Olmesartan Medoxomil/ Metoprolol Succinate
- Introduction to Olmesartan Medoxomil and Metoprolol Succinate Combination
- Composition and Pharmaceutical Formulations
- Medical Uses and Indications
- Mechanism of Action: How Olmesartan and Metoprolol Work in the Body
- Dosage and Administration Guidelines
- Common and Serious Side Effects
- Drug Interactions and Product Combinations
- Contraindications and Conditions Where Use Is Prohibited
- Special Warnings and Important Precautions
- Careful Administration in Specific Populations
- Overdose Risks and Emergency Management
- Storage and Stability Information
- Safe Handling and Patient Education Precautions
Introduction to Olmesartan Medoxomil and Metoprolol Succinate Combination
The combination of Olmesartan Medoxomil and Metoprolol Succinate represents a strategic pharmacologic approach in the management of hypertension. By targeting different pathways involved in blood pressure regulation, this dual therapy offers synergistic benefits for patients requiring more than monotherapy to achieve optimal control.
This formulation was developed to address treatment-resistant hypertension and improve cardiovascular outcomes through the integration of an angiotensin II receptor blocker (ARB) and a β1-selective beta-blocker. Regulatory approvals vary by region, but the combination is typically available by prescription only, adhering to strict clinical indications for use.
Composition and Pharmaceutical Formulations
This combination product contains two active components:
- Olmesartan Medoxomil: an angiotensin II receptor antagonist
- Metoprolol Succinate: a β1-selective beta-adrenergic receptor blocker
Dosage forms typically include extended-release tablets, designed to allow once-daily administration and sustained plasma concentrations. Available strengths may include varying milligram ratios (e.g., 20/25 mg, 40/50 mg, 40/100 mg), offering flexibility in clinical titration.
Formulations are engineered with excipients that enhance bioavailability and ensure stability, including agents for controlled release and pH modulation.
Difference between olmesartan and olmesartan medoxomil
Olmesartan and olmesartan medoxomil are essentially the same medications; however, olmesartan medoxomil is the ester prodrug variation of olmesartan. Once taken orally, the body swiftly converts olmesartan medoxomil into olmesartan. Olmesartan acts as a form that functions to reduce blood pressure by inhibiting the effects of angiotensin II.
Olmesartan medoxomil and Hydrochlorothiazide
Olmesartan medoxomil and hydrochlorothiazide are typically prescribed together to manage blood pressure (hypertension). This combination comprises olmesartan as an angiotensin II receptor blocker (ARB) and hydrochlorothiazide as a diuretic medication. The ARB works to ease the tension in blood vessels while the diuretic aids in eliminating surplus water and salt from the body; together, these actions help reduce blood pressure levels.
Olmesartan medoxomil vs lisinopril
Both have been shown to be successful in reducing blood pressure levels, with research indicating that higher doses of olmesartan may offer longer-lasting control over blood pressure throughout the day compared to regular doses of lisinopril.
Olmesartan medoxomil vs losartan
Olmesartan could potentially have an impact on reducing blood pressure compared to losartan, possibly due to its longer duration in the body, indicating that olmesartan's half-life exceeds that of losartan.
Metoprolol succinate vs tartrate
Metoprolol tartrates are usually taken two to three times a day in an instant-release form. On the other hand, metoprolol succinates are taken once a day in an extended-release form.
