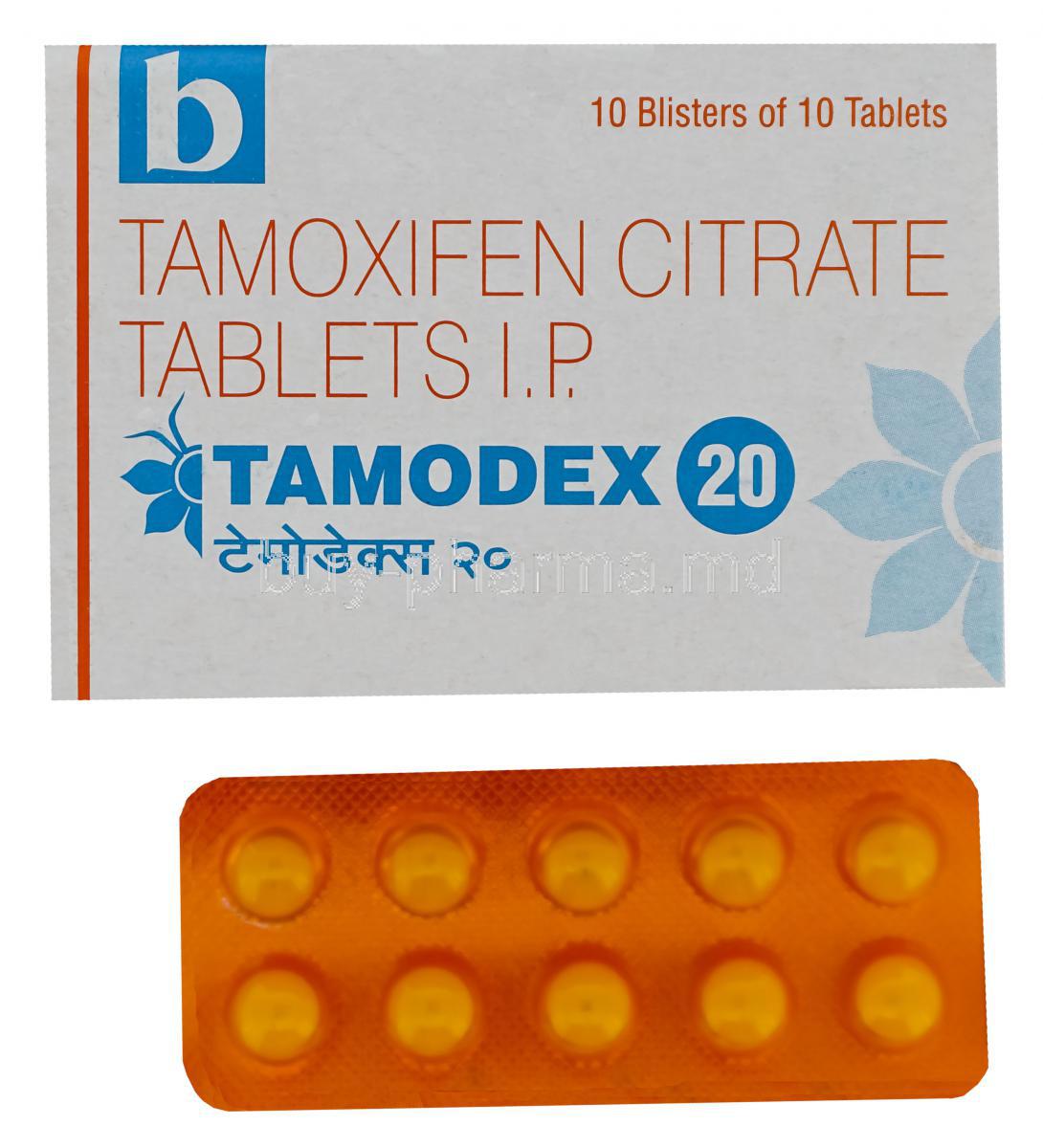
Introduction to Tamodex (Tamoxifen Citrate)
Overview of Tamodex as a Selective Estrogen Receptor Modulator (SERM)
Tamodex, containing tamoxifen citrate, is a well-established selective estrogen receptor modulator (SERM). It demonstrates dualistic pharmacological activity, acting as an estrogen antagonist in breast tissue while exerting partial agonist effects in other tissues such as the bone and endometrium. This selective action has made it an indispensable therapy in hormone-responsive malignancies.
