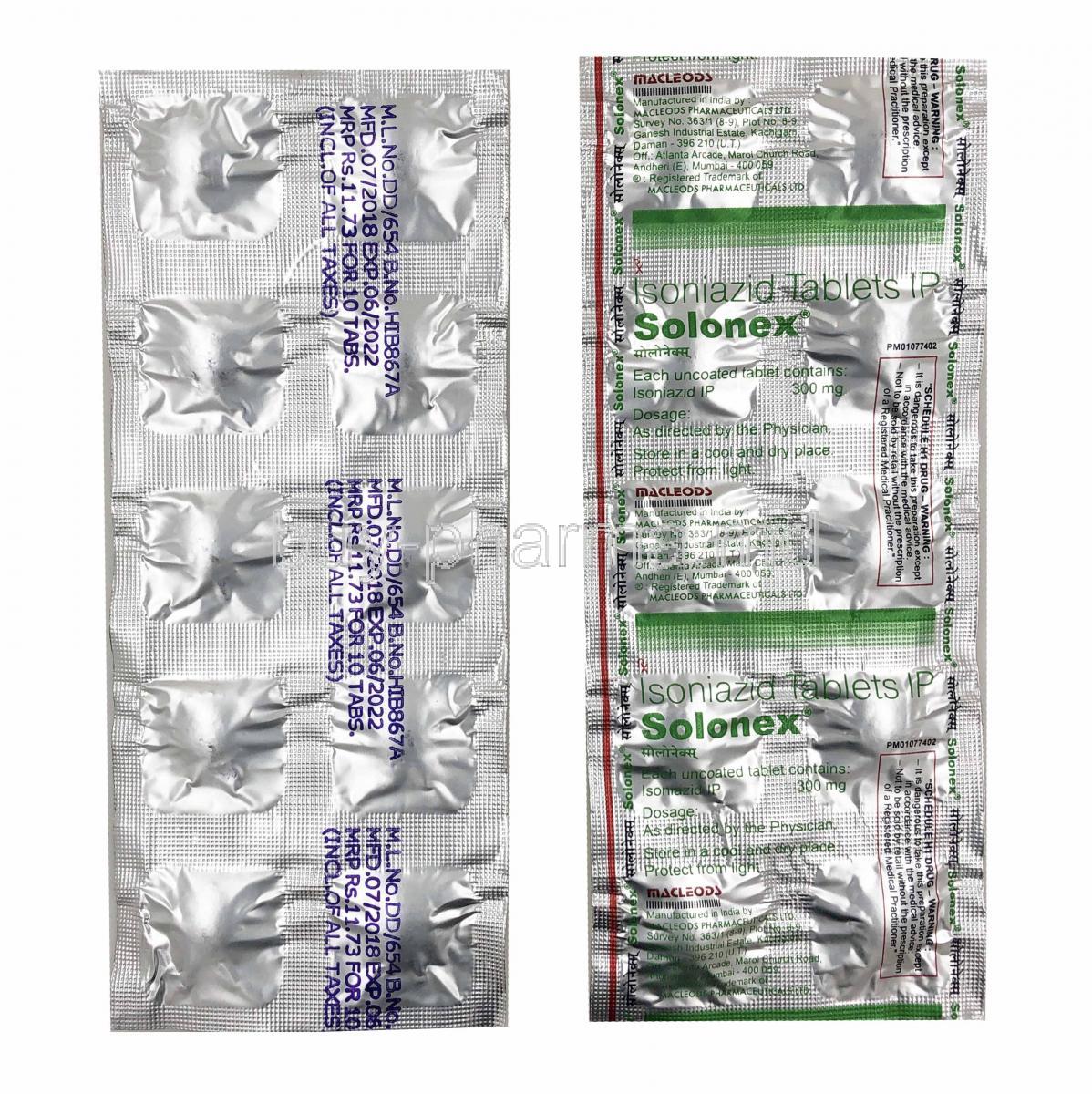
Isoniazid
- Buy Isoniazid and Rifampicin: A Powerful Combination
- Isoniazid Mechanism of Action to Combat Tuberculosis
- Safety Measures: Isoniazid Side Effects and Risks
- Isoniazid Hepatotoxicity: Understanding the Risks
- Isoniazid Contraindications: When to Avoid This Medication
- Isoniazid and Your Lifestyle: Things to Consider
- Can I Eat After Taking Isoniazid?
- Isoniazid and Vitamin B6: The Connection
- How to Properly Store Isoniazid
- FAQs to Buy Isoniazid
- Buy Isoniazid: An Essential Guide to Usage and Safety
Isoniazid, also known as acid hydrazide (INH), is a medication primarily used to treat and prevent tuberculosis (TB) 1. It belongs to a group of drugs that combat mycobacteria, the bacteria responsible for causing TB 1. Since its discovery in the 1950s, isoniazid has been widely used as a component of current TB therapy 1.
Isoniazid is prescribed for treating TB infections when combined with other anti-TB medications 1. It is also used as a measure for individuals at risk of acquiring TB. This combination therapy ensures treatment while reducing the chances of drug resistance. Moreover, it may be recommended as a measure for individuals exposed to active TB cases or those with weakened immune systems 1.
Treating Active Tuberculosis: Isoniazid works effectively in conjunction with anti-TB medications such as rifampicin, pyrazinamide, and ethambutol, in combination therapy 1.
Preventing Tuberculosis: Individuals who have been exposed to TB cases or have weakened immune systems can benefit from taking isoniazid preventively. In addition to its role in combating tuberculosis infection by killing bacteria cells or halting their growth, recent studies suggest that INH may also enhance the immune response against Mycobacterium tuberculosis by promoting autophagy induction within macrophages. Macrophages are players in the innate immune response against invading pathogens, including Mtb, and this can contribute to clearing bacteria from infected cells 2.
Despite its effectiveness, isoniazid can have side effects and may interact with other medications. Therefore, it’s important to be aware of the safety measures associated with this drug before starting treatment 1.
Here are some references that you can use to learn more about Isoniazid:
- StatPearls: This website provides detailed information about Isoniazid, including its dosing, indications, interactions, adverse effects, and more.
- PubMed Central: This website provides information about the role of Isoniazid in enhancing the immune response against Mycobacterium tuberculosis.
Buy Isoniazid and Rifampicin: A Powerful Combination
When it comes to treating tuberculosis (TB), doctors often combine isoniazid with another anti-TB medication called rifampicin. This combination has proven to be highly effective in fighting the disease as both drugs work together to eliminate the TB bacteria from the body. Rifampicin works by blocking the production of RNA, thereby preventing the TB bacteria from multiplying. Combined with isoniazid, which targets an enzyme crucial for building cell walls in Mycobacterium tuberculosis, these two medications form a potent duo that can effectively treat active TB infections and prevent latent infections from becoming involved.
- Dual therapy: Isoniazid and rifampicin are usually prescribed together as part of a drug treatment approach known as Directly Observed Treatment Short course (DOTS). This method ensures that patients receive treatment while minimizing the risk of developing drug resistance.
- Treatment duration: The standard course of treatment for diagnosed cases involves taking both medications daily for at least six months. In situations such as multidrug-resistant TB or severe extrapulmonary TB, more extended treatment periods may be necessary under medical supervision.
- Managing side effects: Both isoniazid and rifampicin have side effects; however, most patients tolerate them well when taken correctly. Regular monitoring during treatment helps identify any reactions early on so that healthcare professionals can manage them appropriately.
Taking isoniazid and rifampicin as prescribed is crucial for achieving treatment results. These two medications work together to effectively combat tuberculosis and help patients recover their health. Isoniazid and rifampicin are commonly used in the management of tuberculosis, and understanding how isoniazid functions can empower you to make decisions about your treatment plan.
Isoniazid Mechanism of Action to Combat Tuberculosis
Isoniazid is a medication that plays a crucial role in the treatment of tuberculosis (TB). Before delving into how it works, let's first understand the nature of TB itself. TB is a disease caused by a bacterium called Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Although it primarily affects the lungs it can also spread to organs. Symptoms such as coughing, fever, weight loss, and exhaustion result from the bacteria multiplying and causing harm to tissues.
The primary function of isoniazid is to hinder the growth and reproduction of Mycobacterium tuberculosis. It specifically targets an enzyme called InhA (enoyl acyl carrier protein reductase), which plays a role in synthesizing mycolic acid. An essential component for building bacterial cell walls. By inhibiting InhA activity, isoniazid disrupts cell wall formation.
Ultimately, it eliminates or prevents further growth of the bacteria responsible for TB. It's worth noting that besides combating active TB infections, isoniazid can also be used as a preventive measure against latent TB infection (LTBI). This refers to cases where individuals carry bacteria without exhibiting any symptoms. Administering a course of isoniazid therapy to LTBI patients significantly reduces their risk of developing TB at a later stage. In terms of efficacy, numerous clinical studies have demonstrated the effectiveness of isoniazid in treating both latent forms of tuberculosis. For instance, a study revealed that isoniazid decreased the chances of developing tuberculosis by 90% in patients with latent tuberculosis infection (LTBI). Combination therapy is often recommended, where isoniazid is prescribed alongside anti-TB medications like rifampicin and pyrazinamide. This comprehensive approach enhances effectiveness and reduces the risk of drug resistance.
