Pyrazinamide Tablet
- Composition of Pyrazinamide Tablets
- How Pyrazinamide Works
- Uses of Pyrazinamide
- Off-Label Uses of Pyrazinamide
- Dosage and Administration
- Administration to Special Populations
- Common Side Effects of Pyrazinamide
- Serious Side Effects and Adverse Reactions
- Interactions with Other Medications
- Contraindications and Cautions
- Important Precautions
- Handling and Storage of Pyrazinamide
- Overdose Information
Introduction to Pyrazinamide
Pyrazinamide is a medication used to fight tuberculosis (TB). Known for its effectiveness, this drug is part of the standard treatment plan for TB, especially during the initial phase of intensive treatment.
Pyrazinamide brand name
Pyrazinamide, first created in the 1950s was developed from nicotinamide. Eventually noted for its special capacity to combat inactive mycobacteria in acidic conditions effectively reducing the treatment duration for individuals, with tuberculosis.
Composition of Pyrazinamide Tablets
Key Components The component found in Pyrazinamide tablets is pyrazinamide, which acts as a bacteriostatic substance effective against Mycobacterium tuberculosis.
- Stabilizers - Ensure the longevity and stability of the active compound.
- Binders - Facilitate tablet cohesion and integrity.
- Disintegrants - Promote tablet disintegration post-ingestion, allowing for rapid release and absorption of the active ingredient.
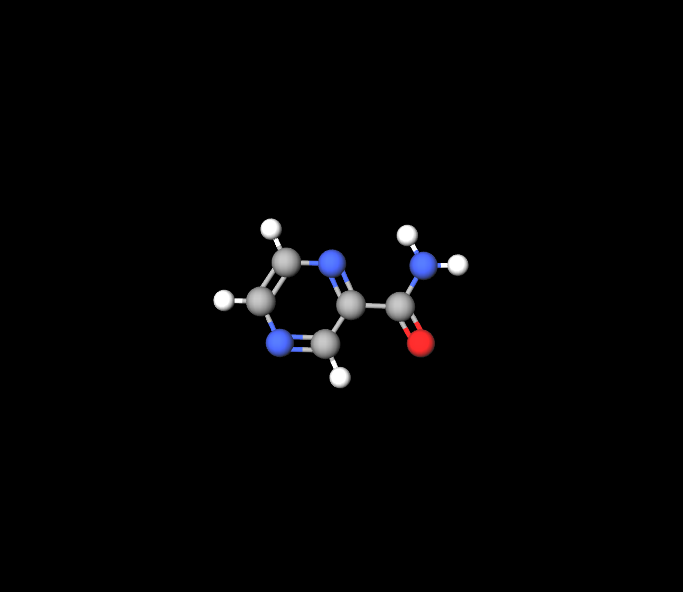
How Pyrazinamide Works
The way Pyrazinamide works in treating tuberculosis is by interfering with the metabolism and transport functions of cell membranes, which ultimately hinders the bacteria's growth. This effect is especially potent in surroundings like those present within the macrophages of the human immune system. When it comes to Mycobacterium tuberculosis, Pyrazinamide stands out for its effectiveness against partially active mycobacteria, playing a crucial role in eliminating TB bacilli from the host's body.
Uses of Pyrazinamide
-
Uses of Pyrazinamide:
- Pyrazinamide is an antituberculosis agent used as a component of tuberculosis (TB) treatment.
- It plays a vital role in both the early and ongoing stages of TB therapy, effectively shortening the overall treatment period1.
-
Contribution to Treating Multi-Drug Resistant TB (MDR TB):
- In situations involving multi-drug resistant TB (MDR TB), Pyrazinamide remains a fundamental component of treatment.
- It is frequently combined with newer medications to address resistance issues1.
Off-Label Uses of Pyrazinamide
-
Repurposing for Mycobacterial Diseases:
-
Potential Applications Beyond Infections:
- Recent data suggests that Pyrazinamide may have applications beyond infections. It shows promise in treating inflammatory conditions by affecting macrophage functions2.
Dosage and Administration
Typical dosing recommendations for adults; The adult dose of Pyrazinamide varies based on body weight and overall health status typically falling between 15 to 30 mg/kg/day usually taken by mouth once or in divided doses. Special dosage adjustments are necessary for individuals, with kidney problems. Undergoing hemodialysis to avoid drug buildup and the risk of toxicity.