Historical Background and Clinical Relevance in Oncology
Introduced in the late 20th century, tamoxifen was initially developed as a contraceptive candidate. However, its profound anti-estrogenic effect in breast tissue redirected its path into oncology, where it became a cornerstone of treatment for hormone receptor-positive breast cancer. Over decades, it has saved countless lives and remains relevant in both curative and preventive oncology.
Role in Breast Cancer Treatment and Prevention
Tamodex is prescribed not only for active treatment but also as a prophylactic agent in women at elevated risk of breast cancer. By blocking estrogen-driven proliferation of malignant cells, it reduces recurrence and provides a significant survival advantage.
Composition and Formulation
Active Ingredient: Tamoxifen Citrate
The principal therapeutic agent is tamoxifen citrate, a crystalline compound with potent receptor-binding capabilities. It functions as the active pharmaceutical ingredient responsible for the drug’s clinical effects.
Available Strengths and Dosage Forms
Tamodex is generally available in tablet form. Common strengths include 10 mg and 20 mg doses, enabling flexible dosing regimens based on patient-specific requirements.
Inactive Ingredients and Excipients
In addition to the active compound, Tamodex tablets may include excipients such as lactose, magnesium stearate, and starch, which aid in stability, absorption, and manufacturing consistency.
Mechanism of Action: How Tamodex Works
Selective Estrogen Receptor Modulation and Antagonistic Activity
Tamodex binds competitively to estrogen receptors in breast tissue, preventing estrogen from activating cellular proliferation pathways. This receptor blockade curtails tumor growth in estrogen receptor-positive cancers.
Effects on Breast Tissue and Tumor Growth Inhibition
By obstructing estrogen-mediated signaling, Tamodex diminishes mitotic activity in malignant cells, leading to reduced tumor progression and lowered recurrence rates in survivors.
Estrogen Agonist Activity in Other Tissues
Interestingly, in bones, Tamodex exhibits partial agonist activity, preserving bone density and reducing the risk of osteoporosis in postmenopausal women. In the endometrium, however, this agonistic action increases vigilance for potential malignancies.
Pharmacokinetics and Metabolism
After oral administration, Tamodex is absorbed and undergoes hepatic metabolism via cytochrome P450 enzymes, notably CYP3A4 and CYP2D6, forming active metabolites such as endoxifen. These metabolites enhance its pharmacological potency and extend its half-life, often exceeding five days.
Approved Medical Uses of Tamodex
Treatment of Estrogen Receptor-Positive (ER+) Breast Cancer
Tamodex is indicated for both pre- and postmenopausal women with ER+ breast cancer, forming a cornerstone of systemic therapy.
Adjuvant Therapy Following Surgery, Chemotherapy, or Radiation
When used after primary interventions, Tamodex lowers the probability of relapse and enhances overall survival rates.
Prevention of Recurrence in Breast Cancer Survivors
Long-term administration significantly reduces the risk of contralateral breast cancer and recurrence in survivors.
Reduction of Risk in High-Risk Women
For women with hereditary predispositions or family history, Tamodex is recommended as a preventive strategy, lowering incidence rates of invasive breast cancer.
Off-Label Uses of Tamoxifen Citrate
Treatment of Male Breast Cancer
Although less common, Tamodex is employed in male breast cancer, offering effective hormonal control similar to female cases.
Management of Gynecomastia in Men
By modulating estrogen activity, Tamodex alleviates painful or excessive breast tissue development in males.
Fertility Induction in Women with Anovulatory Infertility
Tamodex may be prescribed to induce ovulation in women unresponsive to first-line therapies, enhancing reproductive potential.
Use in McCune-Albright Syndrome and Pubertal Gynecomastia
In pediatric endocrinology, Tamodex has niche applications in managing abnormal pubertal development and hormone-driven disorders.