To summarize, isoniazid plays a role in combating tuberculosis by inhibiting bacterial growth and reproduction. Its effectiveness has made it an essential component of TB treatment plans and preventive measures for latent infections. However, it's critical to be aware of side effects before using isoniazid to ensure your safety.
The key takeaway is that isoniazid is a medication used to fight against tuberculosis by targeting Mycobacterium tuberculosis and disrupting its cell wall formation. This ultimately. Hinders the growth of TB-causing bacteria. It can also be used preventively for TB infection (LTBI), significantly reducing the risk of later developing active TB.
Safety Measures: Isoniazid Side Effects and Risks
Although isoniazid is a medication for tuberculosis treatment, it's essential to be mindful of the possible side effects and risks associated with it. In this section, we will discuss the side effects, the rare but severe ones, and any interactions it may have with other medications.
Common Side Effects of Isoniazid
Isoniazid might lead to mild side effects in patients. These could include feeling nauseous or experiencing vomiting feeling dizzy or lightheaded having stomach pain or discomfort and developing a rash or itchy skin. Generally, these temporary symptoms tend to improve as your body adapts to the medication. However, if they persist or worsen over time, it is advisable to consult your healthcare provider.
Rare but Serious Side Effects: What to Watch For
In a few cases, isoniazid can cause more severe effects that require immediate medical attention. These may include abdominal pain along with dark urine and yellowing of the eyes or skin (indicating liver damage) and a tingling or numb sensation, in the hands or feet (known as peripheral neuropathy). If you encounter any side effects while using this medication, it is essential to seek medical attention right away.
Interaction of Isoniazid with Other Medications
Isoniazid can interact with certain medications, such as antacids containing aluminum salts (like aluminum hydroxide suspension). It's important to let your healthcare provider know about all the medicines you're currently taking, including over-the-counter drugs, vitamins, and herbal supplements. This way, you can ensure a treatment plan that suits your specific needs. Before starting the treatment, it's crucial to be aware of any risks and adverse reactions associated with Isoniazid as they can have serious consequences. Understanding the impact of Isoniazid hepatotoxicity on your health is essential for making an informed decision about taking this medication.
Isoniazid Hepatotoxicity: Understanding the Risks
Isoniazid is a medication for tuberculosis treatment, but it can potentially harm the liver in certain patients. The extent of this side effect can vary, ranging from mild and reversible to severe and even life-threatening. In this section, we will delve into how age and other factors can impact the likelihood of experiencing liver damage caused by isoniazid, as well as strategies to reduce this risk.
Risk Factors for Isoniazid Hepatotoxicity
Older individuals face a chance of developing liver issues while taking isoniazid. The risk of liver toxicity from isoniazid rises with age for those who are 35 years old or older. It is essential to refrain from or minimize alcohol consumption during treatment, as alcohol use can amplify the likelihood of liver damage caused by isoniazid. Furthermore, individuals with existing conditions such as chronic hepatitis B or C infections, cirrhosis, or other underlying liver diseases may be more vulnerable to hepatotoxicity associated with isoniazid.
Tips for Minimizing Risk During Treatment
It is essential for healthcare providers to regularly check liver function tests (LFTs) before starting treatment and throughout therapy, based on individual patient factors. Patients should be educated about symptoms of liver injury, including fatigue, nausea, vomiting, and changes in urine color. This information helps ensure that timely intervention can take place if necessary. Before starting Isoniazid treatment, it is crucial to be aware of the possibility of hepatotoxicity and understand the risks involved. Let's explore some precautions to consider when taking Isoniazid.
Isoniazid Contraindications: When to Avoid This Medication
Some situations or circumstances may pose risks or reduce the effectiveness of this medication. In this section, we will explore scenarios where it is best to avoid using isoniazid and consider alternative treatments that may be more appropriate.
Severe Liver Disease
People who have liver disease should steer clear of using isoniazid because it can be harmful to the liver. Isoniazid has the potential to accumulate substances in the liver, which can aggravate existing liver issues. If you've been diagnosed with liver disease, your healthcare provider might suggest alternative medications for treating tuberculosis.
Allergy or Sensitivity to Isoniazid
If you have an allergy or sensitivity to isoniazid or any of the ingredients in the medicine, it's essential not to take it. Doing so could cause side effects such as difficulty breathing and swelling of the face and throat. Make sure to inform your doctor if you have had any reactions related to isoniazid before so they can recommend an alternative treatment option.
Pregnancy and Breastfeeding
The use of isoniazid during pregnancy is still a topic of debate due to risks for both the mother and the baby. While some studies suggest that isoniazid does not pose risks during pregnancy, others indicate the possibility of complications like birth defects. It's essential for women who are considering tuberculosis treatment options to discuss with their healthcare provider about the potential risks and benefits involved. It's also worth noting that isoniazid can pass into breast milk, which could potentially affect a nursing infant. If you are breastfeeding, it's advisable to seek advice before starting isoniazid therapy. Remember, informing your healthcare provider about any existing conditions or factors that may impact your treatment plan before beginning isoniazid therapy is crucial. Taking into account health issues and other medications, it becomes imperative to carefully consider the risks associated with taking Isoniazid when making lifestyle choices for a safe experience.
Key Takeaway: Before using isoniazid for tuberculosis treatment, it's essential to be aware of its contraindications. Individuals with liver disease or allergies/sensitivity to the medication should avoid using it, and pregnant women should discuss potential risks with their healthcare provider. Always inform your doctor about any existing conditions before starting isoniazid therapy.
Isoniazid and Your Lifestyle: Things to Consider
When you are undergoing treatment for tuberculosis with isoniazid, it is essential to take into account how this medication can affect your life. This includes considering aspects like diet, nutrition, alcohol intake, and the necessity of taking the dosage consistently.
Diet and Nutrition
It is essential to maintain a balanced diet while undergoing isoniazid therapy to achieve the best possible results from your treatment. Some individuals may encounter side effects like feelings of nausea or vomiting when taking isoniazid. Consuming meals more frequently throughout the day may be beneficial to help alleviate these symptoms. Furthermore, it is advisable to avoid consuming foods high in tyramine (such as aged cheeses) during your treatment period due to potential interactions with isoniazid.
Alcohol Consumption
It is essential to refrain from drinking alcohol while you are taking isoniazid. When alcohol and this medication are combined, it can significantly raise the chances of liver damage. Moreover, consuming alcohol can hinder the absorption of your medication, which ultimately reduces its effectiveness if you find it challenging to abstain from alcohol, we strongly recommend seeking assistance from a healthcare professional who can provide support and guidance.
The Importance of Regular Dosage
- Adherence: Making sure you stick to a medication schedule is crucial. This ensures your body always has isoniazid to fight against tuberculosis bacteria effectively.
- Avoid doses: It's crucial never to skip a dose as it can lead to drug resistance or even relapse after completing the treatment. If needed, set reminders so you don't forget any scheduled doses.
- Don't stop early; Completing the course of treatment as prescribed by your healthcare provider is vital even if you start feeling better before finishing all of your medication. Stopping prematurely can result in drug resistance and potential relapse.
Incorporating these factors into your routine can lead to a successful outcome from isoniazid treatment while minimizing potential harm to your health and well-being. Before deciding on using Isoniazid, it's essential to consider how this medication may impact your life. It's also important to understand how taking Isoniazid might affect your eating habits, so let's look at whether it's possible to eat after taking isoniazid. Key Takeaway: When undergoing tuberculosis treatment with isoniazid, maintaining a diet and refraining from consuming alcohol are crucial. This helps ensure the effectiveness of the medication and reduces the risk of liver damage. It is essential to stick to the prescribed dosage schedule when treating tuberculosis. This will ensure that the medication works effectively against the bacteria and helps prevent missed doses or premature discontinuation of treatment. Doing so can minimize the risk of drug resistance or a relapse.
Can I Eat After Taking Isoniazid?
Taking isoniazid on a stomach is advisable to ensure optimal absorption and effectiveness. However, if you experience side effects, it may be necessary to find a balance between ensuring proper drug absorption and minimizing discomfort by eating before or after taking isoniazid. In some cases, it becomes crucial to balance these two factors. Ensure the drug is absorbed well while minimizing pain or discomfort.
Eating Before or After Taking Isoniazid
If you have issues and need to eat before taking isoniazid, opting for a light meal consisting of easily digestible foods is best. Avoiding high-fat meals is recommended as they can interfere with the absorption of the medication. Remember to wait at least 30 minutes after finishing your meal before taking your dose. Alternatively, suppose you prefer taking isoniazid on a stomach but still want to eat soon afterward. In that case, it's advisable to wait for at least one hour after consuming the medication before having a meal. This allows time for proper absorption of the drug. Whichever approach you choose, it's essential to maintain a routine throughout your treatment period. This helps your body adapt to the medication and ensures response.
