Introduction to Metaflam Oral Suspension for Dogs
Overview of Metaflam Oral Suspension
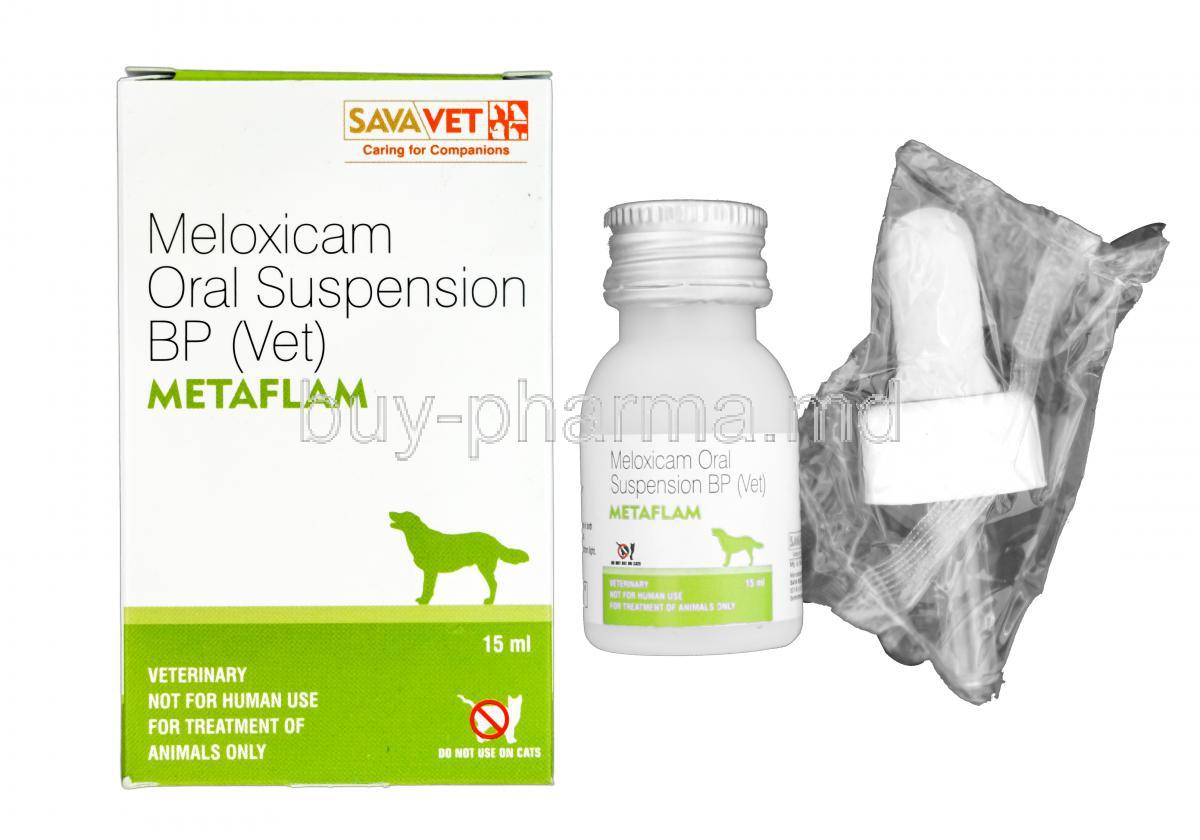
Metaflam Oral Suspension is a veterinary pharmaceutical formulation specifically developed to manage pain and inflammation in canines. It offers a palatable and convenient liquid dosage form, making it ideal for dogs that resist tablets. Metaflam is frequently used to alleviate discomfort associated with degenerative joint conditions and post-operative recovery.
Classification: NSAID for Veterinary Use
Metaflam is classified as a non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) tailored for animal health. Its active ingredient, meloxicam, exerts a selective inhibitory effect on cyclooxygenase enzymes, especially COX-2, thus reducing the production of prostaglandins that mediate inflammation, pain, and fever.
Key Benefits for Canine Inflammatory Conditions
- Provides rapid relief from joint pain and stiffness - Enhances mobility and quality of life in aging pets - Reduces swelling and post-surgical inflammation - Liquid form ensures ease of dosing and better owner compliance
Availability and Regulatory Approval Status
Metaflam Oral Suspension is approved for veterinary use in many countries under stringent regulatory frameworks. It is available by prescription and dispensed through licensed veterinarians and veterinary pharmacies.
Medical and Therapeutic Uses of Metaflam Oral Suspension
Approved Indications
Veterinarians prescribe Metaflam for a variety of inflammatory conditions in dogs. Its efficacy has been demonstrated in:
- Osteoarthritis in dogs: Long-term pain control and reduction in joint inflammation.