Medical Uses and Indications
3.1 Approved Clinical Uses
This medication is primarily indicated for:
- Treatment of essential hypertension in adults
- Adjunctive therapy in patients inadequately controlled with either component alone
3.2 Off-Label and Investigational Uses
Beyond its approved uses, clinicians have explored additional therapeutic applications:
- Supportive therapy in heart failure with preserved ejection fraction (HFpEF)
- Cardioprotective management following myocardial infarction
- Reduction of proteinuria in hypertensive nephropathy
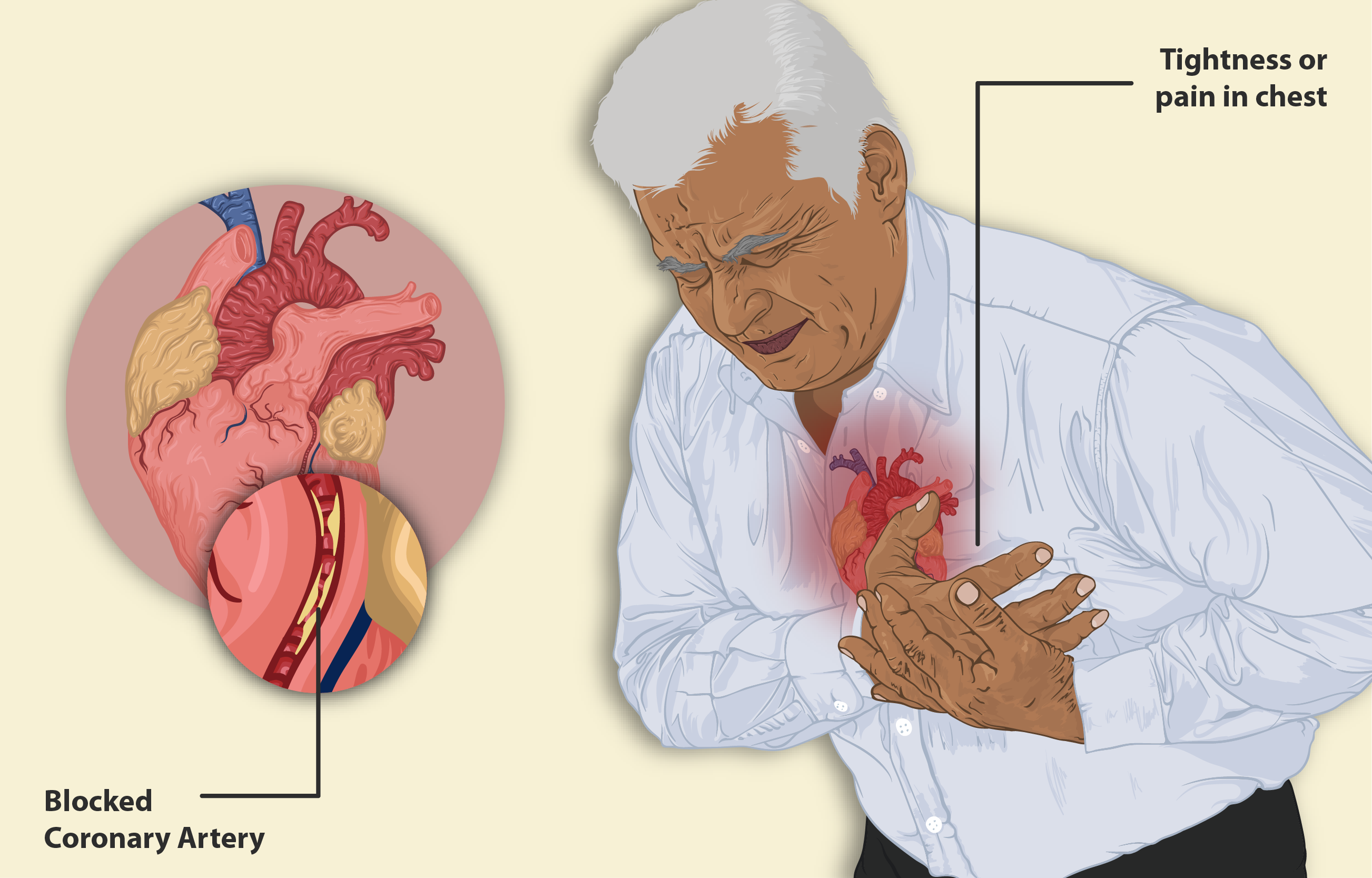
Mechanism of Action: How Olmesartan and Metoprolol Work in the Body
4.1 Olmesartan Medoxomil Mechanism
Olmesartan selectively inhibits the binding of angiotensin II to the AT1 receptor. This prevents vasoconstriction, aldosterone release, and sodium retention, key drivers of elevated blood pressure.
