocardial infarction.
- Narrow-angle glaucoma: Patients should be counseled to report ocular discomfort, blurred vision, or eye pain immediately.
- Renal or hepatic impairment: Pharmacokinetics may be altered, necessitating dose adjustments or enhanced monitoring.
- Urinary tract obstruction: Clinical evaluation should precede therapy to reduce the risk of severe urinary retention.
Overdosage and Emergency Management
Exceeding the recommended dose can precipitate systemic toxicity. Key symptoms include:
- Pronounced dry mouth and mucosal dryness
- Visual disturbances such as blurred vision and pupillary dilation
- Hallucinations, confusion, or disorientation
- Urinary retention and painful difficulty in voiding
- Tachycardia or palpitations
Management: Treatment is primarily supportive. Hydration, airway support, and symptomatic care form the backbone of intervention. Immediate medical assistance should be sought if severe neurological or cardiovascular manifestations appear.
Storage and Handling Precautions
Proper storage and handling ensure both safety and therapeutic integrity:
- Storage conditions: Maintain capsules in a cool, dry place, ideally below 25°C. Protect from direct heat and sunlight.
- Moisture protection: Keep capsules sealed until use, as exposure to humidity may degrade the powder formulation.
- Device care: Use the Rotahaler device exclusively for Tiova capsules. Clean and dry it regularly to prevent powder buildup.
- Disposal: Expired or unused capsules should be discarded responsibly, away from children and pets.
- Accidental ingestion: The capsules are not intended for oral consumption. If swallowed, medical evaluation is recommended.
Tiova Rotacapsule, Tiotropium Bromide FAQ
- What is Tiova used for?
- How to use Tiova rotacaps?
- What is the duration of action of Tiova?
- What are the most common side effects of tiotropium bromide?
- When is the best time to take tiotropium?
- Can we drink water after rotacaps?
- How many rotacaps per day?
- What is tiotropium bromide used for?
- What is the mechanism of action of tiotropium bromide?
What is Tiova used for?
The Tiova Inhaler is a type of medication that works by blocking nerve impulses, which helps to calm the airways. People with pulmonary disease and asthma often use it to manage their symptoms. By relaxing the muscles in the airways, this inhaler makes breathing a lot easier.
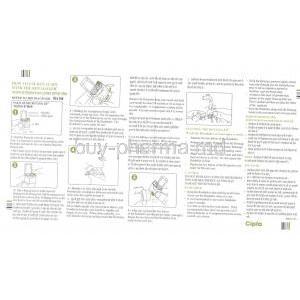
How to use Tiova rotacaps?
To use the rotahaler, start by placing the capsule at the base, making sure it's not inserted into the mouthpiece. Next, twist the mouthpiece all the way around until it clicks into place. Then take a breath in through the mouthpiece.
What is the duration of action of Tiova?
24 hours
What are the most common side effects of tiotropium bromide?
- Blurred vision
- Urinary retention
- Fast hearbeat
When is the best time to take tiotropium?
Morning or evening
Can we drink water after rotacaps?
Yes
How many rotacaps per day?
Up to 6
What is tiotropium bromide used for?
Tiotropium is a medication that helps people with pulmonary disease or COPD breathe more easily.
What is the mechanism of action of tiotropium bromide?
It interferes with the receptors in the muscles that line the airways, which in turn helps to relax them.