- Post-operative pain and inflammation: Used following orthopedic and soft tissue surgery to support recovery.
- Pain management in chronic musculoskeletal conditions: Suitable for ongoing use under monitoring.
- Use in inflammatory disorders of the musculoskeletal system: Beneficial in sprains, strains, and ligament injuries.
- Supportive care for mobility and comfort in aging dogs: Improves overall vitality and ease of movement.
Off-Label and Investigational Uses in Veterinary Practice
Use in Canine Dental Pain Management
Though not officially approved for this use, veterinarians may employ Metaflam to manage inflammation and pain after dental procedures or in cases of periodontal disease.
Management of Intervertebral Disc Disease (IVDD)
In dogs with mild to moderate IVDD, Metaflam can be considered part of a conservative medical management protocol, reducing spinal inflammation and associated discomfort.
Treatment of Inflammation in Skin and Ear Conditions
Metaflam is sometimes used to control secondary inflammation caused by allergic dermatitis or chronic otitis externa, in combination with antibiotics or antifungals.
Application in Trauma-Related Musculoskeletal Injuries
For soft tissue trauma or blunt injuries, Metaflam offers symptomatic relief and aids in reducing inflammation, expediting the healing process.
How Metaflam Oral Suspension Works in Dogs
Mechanism of Action: COX-2 Preferential Inhibition
Meloxicam, the active ingredient in Metaflam, preferentially inhibits COX-2 enzymes, which are primarily involved in inflammatory responses. By sparing COX-1, it helps maintain gastrointestinal and renal safety.
Anti-inflammatory, Analgesic, and Antipyretic Effects
- Anti-inflammatory: Suppresses prostaglandin synthesis to reduce swelling - Analgesic: Alleviates pain by blocking nociceptive pathways - Antipyretic: Lowers fever caused by systemic inflammation
Onset of Action and Duration of Effectiveness
Metaflam typically begins to exert its effects within 1–2 hours after administration. Its clinical benefits often last for up to 24 hours, allowing once-daily dosing.
Pharmacokinetics and Bioavailability in Canines
- Oral bioavailability: High, approximately 89% - Peak plasma levels reached within 3–5 hours - Half-life: Around 20–24 hours - Excretion primarily via feces, with minimal renal elimination
Dosage and Administration Guidelines
Standard Dosing Based on Body Weight
Metaflam is dosed at 0.2 mg/kg body weight on the first day, followed by 0.1 mg/kg once daily. Precise dosage is calculated by the veterinarian based on the dog’s weight.
Initial and Maintenance Dose Recommendations
- Initial loading dose: 0.2 mg/kg on Day 1 - Maintenance dose: 0.1 mg/kg daily thereafter - Dosing syringe provided for accurate administration
Administration Method: Oral Delivery with or Without Food
Metaflam can be given with or without meals. However, administering it with food may help reduce gastrointestinal side effects in sensitive dogs.
Duration of Treatment and Tapering Guidelines
Treatment duration is based on the condition being managed. Chronic conditions may require extended use with periodic veterinary reassessment. Gradual tapering is advisable when discontinuing long-term therapy.
Missed Dose Instructions
If a dose is missed, it should be given as soon as remembered. However, if the next dose is near, skip the missed one and resume the regular schedule. Double-dosing is strictly discouraged.
Use in Different Dog Breeds and Sizes
Metaflam is suitable for small, medium, and large breeds. Dosage must be carefully calculated for toy breeds and dogs with unique metabolic profiles (e.g., Greyhounds).
Composition and Formulation of Metaflam Oral Suspension
Active Ingredient: Meloxicam
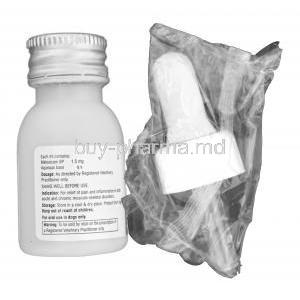
Each mL of Metaflam Oral Suspension contains 1.5 mg of meloxicam, a potent NSAID.
Inactive Components and Excipients
- Sorbitol solution - Sodium benzoate (preservative) - Glycerol - Flavoring and colorants - Purified water
Flavoring Agents for Palatability
The formulation includes artificial flavoring, often resembling meat or liver, to increase palatability and ease of administration.
Available Strengths and Packaging Options
Metaflam Oral Suspension is commonly supplied in: - 10 mL, 32 mL, and 100 mL bottles - Dosing syringe with weight-calibrated markings - Tamper-proof cap for safe storage
Storage Instructions and Shelf Life
Recommended Storage Temperature and Conditions
Store below 25°C (77°F). Avoid exposure to extreme heat and direct sunlight.