Research Applications in Hormone-Related Disorders
Ongoing investigations explore tamoxifen’s role in conditions such as bipolar disorder, desmoid tumors, and other estrogen-related pathologies.
Dosage and Administration Guidelines
Standard Adult Dosing for Breast Cancer Treatment
Typically, 20 mg daily is prescribed, though individualized adjustments may be made based on patient response and tolerance.
Recommended Duration of Therapy
Treatment often spans 5 to 10 years, with evidence supporting extended therapy in reducing recurrence.
Dosage Adjustments for Prevention and Off-Label Uses
In risk-reduction scenarios, lower or alternate dosing regimens may be considered. Off-label indications require tailored strategies under specialist supervision.
Administration Instructions
Tablets are taken orally, with or without food. Regularity in timing enhances therapeutic stability and patient adherence.
Side Effects of Tamodex
Common Side Effects
- Hot flashes and sweating
- Vaginal discharge or dryness
- Menstrual irregularities
- Nausea and gastrointestinal discomfort
- Fatigue, headache, and mood changes
Serious Adverse Reactions
- Endometrial cancer risk due to partial agonist activity
- Thromboembolic events such as deep vein thrombosis, pulmonary embolism, and stroke
- Ocular toxicity including retinopathy and cataracts
- Hepatic dysfunction and abnormal liver enzyme profiles
- Severe hypersensitivity reactions
Drug Interactions with Tamodex
Tamodex interacts with several drug classes, necessitating caution:
- Anticoagulants: May potentiate bleeding risk, especially with warfarin.
- CYP2D6 inhibitors: Antidepressants like paroxetine or fluoxetine can diminish tamoxifen efficacy.
- SSRIs and SNRIs: Potential reduction in therapeutic response.
- Other hormonal agents and chemotherapy: Possible antagonism or enhanced toxicity.
Contraindications
- Known hypersensitivity to tamoxifen citrate or formulation components
- History of deep vein thrombosis or pulmonary embolism
- Concurrent use with coumarin-type anticoagulants in susceptible individuals
- Contraindicated during pregnancy and lactation due to teratogenic and neonatal risks
Warnings and Important Precautions
Long-Term Use and Risk of Uterine Malignancies
Extended administration of tamoxifen may heighten the incidence of endometrial carcinoma and, in rare cases, uterine sarcoma. Vigilance is essential, particularly in women undergoing therapy beyond five years. Abnormal vaginal bleeding should always be investigated without delay.
Regular Gynecological Evaluations During Therapy
Routine gynecological assessments are strongly recommended for all women receiving treatment. These evaluations aid in detecting precancerous lesions early and provide reassurance for long-term users. The protocol generally includes pelvic examinations and ultrasound imaging when clinically indicated.
Risk of Thromboembolic Events and Cardiovascular Monitoring
Tamoxifen therapy is associated with an increased risk of thromboembolic events. Clinical vigilance should focus on:
- Deep vein thrombosis and pulmonary embolism
- Stroke and ischemic cardiovascular episodes
- Peripheral vascular complications
Periodic monitoring of cardiovascular status is necessary, especially in patients with additional risk factors such as smoking, obesity, or a sedentary lifestyle.
Need for Regular Ophthalmic Examinations
Ocular toxicity, including retinopathy and cataract formation, has been observed in long-term use. Regular ophthalmological assessments are advisable to identify early manifestations of visual impairment.
Monitoring Liver Function During Prolonged Therapy
Hepatic enzyme elevations and, in rare instances, hepatotoxicity necessitate periodic liver function tests. Patients with a history of hepatic disease require heightened surveillance and cautious dose adjustment.
Careful Administration and Monitoring
Caution in Patients with Pre-Existing Liver Disease
In patients with compromised hepatic function, tamoxifen metabolism may be impaired, resulting in accumulation and potential toxicity. Dose modifications or alternative therapies should be considered.
Caution in Patients with Thromboembolic Risk Factors
Patients with a history of clotting disorders, prolonged immobilization, or familial predisposition should be treated with heightened caution. Prophylactic measures, such as lifestyle modifications or concurrent anticoagulation, may be warranted in select scenarios.