Nutritional Considerations While on Isoniazid Treatment
Apart from timing your meals around your doses, there are significant nutritional factors to consider during tuberculosis therapy with isoniazid. One is supplementing with Vitamin B6 since isoniazid can cause a deficiency in this nutrient, leading to nerve damage. Healthcare providers often recommend taking Vitamin B6 alongside the treatment to prevent this. Another aspect to keep in mind is avoiding foods that are rich in tyramine. Isoniazid can interact negatively with tyramine in aged or fermented foods like cheese and cured meats. Consuming these items while on isoniazid may result in increased blood pressure and other adverse effects. It's always advisable to consult your healthcare provider regarding your diet and nutrition during isoniazid treatment. They will be able to provide you with recommendations for optimal outcomes. To mitigate the side effects of isoniazid, it's essential to maintain a balanced diet throughout the treatment period.
Additionally, understanding how Vitamin B6 may interact with isoniazid when taken together as part of your treatment plan is crucial.
Key Takeaway: Taking isoniazid on a stomach is recommended for better absorption and effectiveness. However, if you experience side effects, you can have a light meal of easily digestible foods before taking the medication. Throughout your treatment, try to maintain consistency in your routine and consider factors such as vitamin B6 supplementation and avoiding tyramine foods for optimal results.
Isoniazid and Vitamin B6: The Connection
It is crucial to recognize the significance of taking Vitamin B6 (Pyridoxine) supplements while undergoing treatment with Isoniazid. Isoniazid has the potential to result in a deficiency of this vitamin, which can lead to a range of health problems. In this section, we will explore the relationship between Isoniazid and Vitamin B6. Guide ensuring sufficient intake throughout your tuberculosis treatment.
Why is Vitamin B6 Important?
Vitamin B6 is crucial for keeping our health in check as it helps with a range of critical bodily functions, including Keeping our brain function healthy, Producing red blood cells, Creating neurotransmitters like serotonin and norepinephrine, and Supporting the proper functioning of our immune system.
The Impact of Isoniazid on Vitamin B6 Levels
Research has indicated that Isoniazid can disrupt the body's metabolism of Vitamin B6, leading to a decrease in its levels. This depletion caused by Isoniazid might contribute to neuropathy, characterized by numbness or tingling in the hands and feet. Moreover, insufficient amounts of Vitamin B6 can potentially lead to anemia as it affects the production of blood cells.
Vitamin B6 Supplementation During Isoniazid Treatment
Healthcare professionals often suggest taking a pyridoxine supplement to prevent complications while undergoing Isoniazid therapy. According to the CDC, the recommended daily dosage ranges from 25 to 50 mg, depending on age and individual circumstances. Following your doctor's guidance regarding Vitamin B6 supplementation during Isoniazid treatment is crucial. Including foods with Vitamin B6 in your diet can also help maintain adequate levels. Some foods include whole grains, poultry, fish, bananas, and spinach. By taking these measures, you can ensure that you reap the benefits of Isoniazid treatment while minimizing potential side effects related to vitamin deficiencies. Remember that Isoniazid combined with Vitamin B6 plays a role in treating tuberculosis and other infections, so taking the medication as prescribed is essential. Now that you are more informed about this combination treatment let's explore how best to store Isoniazid for effectiveness.
How to Properly Store Isoniazid
It is essential to store your isoniazid medication to maintain its effectiveness and ensure your safety throughout the treatment. This section will give you guidelines on how to store isoniazid and how to dispose of any unused or expired medication correctly.
Suitable Storage Conditions for Isoniazid
Keep isoniazid at room temperature between 20°C to 25°C (68°F to 77°F), avoiding exposure to extreme temperatures like freezing or excessive heat. It's essential to store the medication away from moisture, so avoid keeping it in damp areas such as bathrooms or near sinks. Make sure to keep isoniazid in its original container with the lid tightly closed. This will help protect it from air exposure that may potentially reduce its effectiveness.
Tips for Safe Medication Storage
- Keep medications away from children and pets. Storing your medicines in a place out of reach for children and pets is essential. Consider using a shelf or a locked cabinet as an ideal location.
- Stay updated on expiration dates; Make it a habit to check the expiration dates on your medications regularly. Dispose of any that are expired or no longer needed.
- Avoid sharing medication: It's crucial not to share isoniazid or any other prescription medication with others. Different individuals may have conditions, and taking medication that is unsuitable for them could be harmful.
Disposal of Unused or Expired Isoniazid: A Safe Approach
To ensure the disposal of unused or expired isoniazid, it is crucial to follow the guidelines given by your pharmacist's local waste disposal facility or refer to the recommendations provided by the FDA. It is essential to avoid flushing medications down toilets or sinks unless instructed. Properly disposing of these medications not only protects our environment but also reduces the risk of accidental ingestion by children, pets, or anyone who may come into contact with discarded medicines.
Key Takeaway; Properly storing isoniazid medication plays a role in maintaining its effectiveness and ensuring safety during treatment. It should be stored at room temperature away from moisture and kept in its original container with a tightly closed lid. To safely dispose of any expired medication, following the guidelines given by your pharmacist or local waste disposal facility is essential. This responsible action helps protect our environment and prevents ingestion.
FAQs to Buy Isoniazid
Do I need a prescription for isoniazid?
Yes, you do require a prescription to acquire isoniazid. This medication is crucial for treating tuberculosis. Can only be obtained through a healthcare professional following an accurate diagnosis and thorough evaluation.
What is the box warning for isoniazid?
The warning label on isoniazid emphasizes the potential for liver damage (hepatotoxicity), which can have fatal consequences. It is crucial to observe patients for any indications of liver dysfunction, like yellowing of the skin or increased liver enzyme levels throughout the treatment process.
Who is eligible for isoniazid?
Eligibility for isoniazid depends on factors such as age, medical history of allergies, medications, and the medications being taken. Usually, it is prescribed to patients who have been diagnosed with latent tuberculosis infection and do not have any conditions that would make it unsuitable. Your healthcare provider will assess your eligibility based on these considerations.
Is there an alternative for isoniazid?
If you're unable to take isoniazid due to contraindications or side effects, your healthcare provider may suggest considering alternative medications. Some options include rifampin, ethambutol, pyrazinamide, or other anti-tuberculosis drugs. It's essential to consult with your healthcare provider before changing your medication.
Buy Isoniazid: An Essential Guide to Usage and Safety
Understanding the uses of Isoniazid and its effectiveness in combating tuberculosis is crucial for patients considering it. This medication helps to hinder the growth of TB bacteria. It's essential to be aware of potential side effects like liver damage. Patients should take precautions and follow their doctor's instructions when using this medication. It's worth noting that lifestyle factors, such as diet and vitamin B6 intake, can impact how well Isoniazid works.
Additionally, proper storage of the medication is vital to ensure its effectiveness. If you're interested in purchasing Isoniazid, you can find options at Buy Pharma. However, always consult with your healthcare provider before starting any medications.
Isoniazid FAQ
- What are the side effects of Isoniazid?
- What is the mechanism of action of Isoniazid?
- What are the adverse effects of Isoniazid?
- What is the relationship between Isoniazid and Rifampin?
- What does INH stand for in relation to Isoniazid?
- What is the brand name for Isoniazid?
- What is Isoniazid?
- What is the relationship between Isoniazid and Vitamin B6?
- What are the uses of Isoniazid?
- What is the drug class of Isoniazid?
- What is Isoniazid toxicity?
- What are the interactions of Isoniazid?
- What is the dosage for Isoniazid?
- What is the dose of Isoniazid?
- What is the class of Isoniazid?
- What are the contraindications for Isoniazid?
- What is the relationship between Isoniazid and Pyridoxine?
- What are the long-term side effects of Isoniazid?
- What is an Isoniazid 300 mg tablet?
- What is the role of Isoniazid for latent TB?
- What is the relationship between Isoniazid and Vitamin B6?
- What is the relationship between Isoniazid and B6?
- What is the role of Isoniazid in latent TB?
- What is the antidote for Isoniazid?
- What is the cost of Isoniazid?
- What should be included in patient teaching for Isoniazid?
- What is the generic name of Isoniazid?
- What is Isoniazid medication?
- What are the nursing considerations for Isoniazid?
- What is Isoniazid hepatotoxicity?
- What is the price of Isoniazid?
- What is the relationship between Isoniazid and alcohol?
- What are the side effects of Isoniazid with Vitamin B6?
- What are the warnings associated with Isoniazid?
- What should be included in Isoniazid teaching?
- What is an Isoniazid tablet?
- What is an Isoniazid tab?
- What is the relationship between Isoniazid and Rifampin?
- What is Isoniazid peripheral neuropathy?
- What happens if I stop taking Isoniazid?
- What is the relationship between Isoniazid and Rifapentine?