Protecting the Suspension from Light and Moisture
Keep the bottle tightly closed when not in use. Store in a dry, dark place to maintain formulation integrity.
Shake-Well Instructions Before Use
The oral suspension should be shaken well before each use to ensure uniform distribution of the active ingredient.
Shelf Life Before and After Opening
- Unopened shelf life: 2 years from manufacturing date - After opening: Use within 6 months - Do not use past the expiration date printed on the label
Disposal of Expired or Unused Medication
Unused Metaflam should be discarded in accordance with local pharmaceutical disposal regulations. Avoid pouring into drains or throwing into household waste.
Drug Interactions and Compatibility with Other Medications
Interaction with Other NSAIDs or Corticosteroids
Concurrent use with other NSAIDs (e.g., carprofen) or corticosteroids (e.g., prednisone) is contraindicated due to heightened risk of gastrointestinal ulceration or renal damage.
Potential Interactions with Diuretics and Anticoagulants
- Diuretics may compound renal risk when used with meloxicam - Co-administration with anticoagulants such as warfarin may increase bleeding risk and should be avoided or monitored closely
Caution with Nephrotoxic Agents
Drugs like aminoglycoside antibiotics or certain chemotherapeutics that exert renal toxicity may amplify adverse renal effects when used with Metaflam.
Compatibility with Antibiotics and Anti-Infectives
Generally compatible with common veterinary antibiotics such as amoxicillin, cephalexin, and enrofloxacin, but caution should still be observed.
Monitoring When Used Alongside Sedatives or Anesthetics
Veterinary oversight is recommended when Metaflam is used pre- or post-operatively with anesthetics or sedatives to monitor renal function and blood pressure stability.
Warnings and Safety Considerations
Risk of Gastrointestinal Ulceration and Bleeding
Metaflam, as a non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID), carries a risk of gastrointestinal (GI) complications. Prolonged use or higher-than-recommended doses may lead to the formation of ulcers in the stomach or intestines. Symptoms such as vomiting (especially with blood), dark tarry stools, or abdominal discomfort should be promptly reported to a veterinarian.
Potential for Renal or Hepatic Toxicity
NSAIDs like meloxicam may impair renal perfusion and hepatic function, particularly in dogs with pre-existing organ dysfunction. Regular laboratory monitoring is vital to detect early signs of:
- Elevated liver enzymes
- Increased blood urea nitrogen (BUN) or creatinine
- Changes in urine specific gravity or protein content
Not Recommended for Dehydrated, Hypovolemic, or Hypotensive Dogs
In dogs with compromised blood volume or low blood pressure, renal perfusion may be further reduced by meloxicam, leading to acute kidney injury. Hydration status should be corrected prior to initiating therapy.
Monitoring Requirements During Long-Term Use
For chronic use, it is essential to monitor:
- Complete blood counts (CBC)
- Liver and kidney function tests every 2–4 months
- Overall clinical response and mobility levels
Importance of Periodic Veterinary Evaluations
Routine re-evaluations help assess the therapeutic response, adjust dosage, and detect emerging adverse effects. Owners should maintain an open line of communication with their veterinarian for early intervention if any concerns arise.
Contraindications for Use in Dogs
Known Hypersensitivity to Meloxicam or NSAIDs
Dogs with a documented allergic reaction to meloxicam or other NSAIDs (e.g., carprofen, deracoxib) should not receive Metaflam due to the risk of anaphylaxis or severe adverse reactions.
Dogs with Existing Gastrointestinal Ulcers or Bleeding Disorders
Administering Metaflam in such cases may exacerbate ulceration or lead to life-threatening hemorrhages.
Severe Renal or Hepatic Impairment
In dogs with advanced kidney or liver disease, the metabolism and excretion of meloxicam may be impaired, heightening toxicity risks.
Concurrent Use with Other NSAIDs or Corticosteroids
Co-administration is contraindicated due to additive toxicity. Combination therapy may dramatically increase the likelihood of GI, renal, or cardiovascular complications.
Careful Administration Guidelines
Gradual Introduction for Sensitive Dogs
For dogs with prior NSAID sensitivities or mild organ dysfunction, initiating treatment with a lower test dose may be considered under veterinary supervision.
Monitoring During Initial Days of Treatment
The first 3–5 days of administration are critical. Watch for:
- Changes in appetite
- Vomiting or diarrhea
- Lethargy or behavioral changes
Dose Adjustments for Dogs with Borderline Kidney or Liver Function
Veterinarians may prescribe a reduced dose or extend dosing intervals to mitigate risk in dogs with marginal renal or hepatic reserve.