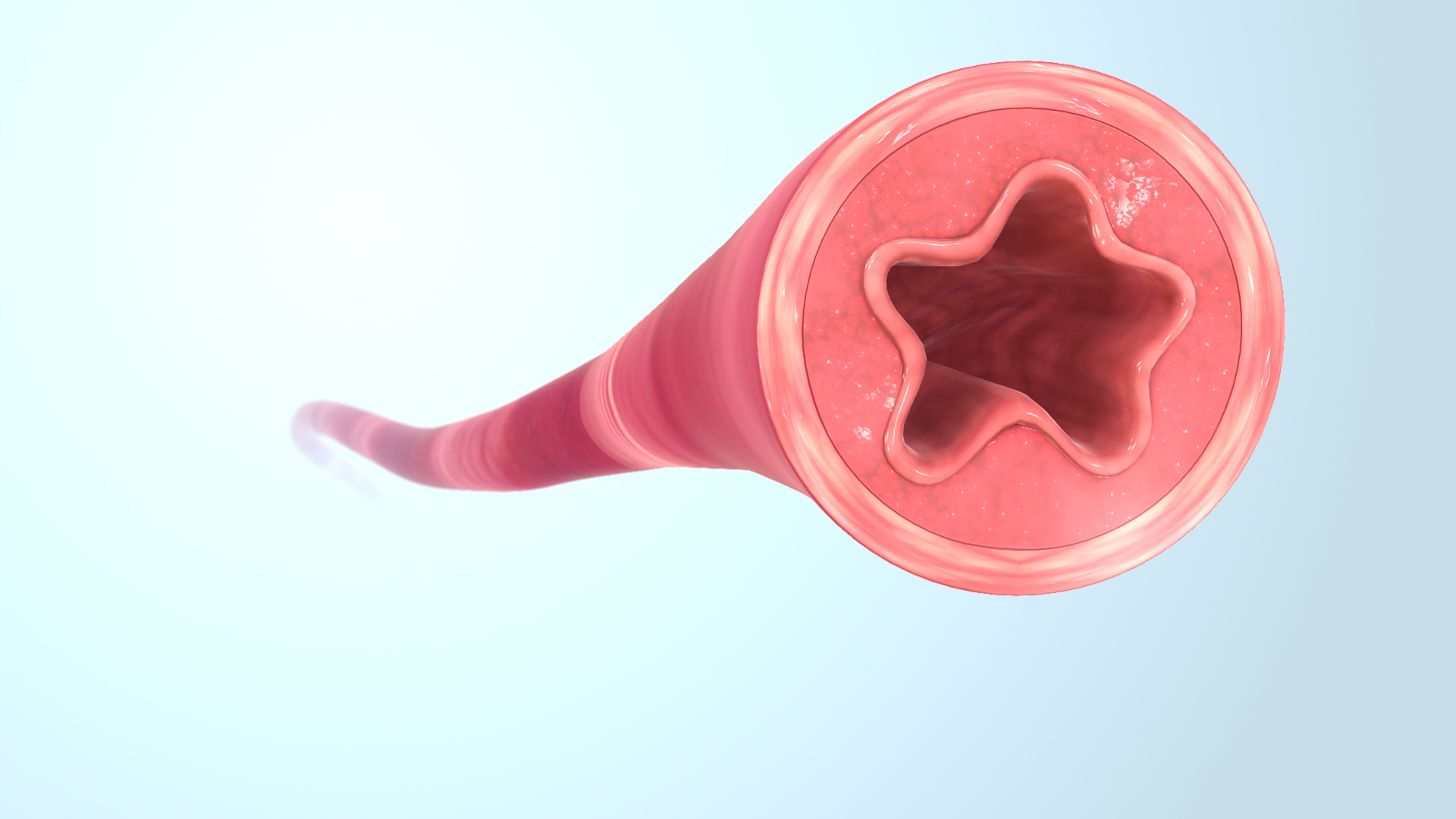
4.2 Metoprolol Succinate Mechanism
Metoprolol Succinate acts on β1-adrenergic receptors located predominantly in cardiac tissue. It reduces myocardial contractility and heart rate, thereby decreasing cardiac output and suppressing renin activity.
4.3 Synergistic Cardiovascular Effects
When combined, the two agents provide comprehensive hemodynamic control by reducing peripheral resistance and modulating sympathetic nervous activity. This dual mechanism minimizes compensatory feedback loops and enhances therapeutic efficacy.
Dosage and Administration Guidelines
5.1 Standard Adult Dosing Regimens
Initial dosing typically begins at a lower fixed-dose combination. Titration is based on patient response:
- Starting dose: 20/25 mg once daily
- Maximum dose: up to 40/100 mg daily

5.2 Administration Timing and Route
Administer orally, preferably at the same time each day. May be taken with or without food. If a dose is missed, it should be taken as soon as possible unless it is close to the time of the next dose.