- What is the structure of Isoniazid?
- What is Isoniazid therapy?
- What is the trade name of Isoniazid?
- What is the role of Isoniazid in treating TB?
- What is the indication for Isoniazid?
- What are the reviews for Isoniazid?
- What is the impact of Isoniazid during pregnancy?
- What is Isoniazid neuropathy?
- What is Isoniazid liver toxicity?
- Why is Isoniazid and Rifampin given together?
- What is the use of Isoniazid for TB?
- What are the long-term side effects of Isoniazid?
- What happens in case of an Isoniazid overdose?
- Does Isoniazid cause orange urine?
- What is Isoniazid treatment?
- How does Isoniazid relate to tuberculosis?
- What is the relationship between Isoniazid and Rifapentine?
- What is the mode of action of Isoniazid?
- What is the effect of Isoniazid on the liver?
- What is Isoniazid hepatitis?
- What are the complications of Isoniazid?
- Which foods should be avoided while taking Isoniazid?
- How is Isoniazid related to vitamins?
- What are the side effects of Isoniazid and Rifapentine?
- What is the safety of Isoniazid in pregnancy?
- Can Isoniazid cause a rash?
- What is the role of monitoring in Isoniazid therapy?
- What are the food interactions with Isoniazid?
- What other drugs can interact with Isoniazid?
- What is the dose of Isoniazid for latent TB?
- What is an Isoniazid drug card?
- Is Isoniazid an antibiotic?
- What is Isoniazid used to treat?
- What does Isoniazid do?
- Can Isoniazid cause liver damage?
- Why is Isoniazid taken with Vitamin B6?
- What is the relationship between Isoniazid and Pyridoxine?
- Is Isoniazid safe during pregnancy?
- Does Isoniazid interact with Vitamin B12?
- Is Isoniazid broad or narrow spectrum?
- What is the dose of Vitamin B6 with Isoniazid?
- Can Isoniazid cause seizures?
- How are seizures caused by Isoniazid treated?
- Can Isoniazid cause sideroblastic anemia?
- Can Isoniazid cause weight gain?
- What are Isoniazid, Ethambutol, and Streptomycin?
- What is the target of Isoniazid?
- Is there an injectable form of Isoniazid?
- What is Isoniazid resistance?
- What is included in the Isoniazid package insert?
- What is Isoniazid prophylaxis?
- What is the combination of Isoniazid plus Rifapentine?
- What are the psychiatric side effects of Isoniazid?
- What is the generic and brand name of Isoniazid?
- Is Isoniazid a MAOI?
- What diet should be followed when taking Isoniazid?
- What is Isoniazid-induced liver damage?
- What labs are monitored when taking Isoniazid?
- Can Isoniazid cause lupus?
- What are the symptoms of Isoniazid-induced liver damage?
- Is there a liquid form of Isoniazid?
- Can Isoniazid cause constipation?
- Does Isoniazid cause weight loss?
- Is Isoniazid safe?
- Can Isoniazid cause hepatitis?
- Is Isoniazid used for depression?
- Is Isoniazid used for HIV?
- Is Isoniazid used for cystic fibrosis?
- Can Isoniazid be taken with alcohol?
- What are some uses of Isoniazid other than TB?
- Can Isoniazid and Phenytoin be taken together?
- What are the side effects of Isoniazid and Priftin?
- What is the relationship between Isoniazid and Ethambutol?
- What is the relationship between Isoniazid and hepatitis?
- Can Isoniazid and Pyrazinamide be taken together?
- What is the connection between Isoniazid and Vitamin B?
- What happens if there is a Vitamin B6 deficiency due to Isoniazid?
- Is there an Isoniazid supplement?
- Can Isoniazid cause optic neuritis?
- Is there an oral solution of Isoniazid?
- Does Isoniazid cause weight loss?
- What is the effect of Isoniazid on the liver?
- How is Isoniazid used in TB treatment?
- Can Isoniazid induce lupus?
- Can Isoniazid cause neuropathy?
- What is the route of administration for Isoniazid?
- What is the generic name for Isoniazid?
- Can Isoniazid cause gout?
- How is Isoniazid-induced neuropathy treated?
- What is the connection between Isoniazid and the B complex vitamins?
- What does the Isoniazid blood test measure?
- Is Isoniazid used in HIV patients?
- What is the chemical structure of Isoniazid?
- How much does Isoniazid cost?
- Does Isoniazid affect birth control?
What are the side effects of Isoniazid?
When taking Isoniazid, individuals may experience specific side effects such as nausea, vomiting, stomach upset, and loss of appetite. In some cases, more serious side effects may arise, including signs of liver disease changes in vision, numbness or tingling of hands or feet, and mental/mood changes. It is essential to be aware of these potential side effects and consult with a healthcare professional if they occur.
What is the mechanism of action of Isoniazid?
Isoniazid was developed as a potent inhibitor of a key biosynthetic step in Mycobacterium tuberculosis cell wall formation, namely, mycolic acid production. This action results in an effective killing response toward rapidly dividing microbes belonging to this species.
What are the adverse effects of Isoniazid?
Isoniazid presents certain risks beyond its common side effects. Most notably, this medication has been linked to various adverse effects that should not be taken lightly. These can range from severe liver damage and peripheral neuropathy to drug-induced lupus erythematosus - an ailment that has been known to lead to fatalities.
What is the relationship between Isoniazid and Rifampin?
To address tuberculosis infection head medical experts often prescribe Isoniazid and Rifampin simultaneously. These complementary medications work in harmony to thwart the insidious bacteria that can complicate respiratory function and overall health.
What does INH stand for in relation to Isoniazid?
In medical situations, the term INH refers to Isoniazid, which can be abbreviated as this acronym.
What is the brand name for Isoniazid?
Isoniazid is marketed under brand names Nydrazid and Laniazid respectfully.
What is Isoniazid?
As one of the most essential antibiotics available today Isoniazid plays a vital role in safeguarding vulnerable populations by both treating existing tuberculosis infections and proactively mitigating potential outbreaks.
What is the relationship between Isoniazid and Vitamin B6?
To alleviate the risk of peripheral neuropathy— a side effect that can be induced by Isoniazid — individuals may be prescribed with pyridoxine (Vitamin B6).
What are the uses of Isoniazid?
Isoniazid is a medication employed to treat and preempt tuberculosis. Typically it is part of a multi drug regimen to ensure optimal control of tuberculosis.
What is the drug class of Isoniazid?
Belonging to the drug classification of antimycobacterials, isoniazid acts specifically as an antitubercular agent.
What is Isoniazid toxicity?
Individuals must note that isoniazid use for an extended period or beyond its recommended dosage may cause toxicity. This results in harmful effects such as nerve damage (peripheral neuropathy) and liver damage (hepatotoxicity). Furthermore, it may even lead to severe consequences such as acute liver failure.
What are the interactions of Isoniazid?
When using isoniazid as a treatment, it's crucial that patients remain vigilant about potential interactions with other drugs or food items. Antacids, any food containing tyramine (like aged cheeses or soy sauce), phenytoin, and alcohol are all substances known to interact poorly with it. Those using this medication should always err on the side of caution to prevent serious complications such as liver damage from occurring.
What is the dosage for Isoniazid?
A person's dosage of Isoniazid will depend on variables such as age, weight, and medical condition. As directed by medical professionals, individuals usually take this medication once a day or according to specific instructions provided by experts in the field.
What is the dose of Isoniazid?
Typically adult patients are advised to take Isoniazid for tuberculosis treatment within a daily dose range of 200 300mg. Nevertheless, its crucial to recognize that this recommended dosage may vary based on diverse individual patient factors.
What is the class of Isoniazid?
Isoniazid is classified as an antimycobacterial medication, specifically an antitubercular agent.
What are the contraindications for Isoniazid?
Careful consideration must be given when deciding whether or not to administer Isoniazid. Those with severe liver disease or acute liver disease due to any cause should avoid this medication altogether. Similarly, individuals with significant renal dysfunction should not use this drug. Individuals who have had a negative response in the past after taking Isoniazid must also exercise caution if considering re-administering.
What is the relationship between Isoniazid and Pyridoxine?
When taking Isoniazid there's a possibility of suffering from Pyridoxine (Vitamin B6) deficiency. Therefore individuals are advised to take Pyridoxine alongside the medication. This advice is especially necessary for certain groups that have a higher likelihood of experiencing this side effect.
What are the long-term side effects of Isoniazid?
Knowing about the possible long term side effects is necessary when considering taking Isoniazid regularly. These complications include hepatotoxicity or liver damage, peripheral neuropathy, and drug induced lupus erythematosus which become increasingly likely after continued use of the medication. Those who require prolonged use will need to be particularly vigilant as they face higher risks than those whose treatment ends earlier.What is an Isoniazid 300 mg tablet?
A commonly prescribed drug for tuberculosis is Isoniazid, specifically the 300 mg tablet form of the antibiotic.
