Introduction to Orcibest (Orciprenaline Sulfate)
Overview of drug category: bronchodilator and β2-adrenergic agonist classification
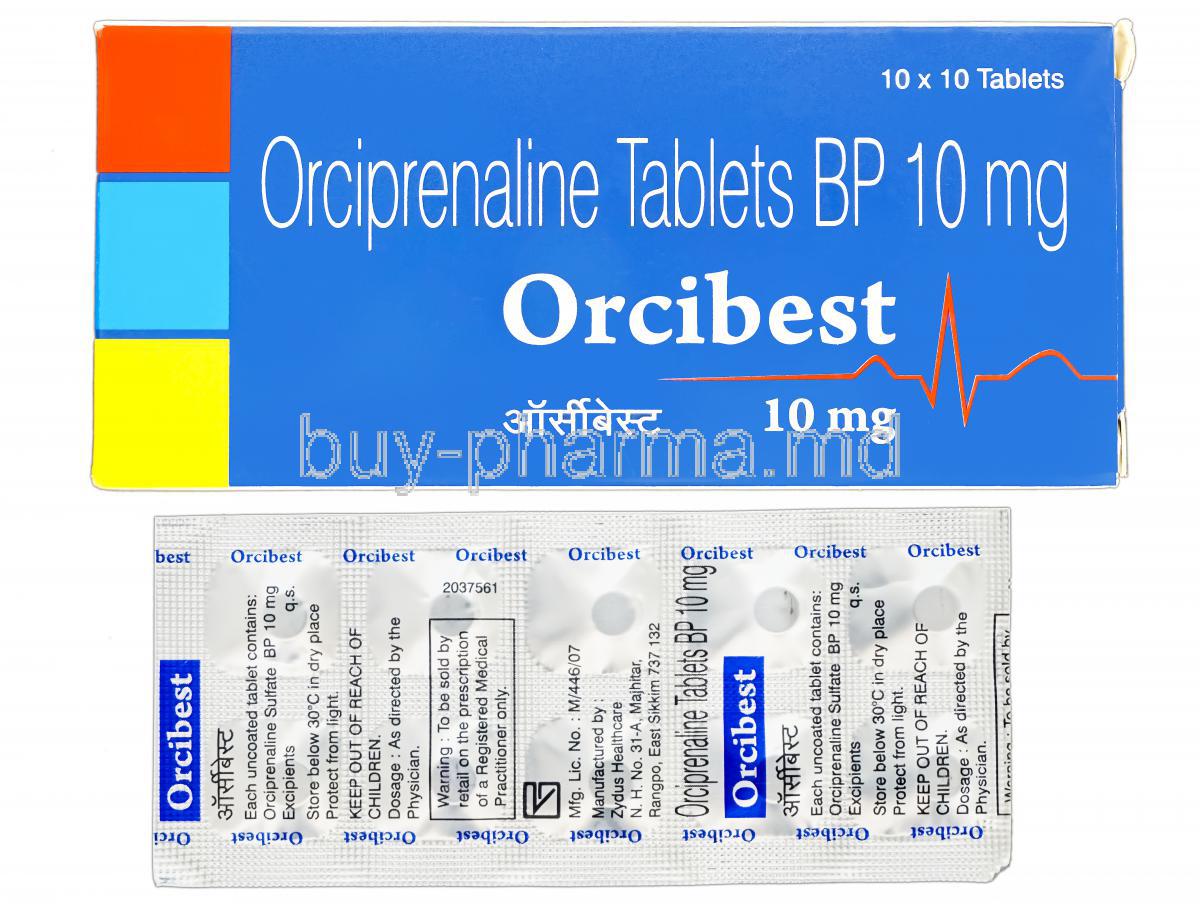
Orcibest (Orciprenaline Sulfate) is a selective bronchodilator belonging to the β2-adrenergic agonist pharmacologic class. It is used to improve airflow and mitigate airflow restriction. In clinical respiratory therapeutics, it is considered a frontline airway smooth-muscle relaxant.
Clinical background and relevance in obstructive airway disease
This medication is commonly utilized in scenarios of airflow compromise such as obstructive bronchial pathology. Patients with intermittent or chronic reactive airway dysfunction benefit from its airway lumen widening effects. With bronchospasm being a hallmark in asthma and certain chronic obstructive pulmonary diseases, Orcibest provides symptomatic relief quickly.