5.3 Titration and Monitoring
Regular monitoring of:
- Blood pressure
- Renal function (serum creatinine, BUN)
- Serum potassium
Adjust dosage in cases of hepatic or renal impairment to avoid accumulation and adverse effects.
Common and Serious Side Effects
6.1 Frequently Reported Side Effects
- Dizziness and fatigue
- Bradycardia
- Hypotension
- Nausea and gastrointestinal upset
6.2 Serious and Rare Adverse Reactions
- Angioedema (particularly with ARBs)
- Hyperkalemia
- Renal dysfunction
- Advanced atrioventricular (AV) block
6.3 Signs Requiring Medical Attention
Patients should seek immediate medical help if they experience:
- Sudden chest pain or palpitations
- Severe lightheadedness or fainting
- Unusual swelling, difficulty breathing, or signs of allergic reaction
Drug Interactions and Product Combinations
7.1 Interactions with Antihypertensives, NSAIDs, and Diuretics
Concomitant use with other blood pressure medications can increase the risk of hypotension or renal dysfunction. NSAIDs may attenuate the antihypertensive effect and exacerbate renal compromise.
7.2 Interactions with Antidiabetics and CYP2D6 Substrates
Metoprolol is metabolized via CYP2D6; co-administration with CYP2D6 inhibitors may elevate plasma levels. Beta-blockers may also mask signs of hypoglycemia in diabetic patients.

7.3 Caution with Alcohol, Lithium, and Calcium Channel Blockers
Alcohol may enhance hypotensive effects. Lithium levels may rise due to impaired renal excretion. Co-use with verapamil or diltiazem can potentiate bradycardia or AV block.
Contraindications and Conditions Where Use Is Prohibited
- History of hypersensitivity to ARBs or beta-blockers
- Severe bradycardia or heart block (second- or third-degree) without a pacemaker
- Cardiogenic shock or decompensated heart failure requiring inotropic support
- Pregnancy, especially beyond the first trimester, due to fetal toxicity risk
This combination is contraindicated in conditions where either monotherapy is individually contraindicated, and close medical supervision is essential for at-risk populations.

Special Warnings and Important Precautions
9.1 Risk of Renal Impairment and Electrolyte Disturbance
The use of Olmesartan Medoxomil and Metoprolol Succinate requires vigilant monitoring of renal function, especially in patients with pre-existing kidney disorders or concurrent nephrotoxic medications. Elevated serum creatinine or progressive decline in glomerular filtration rate (GFR) may necessitate dose modification or discontinuation.
- Frequent monitoring of serum creatinine and estimated GFR is recommended during therapy.
- Serum potassium levels should be routinely assessed due to the risk of hyperkalemia, particularly in those using potassium-sparing diuretics or supplements.
9.2 Worsening of Bradycardia or AV Block
Metoprolol Succinate, a beta-adrenergic blocker, may exacerbate conduction abnormalities such as atrioventricular (AV) block or cause significant bradycardia, especially in predisposed individuals.
- Baseline electrocardiogram (ECG) is advised prior to initiation.
- Regular heart rate monitoring during treatment is essential.
9.3 Masking of Hypoglycemia Symptoms in Diabetics
Beta-blockers like Metoprolol can obscure adrenergic symptoms of hypoglycemia, including tremor, tachycardia, and anxiety. This is particularly concerning in insulin-dependent patients, where early recognition of hypoglycemia is critical to prevent complications.
Diabetic patients should be counseled on alternative signs of low blood glucose, such as increased sweating or cognitive impairment.
9.4 Rebound Hypertension on Sudden Withdrawal
Abrupt cessation of beta-blocker therapy can result in a surge of sympathetic activity, leading to rebound hypertension, angina, or myocardial infarction in high-risk individuals.
- Tapering the dose gradually over 1 to 2 weeks is strongly advised when discontinuing therapy.
Careful Administration in Specific Populations
10.1 Use in Elderly Patients
Elderly individuals often exhibit reduced hepatic metabolism and renal clearance, making them more susceptible to adverse reactions and accumulation of drug metabolites.
- Lower initial doses are recommended to minimize hypotensive episodes.
- Close monitoring for orthostatic hypotension and fall risk is critical.