What is the role of Isoniazid for latent TB?
To prevent latent tuberculosis infection from developing into active tuberculosis disease, the medication isoniazid is utilized.
What is the relationship between Isoniazid and Vitamin B6?
Supplementing with Pyridoxine or Vitamin B6 during Isoniazid treatment has been known to prevent one of its undesirable complications - peripheral neuropathy.
What is the relationship between Isoniazid and B6?
Including Vitamin B6 supplements when using Isoniazid is advised as it could result in a shortfall of Pyridoxine and ultimately lead to peripheral neuropathy.
What is the role of Isoniazid in latent TB?
When it comes to preventing the progression of latent TB infection into an active disease Isoniazid is a reputable option often used as a first line treatment.
What is the antidote for Isoniazid?
When someone experiences toxicity caused by consuming too much Isoniazid, administering Pyridoxine (also known as Vitamin B6) can be a successful antidote. Treatment usually involves giving a dosage equivalent to the amount of Isoniazid ingested.
What is the cost of Isoniazid?
Isoniazid prices can be influenced by several factors, like regional differences among costs set by pharmacies and healthcare providers. Additionally, insurance coverage can impact how much one pays for Isoniazid. For more precise information about cost estimates where you reside, we recommend consulting reliable healthcare professionals or looking up prices at nearby pharmacies.
What should be included in patient teaching for Isoniazid?
To empower individuals in their health management journey, healthcare providers must prioritize educating patients on various aspects surrounding their medications. Specifically, patients need to be made aware of how crucial it is to use their prescribed medicine regularly without fail; aside from this information being vital in ensuring positive health outcomes, its equally critical that they know what potential side effects may arise from taking certain medications such as Isoniazid- including those related to liver toxicity- and when they should consider seeking further medical assistance if necessary. Relatedly keeping up with follow-up appointments cannot be stressed enough since they afford to monitor of adverse effects while enabling opportunities for early interventions where applicable. Lastly shedding light on how different foods or medicines interact with Isoniazid can minimize risks posed by conflicts that may compromise treatment plans.
What is the generic name of Isoniazid?
Isoniazid is the general term for this drug, which is sold under various brand names, including Nydrazid and Laniazid.
What is Isoniazid medication?
Isoniazid, primarily employed to prevent and treat tuberculosis, is an antibiotic medication.
What are the nursing considerations for Isoniazid?
The safety and health of patients entrusted to them are vital concerns for nurses everywhere. One key aspect of patient care involves careful observation of untoward reactions resulting from drugs administered; these include evidence of hepatotoxicity or neuropathy. Nurses must also impart clear knowledge concerning drug dosage schedules and thoroughly instruct relevant individuals on their importance. Finally, emphasizing follow-up consultations remains critical in ensuring optimal outcomes for everyone involved.
What is Isoniazid hepatotoxicity?
Isoniazid can cause harm to the liver resulting in whats known as Isoniazid hepatotoxicity. This severe side effect could potentially lead to death if not acknowledged and treated promptly. As such swift recognition and management of the condition are essential.
What is the price of Isoniazid?
Isoniazid's pricing may differ owing to variables such as pharmacy location and insurance coverage. Checking with nearby pharmacies is advisable for precise pricing information.
What is the relationship between Isoniazid and alcohol?
Its crucial to be aware that drinking alcohol and taking Isoniazid medication concurrently increases your chances of developing hepatotoxicity. Owing to this potential danger it is better to limit your alcohol intake if not steer clear of it altogether while on this drug therapy.
What are the side effects of Isoniazid with Vitamin B6?
Isoniazid has the potential to cause a deficiency in Vitamin B6, which can subsequently result in peripheral neuropathy. However this side effect can be managed by incorporating Vitamin B6 supplements into ones Isoniazid therapy plan.
What are the warnings associated with Isoniazid?
Taking isoniazid comes with a fair share of risks that patients ought to know before commencing treatment. These include possible liver damage, peripheral neuropathy or unfavorable drug interactions. As a result physicians should provide adequate information to their patients before prescribing this medication.
What should be included in Isoniazid teaching?
The importance of comprehensive patient education cannot be overstated when it comes to treating Isoniazid. In order for patients to feel empowered in their treatment plan it is necessary to provide clear instructions on medication therapeutic objectives as well as specific dosing schedules which will result in optimal efficacy. Adherence must be taken seriously by all individuals who have been prescribed this anti-tuberculosis drug--this means staying alert for symptoms such as peripheral neuropathy, which can result from prolonged exposure without modification or ceasing medication use altogether due to adverse consequences they may cause beyond what has already been experienced by taking them alone. Furthermore, hepatotoxicity risk is a serious consideration requiring routine monitoring through regular liver function tests during treatment period especially if other drugs taken concurrently like acetaminophen which can exasperate the situation. Avoidance of alcohol consumption or
What is an Isoniazid tablet?
Isoniazid tablets represent an important form of dosage for those requiring treatment or preventive care for tuberculosis. As an antibiotic Isoniazid has proven to be a reliable solution for many patients facing this challenging disease.
What is an Isoniazid tab?
For those looking to prevent or treat tuberculosis the tablet form of Isoniazid - commonly referred to as an Isoniazid tab - may be prescribed by healthcare professionals.
What is the relationship between Isoniazid and Rifampin?
To combat tuberculosis effectively and minimize risks associated with drug resistance, healthcare providers often rely on a combination approach that includes both Isoniazid and Rifampin. This dynamic duo offers complementary effects that work synergistically for maximum efficacy; by targeting different aspects of TB bacterias physiology simultaneously within the body patients may achieve better outcomes than they would using either medication alone. By using both drugs in tandem as part of a comprehensive treatment plan for tuberculosis infection, healthcare providers can increase patient-centered care outcomes while minimizing complications associated with prolonged illness or risk factors for reinfection over time.
What is Isoniazid peripheral neuropathy?
Physicians who prescribe Isoniazid should take into account instances where its use may give rise to negative health outcomes in order that patients are informed on what they might expect when taking it. One condition whose onset could occur is peripheral neuropathy; this state, being characterized by damage within several nerve endings within numerous areas throughout one's body, typically produces unpleasant symptoms like numbness or sharp needle-like tingling sensations and sometimes even outright painful experiences for those who suffer from it. Those with Vitamin B6 (Pyridoxine) deficiencies maybe even more likely to develop peripheral neuropathy when treated with Isoniazid.
What happens if I stop taking Isoniazid?
To effectively manage tuberculosis, one must diligently finish a complete course of Isoniazid. Halting treatment prematurely may trigger a resurgence or aggravation of the illness and heighten the risk of cultivating drug-resistant variants of the bacteria.
What is the relationship between Isoniazid and Rifapentine?
When tackling latent tuberculosis infection, healthcare providers often recommend a dual course of treatment comprising Isoniazid and Rifapentine – two potent antituberculosis drugs.
What is the structure of Isoniazid?
A pyridine ring connected to a hydrazide group form the basic building blocks of Isoniazid, making it an uncomplicated organic compound.
What is Isoniazid therapy?
Isoniazid therapy pertains to administering the antibiotic Isoniazid to cure and stave off tuberculosis. Maintaining regular usage over a period of several months is often necessary.
What is the trade name of Isoniazid?
Nydrazid and Laniazid are two widely employed trade names for Isoniazid, a medication renowned for its efficacy in combating tuberculosis.
What is the role of Isoniazid in treating TB?
An important tool in managing tuberculosis is utilizing isoniazid as a first resort medication option. By impeding the creation of mycolic acid present in bacteria its growth can be hindered, enabling effective prevention and treatment strategies to be implemented accordingly.
What is the indication for Isoniazid?
Isoniazid serves as the main solution for treating and preventing tuberculosis an infectious illness caused by bacteria that can negatively impact ones health.
What are the reviews for Isoniazid?
Individual experiences greatly influence the reviews for Isoniazid. Its effectiveness in treating tuberculosis is subject to variation as some patients may encounter side effects while on it. Remember to seek personal medical advice from a healthcare provider at all times.
What is the impact of Isoniazid during pregnancy?
When dealing with tuberculosis treatment during pregnancy, Isoniazid is commonly regarded as a viable option without posing any significant harm. Nonetheless, medical professionals advise consuming Vitamin B6 concurrently to prevent potential neuropathic effects.
What is Isoniazid neuropathy?
Its essential to recognize that taking Isoniazid comes with a possible cost: neuropathy and subsequent peripheral nerve injury. Research into this topic has revealed that such an outcome frequently occurs when there is inadequate Vitamin B6 (Pyridoxine) available in the system.
What is Isoniazid liver toxicity?
As hepatotoxicity poses a grave threat when using Isoniazid, its critical to carefully observe liver function during therapy. To ensure safety and minimize any associated risks, regular monitoring is highly recommended.
Why is Isoniazid and Rifampin given together?
Giving Isoniazid and Rifampin together is a strategy used to amplify the efficacy of tuberculosis therapy and to hinder the emergence of drug resistance. By acting upon distinct mechanisms in the tuberculosis bacterium, both drugs enhance the treatment's effectiveness.