Administration to Special Populations
- Elderly Patients; When it comes to older patients it's important to adjust dosages carefully to reduce the chances of liver related issues and other negative effects. Adjustments and Monitoring; Regularly checking liver function tests is advised to identify and address any liver related problems.
- Pyrazinamide Nursing Considerations; Even though Pyrazinamide falls under Pregnancy Category C it should only be used if the benefits outweigh the risks. Studies on animals have shown some effects and there isn't enough information on how it affects pregnant women. Safety Profile and Recommendations; It's crucial to weigh the benefits of treatment against risks with close monitoring for any harmful effects on fetal development or newborns.
- Children: Pyrazinamide is safe for children at a dose adjusted based on their weight, ensuring safety and effectiveness in this group. Dosage Adjustments and Safety Considerations: Special care is necessary when determining doses for children, along with monitoring to achieve optimal treatment outcomes while minimizing potential side effects.
Common Side Effects of Pyrazinamide
Frequent Gastrointestinal and Hepatic Concerns
Pyrazinamide is recognized for causing digestive problems, like queasiness, throwing up, and reduced desire to eat. Liver-related concerns, hepatotoxicity may show up subtly through increased liver enzymes, suggesting possible liver damage.
Management of Common Adverse Effects
- It is recommended to check liver function to identify and address liver damage promptly.
- Treatment for issues may involve using anti-nausea medications and making dietary changes.
Serious Side Effects and Adverse Reactions
Hepatotoxicity and Hyperuricemia
Liver damage is an issue associated with Pyrazinamide, which could result in severe liver injury. Elevated levels of acid in the blood, known as hyperuricemia, can trigger gout in people who are prone to it.
Risk Mitigation and Emergency Responses
Patients should be well informed about identifying indications of liver issues and high levels of uric acid. It's important to have emergency procedures to handle sudden episodes efficiently, such as stopping the medication and starting suitable medical treatment.
Interactions with Other Medications
Common Drug-Drug Interactions
Pyrazinamide has the potential to interact with medications, leading to a decrease in their effectiveness or an increase in side effects. Specifically, when combined with rifampicin, there is a risk of liver damage, and when used alongside uricosuric agents, their effectiveness may be reduced.
Impact on Efficacy and Safety
It's crucial to grasp these connections to uphold the effectiveness of Pyrazinamide in therapy while also safeguarding the patients well being. Changes, in medication schedules or amounts might be needed depending on the medications the patient is taking.
Contraindications and Cautions
Absolute Contraindications for Use
Patients with liver disease, acute gout, or a known hypersensitivity to the drug, should avoid taking Pyrazinamide.
Conditional Risks and Considerations
Patients who have underlying health conditions, like mild to liver problems or high levels of uric acid, should exercise caution when using Pyrazinamide, and it should only be considered if the benefits outweigh the potential risks.
Important Precautions
Liver Function Monitoring
It's important to check liver function when using Pyrazinamide, particularly for patients with a history of liver issues or those undergoing long-term treatment.
Management of Underlying Conditions
In planning patient care it's important to consider ways to manage conditions that may worsen due, to Pyrazinamide like gout or liver issues.
Handling and Storage of Pyrazinamide
Proper Storage Conditions
Be sure to keep Pyrazinamide tablets in a dry spot away from light and moisture to maintain their effectiveness and avoid deterioration.
Disposal and Handling Safety
It's important to follow the procedures for disposing of Pyrazinamide to prevent any accidental exposure or environmental harm. Taking precautions when handling it is essential to avoid ingestion or contact by individuals who are not prescribed to use it.
Overdose Information
Signs and Symptoms of Overdose
Symptoms of taking too much Pyrazinamide may consist of severe liver damage, feelings of sickness, throwing up, and tiredness. Elevated levels of acid could result in sudden gout episodes.
Immediate Actions and Treatment Protocols
Swift medical attention is essential in cases of Pyrazinamide overdose. The treatment includes providing relief for symptoms, closely monitoring and addressing any liver damage and uric acid imbalances, and considering dialysis to help eliminate the drug from the body.