- Rapid onset bronchodilation
- Reduction of airway hyperreactivity
- Enhanced expiratory flow rates
Brand names, generic name, pharmaceutical company notes
The generic designation is Orciprenaline Sulfate. It is marketed under several brand names in different markets and may vary depending on the region and distributor. Pharmaceutical manufacturers produce both single-drug preparations and combination forms in specific territories.
Composition and Formulation Specifications
Active ingredient: Orciprenaline Sulfate composition details
The active molecule is Orciprenaline Sulfate, a synthetic catecholamine derivative. It interacts with β2 receptors in bronchiolar musculature and ameliorates bronchospasm.
Available dosage forms: tablets, syrup, inhalation preparations
Commercial availability includes:
- Oral tablets
- Oral syrup formulations
- Inhalation presentations in some markets
Excipients and inactive ingredients relevance to tolerance
Inactives may include stabilizers, sweeteners, and suspension vehicles. In susceptible patients, excipients like dyes or preservatives may influence tolerability.
Primary Uses of Orcibest (Approved Indications)
Relief of bronchospasm in asthma
Orcibest alleviates episodic constriction of bronchial musculature. It allows better alveolar ventilation and mitigates wheeze episodes.
Symptom management in COPD and chronic bronchitis
In COPD phenotypes with reversible components, this molecule plays a role in controlling breathlessness. It optimizes airflow by reducing bronchial tone.
Acute bronchoconstriction episodes due to allergens or environmental triggers
Acute bronchial narrowing following exposure to irritants may respond to Orciprenaline administration.
Expanded Off-Label Uses
Off-label role in bronchiolitis in selected pediatric populations
In some clinical settings, its use may be considered in bronchiolitis where bronchial spasm predominance is notable.
Off-label consideration in exercise-induced bronchospasm
Certain specialists consider this β2 agonist for prophylactic use in exercise-triggered airway narrowing.
Off-label use in emphysema symptom control scenarios
In emphysematous deterioration with bronchial reactivity, the drug may provide symptom relief under controlled regimens.
How Orciprenaline Works – Mechanism of Action
β2 receptor agonism and smooth muscle relaxation
The molecular effect is mediated by stimulation of β2-adrenergic receptors. Smooth muscle relaxation occurs promptly.
Bronchodilation and airway resistance reduction mechanism
Bronchial luminal diameter increases. Airway resistance decreases. This culminates in improved ventilatory throughput.
Impact on intracellular cAMP levels and airway tone modulation
By increasing intracellular cyclic AMP, smooth muscle contraction forces diminish and airway tone becomes less restrictive.
Dosage and Administration Recommendations
Standard adult dosing guidelines and titration
Dosing varies based on severity. Individual titration may be required for optimal symptom control.
Pediatric dosing ranges and safety considerations
Pediatric regimens are weight-oriented and require cautious escalation.
Frequency of dosing and onset of action expectations
Onset of bronchodilation often occurs rapidly. Duration may differ based on formulation.
Administration tips for tablets, syrup, inhalation forms
- Tablets should be swallowed whole
- Syrups require accurate volumetric measurement
- Inhalation forms must be used with correct technique
Important Precautions Prior to Initiating Therapy
Pre-existing cardiovascular disease assessment
Cardiac status should be evaluated due to potential adrenergic effect intensity.
Monitoring requirement in arrhythmia-susceptible patients
Patients with arrhythmogenic tendencies may require more vigilant monitoring strategies.
Assessment of thyroid disease and metabolic conditions prior to use
Hyperthyroidism may magnify adverse adrenergic responses.
Contraindication Profile
Known hypersensitivity to orciprenaline sulfate
Absolute avoidant use applies if hypersensitivity reactions have occurred historically.
Prohibited use in patients with severe tachyarrhythmias
Tachyarrhythmic status conflicts with β2 agonist stimulation.
Contraindication in acute hypertrophic cardiomyopathy instability
In unstable ventricular outflow obstruction, use is inappropriate.
Side Effects Profile
Comprehensive adverse events classification
Adverse reactions span cardiovascular, neurologic and metabolic domains.
Cardiovascular-related adrenergic effects
Possible increases in pulse rate and pressure fluctuations may appear.