What is the use of Isoniazid for TB?
When it comes to seeking out reliable treatment options for tuberculosis Isoniazid has become a go to first line medication choice for many health professionals. With this infectious disease originating from exposure to the bacterium Mycobacterium tuberculosis -Isoniazids' key function involves disrupting and thus preventing formation of said bacteriums cell wall. This sequence of events ultimately leads to an inhibition of growth itself.
What are the long-term side effects of Isoniazid?
The use of Isoniazid warrants careful consideration as it could give rise to lasting side effects encompassing liver harm (hepatotoxicity) peripheral neuropathy or other detrimental impacts. Evidently this risk ratio hinges on an array of unique patient related aspects, including age and overall health status.
What happens in case of an Isoniazid overdose?
The consumption of Isoniazid beyond the recommended dosage can cause adverse reactions, including but not limited to nausea and repeated vomiting episodes. Dizziness or disorientation accompanied by blurred vision may also ensue. In more serious incidents, seizures could manifest themselves, leading ultimately to coma-like conditions. One must act promptly and avail expert medical aid if confronted with any such ferocious side effects stemming from the overdose of the drug mentioned above.
Does Isoniazid cause orange urine?
It is worth noting that generally, Isoniazid use does not result in orange urine. Yet it should be mentioned that Rifampin, another drug frequently administered alongside Isoniazid in tuberculosis treatment, possesses the potential to tinge bodily fluids - including urine - an orange-red color.
What is Isoniazid treatment?
An integral part of preventing and treating tuberculosis entails utilizing Isoniazid antibiotics referred to as Isoniazid treatment. To succeed in this clinical approach, considerable devotion to taking medication consistently over an extended period - usually lasting several months - is vital.
How does Isoniazid relate to tuberculosis?
As one of the initial medicinal treatments utilized for fighting tuberculosis- an infectious disease spawned by Mycobacterium tuberculosis bacteria- Isoniazid holds immense value. Its categorized as one of the first line agents for alleviating symptoms of this illness.
What is the relationship between Isoniazid and Rifapentine?
The combination of Isoniazid and Rifapentine is often used to treat latent tuberculosis infections. These medications possess antituberculosis properties essential in treating this illness.
What is the mode of action of Isoniazid?
Isoniazid stops tuberculosis from spreading through its mechanism for impeding mycolic acid synthesis. Mycobacterium tuberculosis requires this vital element to form its cell wall successfully. When Isoniazid disrupts this process it inhibits the bacterias ability to multiply and spread throughout the body.
What is the effect of Isoniazid on the liver?
Hepatotoxicity caused by Isoniazid remains a valid concern that could cause lasting damage. Any symptomatology linked to this condition must be immediately addressed by qualified healthcare providers with appropriate oversight. Routine monitoring related directly or indirectly alludes specifically towards underlying inconsistencies with liver functionality during any course underlined by medication containing Isoniazid components within its formulation profiles across multiple patients as deemed necessary given prior established guidelines or industry standards at large surrounding similar interventions in question constantly evolving preventive care strategies relating medical agencies report regularly upon revealing pertinent findings otherwise left unknown without data-driven analysis over time per se such initiatives' inherent implications imply various health concerns worth tackling head-on always holding transparent discussions with patients concerning benefits and risks alike
What is Isoniazid hepatitis?
In the sphere of Isoniazid therapy, hepatitis is a grave condition that arises from liver inflammation. It necessitates urgent medical intervention to prevent further complications.
What are the complications of Isoniazid?
Those administered with Isoniazid treatment ought to be conscious of the potential medical challenges associated with its usage including; liver damage (hepatotoxicity), peripheral neuropathy as well as skin irritation, amongst others, such as occasional drug-mediated lupus reaction. Nonetheless, not every patient is equally susceptible since each person’s unique biological characteristics require special attention.
Which foods should be avoided while taking Isoniazid?
When taking Isoniazid medication, its essential to abstain from consuming food and drink items that have tyramine. These may include some kinds of cheese or alcohol beverages in addition to preserved meats. Interactions could occur between these substances and the medication which can cause unwanted side effects.
How is Isoniazid related to vitamins?
Isoniazid usage bears a significant impact on the metabolism of Vitamin B6 indicating a possible deficiency. As such during Isoniazid therapy healthcare practitioners may suggest patients take Vitamin B6 supplements as an appropriate course of action.
What are the side effects of Isoniazid and Rifapentine?
Certain medications, such as Isoniazid and Rifapentine, have the potential to cause undesirable outcomes in some individuals who take them regularly. Common reactions comprise of nausea and vomiting accompanied by a loss of appetite and sometimes even yellowing of the skin (jaundice). In other cases, more severe symptoms such as liver damage or intense abdominal pain may require medical assistance promptly. Though extremely rare - but possible- are instances where an allergic reaction requires immediate intervention without delay!
What is the safety of Isoniazid in pregnancy?
As part of tubercular healthcare during pregnancy, experts generally deem using isoniazid safe for expectant mothers. The rationale behind this perspective hinges on an understanding of how much damage can result from leaving TB untreated in pregnant women - it can cause serious harm to both mother and fetus alike. Even so weighing up ones options involves taking into account all of the possible consequences that come with medication use.
Can Isoniazid cause a rash?
It's essential to understand that Isoniazid can provoke rashes in specific cases. Such instances could signify an adverse drug effect or an allergic response. Individuals must seek advice from their healthcare specialist if they observe any fresh or intensifying skin reactions.
What is the role of monitoring in Isoniazid therapy?
Efficient and effective management of Isoniazid therapy requires ongoing monitoring to safeguard against potential complications or setbacks during treatment. Specifically, constant vigilance is necessary to identify signs of liver damage or drug resistance - both risks that can challenge successful outcomes if not detected early on. Moreover, continuous monitoring ensures compliance with the recommended dosage regimen at all times throughout treatment. To accomplish these objectives successfully entails routine medical appointments and lab testing as integral aspects thereof.
What are the food interactions with Isoniazid?
Proper usage of Isoniazid requires awareness of various dietary restrictions while on this medication. It is advised to avoid foods containing tyramine and histamine, like cheese and fish since they could heighten the likelihood of a hypertensive crisis. Furthermore, alcohol should also be excluded from your diet as it may raise the possibility of hepatotoxicity.
What other drugs can interact with Isoniazid?
Pharmacological investigations reveal that there exist several significant drug interactions pertaining to isoniazid consumption. These associations primarily include antacids which decrease its absorption capacity, and hepatically metabolized medicines like phenytoin and carbamazepine which are likely to show increased levels after administration alongside this drug therapy. As a consequence, patients consuming such medication combinations should be monitored closely for signs of toxicity or adverse events.
What is the dose of Isoniazid for latent TB?
To address latent tuberculosis, the customary course of action often includes a daily regimen consisting of Isoniazid at a quantity of 300mg. Standard practice generally requires continuing this routine for up to nine months; however, its crucial to discuss your personal situation with your healthcare provider, as various factors may influence your precise dosing requirements or timeline.
What is an Isoniazid drug card?
It is always advisable to have an accessible source of crucial facts regarding any prescribed medication— especially when it concerns powerful preparations like Isoniazid. That is where an Isoniazid drug card comes into play; it serves as a go-to resource for essential information that includes precise dosing advice alongside adverse reactions and possible contraindications with medications or food substances. The card ensures that patients stay informed on how to best manage their treatment by providing key data on these vital aspects of the medicine!
Is Isoniazid an antibiotic?
An antibiotic drug that specifically targets tuberculosis treatment is referred to as Isoniazid. Its modus operandi includes restraining the synthesis mechanism involved in producing essential elements like mycolic acids found in bacterial cell walls and membranes.What is Isoniazid used to treat?
Healthcare professionals turn to Isoniazid to tackle tuberculosis - a serious and contagious disease caused by the bacterium Mycobacterium tuberculosis - both for treatment and prevention purposes.
What does Isoniazid do?
Isoniazid prevents Mycobacterium tuberculosis from synthesizing mycolic acid- a critical element necessary for maintaining its cellular membrane integrity. This crucial intervention greatly curbs bacterial multiplication and spread, facilitating effective oversight and elimination strategies targeting tuberculosis.
Can Isoniazid cause liver damage?
It is crucial for patients undergoing treatment with Isoniazid for tuberculosis infections to be mindful of the possible side effects they may experience. One example is the risk of hepatotoxicity or liver damage, which can lead to symptoms such as fatigue or nausea alongside jaundice and abdominal pain. To mitigate these negative outcomes and promote optimal outcomes during therapy, monitoring of the patient's liver function would help in such situations.
Why is Isoniazid taken with Vitamin B6?
When using Isoniazid as part of a treatment regimen, there's a risk of experiencing peripheral neuropathy. Taking Vitamin B6 (Pyridoxine) simultaneously can alleviate this risk since it counters complications arising from disruptions in Vitamin B6 metabolism brought about by Isoniazid.