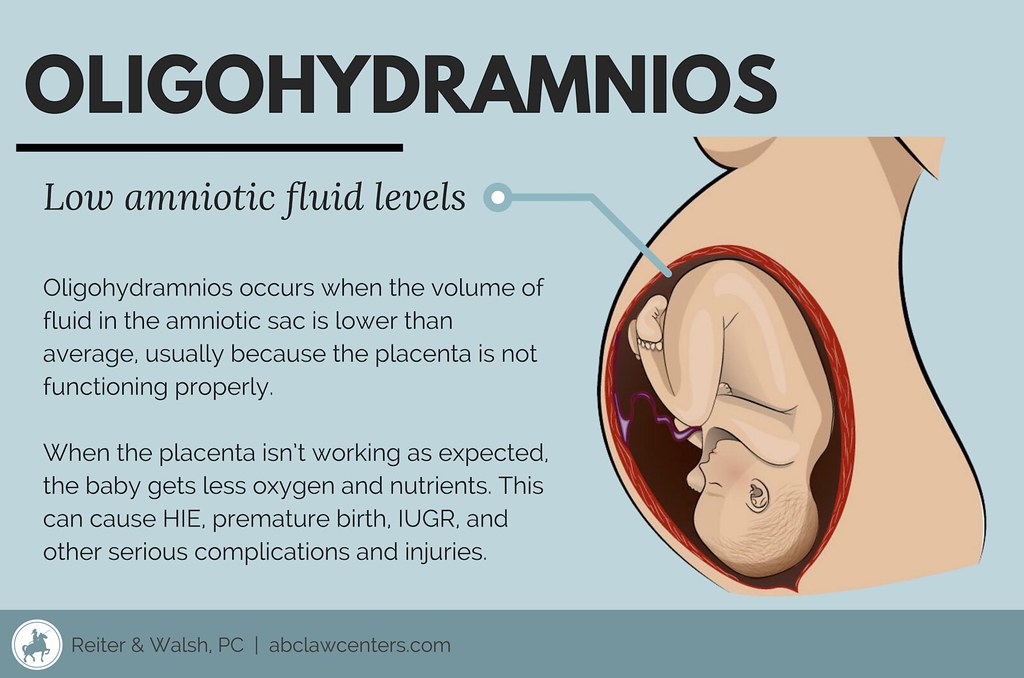
10.2 Use During Pregnancy and Lactation
Olmesartan, an ARB, is contraindicated during the second and third trimesters of pregnancy due to its association with fetal renal damage, oligohydramnios, and potential neonatal death.
Although data on Metoprolol excretion in breast milk is limited, caution is advised during lactation as beta-blockers may cause bradycardia or hypoglycemia in neonates.
10.3 Use in Pediatric Patients
The safety and efficacy of the combination therapy in children under 18 years of age remain insufficiently established.
Use in pediatric populations should be restricted to off-label cases under specialist supervision, ideally supported by clinical justification and careful monitoring.
Overdose Risks and Emergency Management
Overdosage of Olmesartan Medoxomil and Metoprolol Succinate can be life-threatening, with the potential to cause profound hypotension, bradycardia, shock, or renal failure.
- Symptoms may include extreme dizziness, weakness, cyanosis, or loss of consciousness.
- Supportive care, including IV fluids, vasopressors, and cardiac monitoring, is the mainstay of treatment.
- Atropine may be administered to counteract bradycardia; glucagon or high-dose insulin therapy can also be considered in severe beta-blocker toxicity.
Storage and Stability Information
To maintain efficacy and product integrity, this medication should be stored in a controlled environment:
- Recommended storage temperature: 20°C to 25°C (68°F to 77°F), with brief excursions permitted between 15°C and 30°C.
- Protect from excessive moisture, heat, and direct sunlight.
- Check packaging for expiration date, and do not use beyond this period.
Safe Handling and Patient Education Precautions
Proper handling of Olmesartan/Metoprolol ensures safety and minimizes therapeutic risk, especially in sensitive populations.
- Unused or expired tablets should be discarded in accordance with local pharmaceutical waste regulations.
- Caregivers must ensure the medication is stored securely and administered accurately, particularly in elderly or cognitively impaired patients.
- Patients should be educated on adherence, recognition of adverse effects, the importance of blood pressure monitoring, and when to seek medical attention.
Olmesartan Medoxomil/ Metoprolol Succinate FAQ
- Can you take olmesartan and metoprolol together?
- Can I take metoprolol and olmesartan together?