Neurologic and metabolic effects potential
Patients may describe tremor, agitation, or metabolic perturbations.
Common Side Effects
Palpitations, tremor, nervousness
These are frequently described in routine ambulatory practice.
Mild tachycardia and dizziness
Dizziness may appear with rapid sympathetic stimulation.
Headache, nausea, sweating
These symptoms are usually transient and dose-associated.
Drug Interaction Considerations
Interaction with MAO inhibitors and TCA antidepressants
Co-administration may potentiate systemic adrenergic response.
Interaction with beta-blockers lowering efficacy
Non-selective beta-blockers antagonize bronchodilation effects.
Interaction with stimulants and sympathomimetic agents
Stacking adrenergic agonists may provoke undesirable synergistic effects.
Careful Administration Guidance
Administration in individuals with pre-existing ventricular arrhythmias
Extra caution is mandatory as arrhythmia aggravation is possible.
Dose caution in hypertension or hyperthyroidism
Adrenergic stimulation may escalate underlying hypertension.
Adjustment consideration in diabetic patients due to glycemic effect
Blood glucose shifts may require monitoring for glycemic recalibration.
Administration in Elderly Individuals
Age-related cardiovascular risk and dosage reduction
Lower doses may mitigate cardiac over-excitation in seniors.
Monitoring of hypertension and arrhythmia development
Physiological frailty increases the risk of hemodynamic fluctuations.
Polypharmacy interaction caution in geriatrics
Concomitant medications must be appraised to avoid interaction clusters.
Administration to Pregnant Women and Nursing Mothers
Placental crossing and fetal exposure concerns
Systemic β2 agonists may cross placental barriers. Fetal exposure risk must be weighed carefully.
Breast milk excretion potential and neonatal effects
Breastfeeding infants may be exposed to trace quantities through maternal milk.
Clinical risk-benefit evaluation during pregnancy
Therapy decisions require individual benefit justification and clinical prudence.
Administration in Pediatric Populations
Safety guidance for infants and children
Doses must be substantially smaller and precisely calculated.
Risk of overstimulation and tachycardia in pediatric dosing
Sympathetic overdrive is more prominent in children. Monitoring is prudent.
Monitoring growth and respiratory symptom control patterns
Regular respiratory performance assessment helps calibrate therapeutic response.
Overdosage and Toxicity Management
Signs of overdose such as severe tachyarrhythmia and tremors
Excessive intake may trigger profound sympathetic excitation. Manifestations may escalate rapidly. Patients may describe alarming sensations such as heart racing, tremors, agitation, and pounding pulse.
- Severe tachyarrhythmia
- Pronounced tremulousness
- Palpitations and chest discomfort
- Anxiety, diaphoresis, nausea
If untreated, physiologic instability may occur. Rapid recognition is critical.
Emergency stabilization guidelines
Acute stabilization requires immediate medical oversight. Clinical teams prioritize cardiopulmonary parameters and hemodynamic stability. Interventions are tailored to the degree of adrenergic overstimulation.
- Continuous cardiac rhythm monitoring
- Blood pressure trend assessment
- Rapid intervention if malignant arrhythmias manifest
Supportive sedation or controlled beta blockade may be evaluated depending on clinical discretion.
Decontamination or supportive measures in toxicity presentation
Management can include gastrointestinal decontamination if the ingestion was recent. Activated charcoal may be considered early. Once absorbed, pharmacologic antagonism and supportive therapy take precedence.
- Electrolyte monitoring and correction
- IV fluids for circulatory support
- Metabolic parameter assessment
Handling and Storage Precautions
Proper room temperature storage conditions
The product should be stored at stable room temperature. Excessive thermal fluctuation may degrade potency. A cool, dry cabinet is ideal.
Light and moisture protection guidelines
Exposure to direct light or humidity may alter chemical stability. Storage in sealed containers reduces spoilage risk and maintains pharmaceutical integrity.
- Keep away from sunlight
- Avoid bathroom or kitchen humidity zones
- Ensure lid closure after each opening
Safe handling and disposal of medication to avoid misuse
Unused medication should not be left accessible to children or unauthorized individuals. Disposal through regulated pharmaceutical take-back programs is recommended. Flushing into public wastewater should be avoided unless specifically directed.
- Keep out of sight of minors
- Do not share medication
- Dispose via approved medical waste channels