What is the relationship between Isoniazid and Pyridoxine?
It's crucial to understand that receiving treatment with Isoniazid may lead to a shortage of Pyridoxine - an essential B vitamin needed for various bodily processes such as nerve function and blood cell production. This occurs due to the drug's ability to interfere with its metabolism. To minimize any damage caused by associated neuropathy and avoid further health issues caused by the deficiency its recommended to take supplemental doses of Pyridoxine during treatment.
Is Isoniazid safe during pregnancy?
Expectant mothers who have tuberculosis can rest easy knowing that isoniazid treatment is generally safe during pregnancy. Its imperative to treat this condition while pregnant as the consequences for both mother and child could be serious.
Does Isoniazid interact with Vitamin B12?
Although ample empirical data is indicating an impact of Isoniazid on the efficacy of Vitamin B6 (Pyridoxine), there's a paucity in evidence supporting a similar correlation between Isoniazid and Vitamin B12. Nevertheless, it is advisable for patients prescribed this medication to consult their healthcare provider before utilizing various kinds of pharmaceuticals or nutraceuticals, as potential interference from such combinations could have unforeseeable consequences.
Is Isoniazid broad or narrow spectrum?
Isoniazid has earned recognition as a narrow-spectrum antibiotic owing to its unique efficacy against Mycobacterium species, specifically in the case of Mycobacterium tuberculosis.
What is the dose of Vitamin B6 with Isoniazid?
For patients undergoing Isoniazid therapy incorporating Vitamin B6 (Pyridoxine) into their treatment plans can be instrumental in alleviating associated symptoms such as peripheral neuropathy; recommended dosages are commonly in the range of 25 to 50mg per day, although it should be noted this amount may fluctuate based upon various parameters and guidelines. Utilizing Pyridoxine effectively has many benefits beyond just preventing peripheral neuropathy - according to research, it can also yield other notable health advantages!
Can Isoniazid cause seizures?
If taken in excess Isoniazid can trigger seizures - a severe reaction that must be treated promptly by medical professionals.
How are seizures caused by Isoniazid treated?
The typical course of action for dealing with seizures brought on by Isoniazid includes utilizing anticonvulsants and halting the use of the medication. Whenever an individual has taken too much, more extreme interventions may become necessary, like offering supportive treatment or perhaps providing Pyridoxine.
Can Isoniazid cause sideroblastic anemia?
Although not common, there have been reports linking isoniazid use with drug-induced sideroblastic anemia. Essentially this complication impairs the body's capacity to utilize iron and synthesize hemoglobin.
Can Isoniazid cause weight gain?
Weight gain isn't typically associated with Isoniazid usage; however, it is critical to report any dietary or physical fluctuations experienced during treatment to avoid unwanted outcomes. It's important for patients undergoing TB therapy to comprehend that healthier body function and possible swelling may lead them to believe they have gained additional mass when they haven't indeed done so - these are just normal physiological responses.
What are Isoniazid, Ethambutol, and Streptomycin?
Mycobacterium tuberculosis is a deadly bacterium found in individuals suffering from TB. Fortunately, those infected by TB disease can undergo treatment through several medications such as Isoniazid, Ethambutol, and Streptomycin. Although these drugs differ in their mechanisms of operation when used simultaneously create a potent combination that halt MTBs spread and consequently clears out any traces after successful treatment.
What is the target of Isoniazid?
Isoniazids main purpose is to curtail Mycobacterium tuberculosis bacterium growth. The drug functions by inhibiting the production of mycolic acid used in creating bacterial cell walls which ultimately impairs their viability and replication.
Is there an injectable form of Isoniazid?
Although ordinarily taken orally, Isoniazid has an injectable option that can be utilized under certain conditions. Yet, only health professionals can determine when such circumstances are necessary.
What is Isoniazid resistance?
Isoniazid resistance happens when Mycobacterium tuberculosis undergoes a mutation that enables it to endure in the face of Isoniazid. This leads to the lessened effectiveness of the drug in treating the ailment.
What is included in the Isoniazid package insert?
The Isoniazid package insert contains vital information about the medication's uses, limitations, optimal dosage, and administration methods. The document also notes potential side effects and interactions with other drugs alongside warnings and precautions.
What is Isoniazid prophylaxis?
Isoniazid prophylaxis entails providing Isoniazid beforehand to persons at elevated danger of contracting active tuberculosis. Such individuals might involve those infected with latent TB or near patients affected by active TB.
What is the combination of Isoniazid plus Rifapentine?
One successful strategy for warding off and treating tuberculosis is using Isoniazid in conjunction with Rifapentine. Given on a weekly basis over three months (or 12 weeks) this regimen is able to effectively address cases of latent tuberculosis infection.
What are the psychiatric side effects of Isoniazid?
In very rare cases, when administering Isoniazid medication during treatment for tuberculosis (TB) individuals may experience psychiatric side effects such as changes in mood or mental state leading to psychotic manifestations. Therefore it's vital to seek prompt medical help if such circumstances arise.
What is the generic and brand name of Isoniazid?
A highly utilized medication for treating tuberculosis is Isoniazid. Despite variations between countries and manufacturers, Nydrazid remains a prominent brand name for this drug.
Is Isoniazid a MAOI?
Its worth noting that Isoniazid has been deemed a weak monoamine oxidase inhibitor (MAOI). Its primary purpose is as an antituberculosis treatment however it can still have interactions with specific foods and medications.
What diet should be followed when taking Isoniazid?
To make sure that Isoniazid works effectively whilst being taken it is important to avoid consuming food items that have an excessive amount of tyramine or histamine. This is because these types of food can have negative interactions with the medication. Examples include various types of aged cheese cured meats along with certain beers and wines.
What is Isoniazid-induced liver damage?
A critical side effect that warrants close monitoring following the administration of isoniazid is liver damage, which leads to hepatotoxicity. Indicators of this deleterious consequence consist of symptoms such as jaundice, fatigue, nausea and acute abdominal discomfort.
What labs are monitored when taking Isoniazid?
While taking Isoniazid, it is crucial to maintain regular monitoring of liver function tests because this medication has the potential to cause negative impacts on the liver. Additionally, periodic assessments of complete blood counts could help detect any possible occurrences of anemia or blood disorders.
Can Isoniazid cause lupus?
It is worth noting that individuals taking Isoniazid are at a higher risk for drug-induced lupus - an ailment triggering an adverse immune response against one’s own bodily tissues leading to swelling and damage. While this illness shares some similarities with systemic lupus erythematosus regarding signs exhibited, ending treatment with Isoniazid generally brings about recovery for affected patients.
What are the symptoms of Isoniazid-induced liver damage?
It is important for individuals taking Isoniazid to note potential liver damage symptoms that may arise during use. Some common indications can include chronic fatigue and loss of appetite alongside recurrent feelings of nausea/vomiting episodes as well as dark-colored urine production patterns along with abdominal discomfort/pain. Jaundice development (the appearance of yellow skin/eyes) may also arise in these individuals, which would warrant immediate medical attention since this could prove serious for one's overall health status.
Is there a liquid form of Isoniazid?
For those who struggle with swallowing pills Isoniazid presents a viable solution as it comes in liquid form. Additionally, parents may prefer to administer this form of medication to their children due to its ease of dosing.
Can Isoniazid cause constipation?
Although Isoniazid does not usually cause constipation, it may cause gastrointestinal issues like nausea or vomiting. Seeking consultation from a healthcare provider is necessary if one experiences constipation as discomfort.
Does Isoniazid cause weight loss?
It's unlikely that Isoniazid will lead to weight loss, but it's crucial to promptly communicate any major changes in appetite or weight while taking the drug with your healthcare provider.
Is Isoniazid safe?
Undoubtedly Isoniazid is generally safe if utilized correctly and with the guidance of a healthcare provider. However, as with any medicine, it can cause side effects and interactions. Special care must be taken for patients with liver disease or alcohol addiction.
Can Isoniazid cause hepatitis?
Patients must be aware that Isoniazid use has potential hepatotoxicity- a form of drug-induced hepatitis leading to liver injury. Although uncommon, chronic administration or being above a particular age threshold could elevate the chances. To prevent any adverse effects during treatment, healthcare providers must continuously monitor the patient's liver function by performing frequent checks and blood tests regularly.
Is Isoniazid used for depression?
Isoniazid is not usually recommended for treating depression. This medication is primarily used for treating tuberculosis infection and it lacks the properties of an antidepressant.
Is Isoniazid used for HIV?
To clarify isoniazid should not be utilized as a form of treatment for HIV. Nonetheless individuals diagnosed with both HIV and latent tuberculosis infection may find that taking isoniazid can mitigate the risk of developing active tuberculosis.
Is Isoniazid used for cystic fibrosis?
While Isoniazid has been proven effective in treating tuberculosis, it, unfortunately, does not offer any benefits when treating cystic fibrosis. Since this genetic condition impacts the lungs and digestive system, alternative treatments are necessary to manage its symptoms.