- What is metoprolol succinate and olmesartan Medoxomil for?
- What drugs should not be taken with metoprolol succinate?
- Can I take blood pressure medicine with metoprolol?
- Is metoprolol succinate a good blood pressure medicine?
- When is the best time to take olmesartan Medoxomil?
- Who should not take olmesartan Medoxomil?
- Can I eat bananas with metoprolol?
- What is the most serious side effect of metoprolol?
- What are the most common side effects of olmesartan?
- What is the use of olmesartan medoxomil and metoprolol succinate?
- What foods to avoid while taking olmesartan?
- What is the difference between olmesartan and olmesartan Medoxomil?
- Can you take amlodipine and olmesartan and metoprolol together?
- Who should not take metoprolol succinate?
- Can metoprolol cause kidney problems?
- What are the benefits of taking metoprolol?
- What to expect when you stop taking metoprolol?
- Is olmesartan Medoxomil safe?
- What is the warning on Olmesartan Medoxomil?
- What are the benefits of olmesartan Medoxomil?
Can you take olmesartan and metoprolol together?
Yes
Can I take metoprolol and olmesartan together?
Combining metoprolol succinate and olmesartan medoxomil through oral administration has been shown to be more effective in treating hypertension in patients, compared to using each medication individually.
What is metoprolol succinate and olmesartan Medoxomil for?
Olmesartan and metoprolol are two medications combined to reduce blood pressure levels when taken together. Olmesartan functions as an angiotensin receptor blocker (ARB), by inhibiting the hormone angiotensin and promoting relaxation of blood vessels.
What drugs should not be taken with metoprolol succinate?
Certain calcium channel blockers, digoxin, and diphenhydramine
Can I take blood pressure medicine with metoprolol?
The mixture of metoprolol may occasionally cause a drop in your blood pressure levels, which can result in feelings of dizziness or faintness.
Is metoprolol succinate a good blood pressure medicine?
Metoprolol is as effective as other beta blockers in lowering blood pressure, but tends to have fewer side effects.
When is the best time to take olmesartan Medoxomil?
Before bedtime
Who should not take olmesartan Medoxomil?
- Allergic reaction to olmesartan
- Bile duct or gallbladder problems
Can I eat bananas with metoprolol?
No. Metoprolol contains potassium, which can cause heartbeats and kidney issues if consumed excessively.
What is the most serious side effect of metoprolol?
Heart failure
What are the most common side effects of olmesartan?
- Dizziness
- Headaches
- Flu-like symptoms
- Cough
- Bronchitis
- Nausea
- Indigestion
- Stomach Ache
- Diarrhea
- Swollen feet
- UTI
What is the use of olmesartan medoxomil and metoprolol succinate?
Olmesartan Medoxomil combined with Metoprolol Succinate is prescribed for managing hypertension.
What foods to avoid while taking olmesartan?
Potassium supplements, salt substitutes, potassium-rich foods
What is the difference between olmesartan and olmesartan Medoxomil?
Olmesartan medoxomil is a type of inactive ester prodrug that transforms entirely into its active form as olmesartan, once absorbed from the stomach and intestines.
Can you take amlodipine and olmesartan and metoprolol together?
In some cases, this mix can be helpful and efficient; however, it may lead to cardiovascular issues like congestive heart failure or worsened angina symptoms with a significant drop in blood pressure.
Who should not take metoprolol succinate?
- Allergic reaction to olmesartan
- Bile duct or gallbladder problems
- Low blood pressure
- Asthma
Can metoprolol cause kidney problems?
Yes
What are the benefits of taking metoprolol?
It helps reduce your blood pressure and heart rate, which allows your heart to efficiently circulate blood throughout your body; it is beneficial for managing hypertension. It can also aid in preventing chest discomfort or additional harm following a heart attack.
What to expect when you stop taking metoprolol?
Stopping metoprolol suddenly could cause a withdrawal syndrome that might make chest pain and arrhythmias worse. It could also lead to high blood pressure and increase the chances of having a heart attack.
Is olmesartan Medoxomil safe?
Yes
What is the warning on Olmesartan Medoxomil?
Diarrhea and weight loss warning
What are the benefits of olmesartan Medoxomil?
Olmesartan is a medication prescribed for managing hypertension. It reduces blood pressure levels and facilitates blood circulation throughout your body, easing the workload on your heart.