Importance of Water Intake and Hydration
Adequate hydration is crucial to maintain renal perfusion and ensure safe NSAID metabolism. Ensure dogs have constant access to clean, fresh water.
Important Precautions and Veterinary Monitoring
Regular Blood Work and Urinalysis for Long-Term Use
Veterinary teams should conduct baseline testing before initiation and repeat panels every few months for chronic therapy.
Monitoring Signs of Vomiting, Diarrhea, Lethargy, or Appetite Loss
These are early indicators of intolerance or emerging organ toxicity. Immediate cessation and evaluation are warranted.
Assessment of Pain Relief Effectiveness
If pain control is inadequate, reassessment of dosage, or consideration of alternative therapies, may be required.
Adherence to Prescribed Dosage Schedule
Overdosing or inconsistent administration increases the risk of adverse events and diminishes therapeutic benefit.
Avoiding Abrupt Discontinuation
While tapering is not always necessary, sudden cessation in long-term users may result in pain rebound or inflammation flare-up.
Administration to Geriatric Dogs
Age-Related Sensitivity to NSAIDs
Older dogs often exhibit reduced hepatic and renal clearance, making them more susceptible to drug accumulation and toxicity.
Baseline and Ongoing Renal and Liver Function Tests
Routine biochemical profiling ensures early detection of organ stress or damage.
Lower Starting Doses and Gradual Titration
Start low and increase cautiously. Even minor dose increases can impact tolerability in elderly canines.
Increased Risk of Adverse Effects and Monitoring Strategies
Geriatric dogs require closer clinical supervision, particularly when Metaflam is used in conjunction with other medications for age-related conditions.
Administration to Pregnant, Breeding, and Lactating Dogs
Safety During Pregnancy: Lack of Sufficient Data
No definitive studies exist regarding Metaflam's safety in pregnant bitches. Use only if benefits outweigh potential risks.
Avoidance in Late Pregnancy Due to Risk of Fetal Harm
NSAIDs may affect fetal cardiovascular development or delay labor by reducing prostaglandin levels.
Use in Lactating Females: Excretion in Milk and Risk to Puppies
Meloxicam may be excreted in small quantities into breast milk. Neonatal exposure could lead to adverse effects on renal or GI function.
Breeding Dogs: Effects on Fertility
While not directly contraindicated, prolonged NSAID use may affect ovulation and implantation in breeding animals.
Use in Puppies and Younger Dogs
Minimum Age and Weight Requirements for Use
Metaflam is typically indicated for dogs over 6 weeks of age and above a certain body weight threshold, depending on formulation strength.
Caution in Immature Organ Systems
Developing liver and kidneys may not efficiently metabolize meloxicam, increasing exposure and risk.
Adjusted Dosage Based on Developmental Stage
Pediatric dosing should be individualized and always under veterinary discretion.
Veterinary Discretion and Case-by-Case Assessment
Use in young dogs should be reserved for clear clinical indications where benefits justify potential risks.
Signs and Management of Overdosage
Symptoms of Overdose: Vomiting, Bloody Stools, Seizures, Lethargy
Acute overdose may lead to:
- Profound gastrointestinal distress
- Neurological symptoms including ataxia or seizures
- Systemic inflammation or shock
Emergency Veterinary Intervention
Immediate care is critical. Delay can result in irreversible organ damage or fatal outcomes.
Induction of Emesis and Activated Charcoal Use
Decontamination strategies may be effective if the overdose is recent (within 1–2 hours).
Supportive Care: IV Fluids, Gastroprotectants, Renal Support
Therapeutic measures include:
- Intravenous fluid therapy to maintain perfusion
- Gastrointestinal protectants (e.g., sucralfate, omeprazole)
- Monitoring urine output and renal indices
Prognosis Depending on Dose and Timing of Treatment
The earlier treatment is initiated post-ingestion, the more favorable the prognosis. Large overdoses may carry guarded outcomes.
Handling and Dispensing Precautions
Safety for Pet Owners Administering the Product
Metaflam should be administered using the provided calibrated syringe. Accidental ingestion by humans must be avoided.
Proper Hygiene: Washing Hands After Handling
Handwashing after dosing helps prevent inadvertent contact with mucous membranes or eyes.
Avoiding Contact with Skin or Eyes
If contact occurs, rinse thoroughly with water. Seek medical advice in case of irritation or reaction.
Keep Out of Reach of Children and Other Pets
Accidental ingestion by children or non-target species can result in severe toxicity.
Veterinary Dispensing and Labeled Instructions
Always follow label directions and veterinary instructions precisely. Unauthorized modifications to the dosage or schedule can lead to serious consequences.