Can Isoniazid be taken with alcohol?
Taking Isoniazid along with alcohol is not advisable as it elevates the danger of developing hepatotoxicity, which can cause liver damage.
What are some uses of Isoniazid other than TB?
The primary function of Isoniazid is treating tuberculosis; there are occasions when physicians may use this drug outside its original purpose. Such situations include providing remedies against latent tuberculosis infections and administering prophylactic measures against high-risk populations like individuals who live near someone experiencing TB symptoms or those diagnosed with HIV.
Can Isoniazid and Phenytoin be taken together?
Careful attention should be paid when taking both Isoniazid and Phenytoin at the same time due to the possibility of heightened blood levels of the latter drug resulting in toxicity concerns. Therefore regular monitoring along with dosage adjustments may be necessary when these two medications are coadministered in order to mitigate any potential risks associated with their use. Note: While there isn't necessarily a "correct" number of times one should rewrite the text to improve its readability or style, it can vary depending on factors such as length or complexity of sentences/ideas, specific target audience/reader context/purpose or criteria which need called out or parameters that need to be met (think Twitter max characters policy, specific publication guidelines or formats). The above response offers 4 slightly varied options each attempting to deliver the same argument in a slightly different tone and structure.
What are the side effects of Isoniazid and Priftin?
While Isoniazid and Priftin (Rifapentine) have common side effects like nausea, vomiting, loss of appetite and mild rashes — which should not be overlooked – those who use them should also exercise caution with respect to rare yet serious conditions. This includes the risk of hepatotoxicity or a severe allergic reaction.
What is the relationship between Isoniazid and Ethambutol?
In the treatment of tuberculosis, Isoniazid and Ethambutol are commonly used together in a combination therapy regimen to improve efficacy and reduce drug resistance. Despite their shared use these two drugs work differently due to their distinct mechanisms of action.
What is the relationship between Isoniazid and hepatitis?
An individual taking Isoniazid may experience hepatitis, which is characterized by inflammation of the liver. Those with a history of prior liver disease, alcohol abuse or prescribed certain other medications are at a higher risk for this potential side effect.
Can Isoniazid and Pyrazinamide be taken together?
In the management of tuberculosis combined therapy employing Isoniazid and Pyrazinamide is often utilized. It is noteworthy though that both medications carry a risk of hepatotoxicity. As such diligent monitoring of liver function must be carried out throughout the treatment process.
What is the connection between Isoniazid and Vitamin B?
For individuals undergoing treatment with Isoniazid, it is crucial to be aware of its impact on Vitamin B6 metabolism and potential effects on overall nutritional status. Taking preventative measures such as using supplementary sources of Vitamin B6 is highly recommended and may prove essential for some patients receiving this medication. In particular, certain groups who are more susceptible should prioritize discussing their options further with their healthcare provider.
What happens if there is a Vitamin B6 deficiency due to Isoniazid?
To reduce the incidence of peripheral neuropathy during Isoniazid therapy caused by low levels of vitamin B6, healthcare professionals will often advise patients to augment their dietary intake with supplements. This condition causes sensations such as numbness or pins and needles paired with physical weakness, particularly in the extremities such as hands and feet. Hence, keeping recommended vitamin b6 prior to or alongside medication could alleviate unpleasant sensations associated with poor nutritional status among patients undergoing INH therapy.
Is there an Isoniazid supplement?
Its unfortunate that at present there are no available supplements for Isoniazid. Nevertheless providing individuals taking this medication with Vitamin B6 supplements concurrently helps prevent any plausible complications that may arise from a resultant Vitamin B6 deficiency.
Can Isoniazid cause optic neuritis?
While infrequent, there exist cases where taking Isoniazid medication associates with optic neuritis- an inflammatory disease that might damage one's optical nerves causing eventual blindness. It is wise for patients undergoing treatment with this drug to keep up with regular eye examinations.
Is there an oral solution of Isoniazid?
An oral solution of Isoniazid is available, which can potentially aid those who struggle with swallowing tablets or pediatric patients.
Does Isoniazid cause weight loss?
When treating active tuberculosis using Isoniazid or similar medications, patients commonly experience some degree of bodily discomfort and unintentional shedding of pounds. While the drug itself isn't directly responsible for these effects on body mass index, modern medical insights have confirmed its association with TB treatments resulting in noticeable reductions in the patient's overall size and health condition. If such an outcome arises unexpectedly during therapy sessions on Isoniazid and other medications used for long-term care protocols over several months, then medical practitioners must be called upon immediately.
What is the effect of Isoniazid on the liver?
The use of Isoniazid carries a potential risk of harmful impact on the functioning of an individual's liver - referred to as hepatotoxicity. It may manifest itself with different types of symptoms, such as a significant rise evident in specific forms of enzyme activity present within an individual's organ system, or even result in cases like hepatitis and critical instances leading up to acute forms like severe (acute) loss observed due to damaged function (failure) within an individual's respective organ system. Therefore utmost caution must be upheld while prescribing/administering this drug, and maintaining a constant vigilance towards most probable signals indicating ill effects on an individual's organ system caused due to its usage is widely recommended within medical circles.
How is Isoniazid used in TB treatment?
Isoniazid serves as a primary medication for curing tuberculosis illness - whether its active or latent form. Its advisable to combine it with other antituberculosis drugs as part of a comprehensive treatment plan so as not to promote drug resistance growth.
Can Isoniazid induce lupus?
It has been reported in some instances that taking Isoniazid for treatment of tuberculosis may lead to a rare side effect called drug-induced lupus, where the autoimmune reaction occurs due to this medication. The symptoms include rashes along with joint pain and fatigue. However, this side effect does not occur frequently, and ceasing the use of such medicine generally resolves its unwanted consequences.
Can Isoniazid cause neuropathy?
In some cases, patients taking Isoniazid may experience peripheral neuropathy - a condition that affects sensations of the hands and feet, causing them to feel weak or painful at times. This occurs because Isoniazid hinders the proper conversion of Vitamin B6 (pyridoxine) into its active form leading to these discomforting side effects. Fortunately, one preventative measure involves supplementation with more pyridoxine during treatment – which may help prevent the onset or improve pre-existing symptoms entirely!
What is the route of administration for Isoniazid?
To take Isoniazid, one can usually swallow it in the form of a tablet or concentrated liquid solution. For particular cases, medical professionals may recommend receiving the medication through an injection.
What is the generic name for Isoniazid?
Isoniazid refers to a medication that has several brand names, including Nydrazid and Laniazid. However it is commonly referred to by its generic name of Isoniazid.
Can Isoniazid cause gout?
According to reports, Isoniazid administration may elevate uric acid levels in blood and potentially lead to gout flare among predisposed individuals. Nonetheless, this is not frequently observed.
How is Isoniazid-induced neuropathy treated?
Those who encounter neuropathy resulting from taking Isoniazid are commonly instructed to take Vitamin B6 (pyridoxine) supplements, which can become depleted by the medication. Should symptoms be critical, one may need to decrease their intake of Isoniazid or cease usage entirely.
What is the connection between Isoniazid and the B complex vitamins?
It is not uncommon for Isoniazid medication to have adverse effects on essential nutrient absorption and utilization, particularly on pyridoxine (Vitamin B 6). The use of this drug has been known even more concerning because it may increase peripheral neuropathy chances due to pyridoxine deficiency associated with metabolic interference caused by the medication. Thus physicians usually recommend adding supplementary doses of Vitamin-B 6 supplements during patients' treatment regimes.
What does the Isoniazid blood test measure?
The therapeutic efficacy of Isoniazid depends on maintaining its levels within a certain range during treatment, which requires periodic blood tests. Further these tests can potentially reveal any ill effects cause by medication interactions and shed light on how effectively patients are following their prescribed therapy.
Is Isoniazid used in HIV patients?
Isoniazid is a commonly utilized medication for patients who have latent tuberculosis infection or are vulnerable to contracting tuberculosis due to their weakened immune system particularly in HIV cases.
What is the chemical structure of Isoniazid?
Comprising the fundamental elements of carbon, hydrogen, nitrogen, and oxygen alongside the empirical formula C6H7N3O Isoniazid stands as an organic compound marked by its structural components - namely the pyridine ring (composed of six members and one unique nitrogen atom) and hydrazide group (consisting of two closely bonded nitrogen atoms attached to the carbonyl unit).
How much does Isoniazid cost?
Countless variables can impact the expense of Isoniazid from dosage amount and medication form (tablet or solution) to insurance coverage. For detailed pricing information related to your situation, we suggest consulting your healthcare professional or local pharmacy.
Does Isoniazid affect birth control?
Although there is no direct evidence indicating that Isoniazid impairs hormonal birth control potency its crucial to understand that certain tuberculosis medications may interfere with the effectiveness of birth control. We highly recommend seeking professional advice from a healthcare expert about potential medication interactions.