Considerations in Patients with Visual Disturbances
Any patient reporting blurred vision, photophobia, or unexplained ocular discomfort should undergo comprehensive evaluation. Treatment discontinuation may be necessary if ocular pathology is confirmed.
Monitoring Bone Health in Long-Term Users
Tamoxifen may exert protective effects on bone density in postmenopausal women, yet its influence in premenopausal patients remains variable. Long-term therapy should be accompanied by periodic bone mineral density testing to mitigate fracture risk.
Use in Special Populations
Administration in Elderly Patients
Elderly individuals often exhibit altered pharmacodynamics and pharmacokinetics, necessitating cautious dosing. Special attention should be directed toward:
- Cardiovascular and thrombotic risks
- Drug–drug interactions with polypharmacy
- General tolerability and adherence
Administration in Pregnant Women and Nursing Mothers
Tamoxifen is contraindicated during pregnancy due to its teratogenic potential. Documented cases reveal congenital malformations linked to in utero exposure. Women of childbearing age must employ effective contraception throughout therapy and for several months post-treatment.
Excretion into breast milk poses risks to nursing infants, including potential developmental toxicity. Breastfeeding is therefore discouraged during therapy.
Fertility Implications and Need for Contraception During Treatment
Tamoxifen may restore ovulation in anovulatory women, inadvertently increasing the risk of unplanned pregnancy. Stringent contraceptive measures are recommended to avoid teratogenic exposure.
Administration in Children
Clinical data regarding pediatric use remain scarce. Safety and efficacy are not well established, limiting administration to specialized circumstances such as pubertal gynecomastia or rare endocrine disorders. Such usage requires specialist supervision and careful monitoring.
Overdosage and Emergency Management
Symptoms of Overdose
Excessive ingestion of tamoxifen may provoke neurotoxicity, cardiac arrhythmias, and severe gastrointestinal disturbances. Symptoms often present as dizziness, tremors, and prolonged nausea.
Supportive Measures and Symptomatic Treatment
There is no standardized antidote. Management relies on supportive care:
- Gastric decontamination if ingestion is recent
- Electrocardiographic monitoring for arrhythmias
- Intravenous fluids and electrolyte balance correction
Lack of Specific Antidote for Tamoxifen Overdose
No targeted reversal agent exists. Therapeutic efforts focus on stabilizing the patient and alleviating emergent complications.
Handling and Storage Precautions
Proper Storage Conditions
Tablets should be stored at controlled room temperature, typically below 25°C, protected from excessive humidity and direct sunlight. Proper storage preserves potency and shelf life.
Safe Handling of Tablets to Avoid Contamination
Handling should be minimized to avoid contamination or degradation. Tablets should not be crushed or altered unless explicitly directed by a healthcare professional.
Disposal Guidelines for Unused or Expired Medication
Expired or unused medication must be disposed of responsibly, in accordance with local pharmaceutical waste guidelines. Flushing down the toilet or discarding in household waste is discouraged due to environmental concerns.
Tamodex, Tamoxifen Citrate FAQ
- What is tamodex used for?
- Are tamodex and tamoxifen the same?
- Is tamodex 10 mg a steroid?
- Is a prescription needed for Tamodex 10 mg?
- Can I drink alcohol with Tamodex 10 mg?
- What are the side effects of the drug Tamodex?
- What is the use of Tamodex 10 mg tablet?
- Is Tamodex 20 a steroid?
- What is the drug tamoxifen used for?
- What is the most alarming side effect of tamoxifen?
- What to avoid when taking tamoxifen?
- What is the difference between tamoxifen and letrozole?
- Can tamoxifen cause weight gain?
- How long can you take tamoxifen?
- What can I take instead of tamoxifen?
- What organs does tamoxifen affect?
- Is tamoxifen expensive?
- Who cannot take tamoxifen?
- Can I drink coffee while taking tamoxifen?
- What is the new drug replacing tamoxifen?
- Does tamoxifen cause hair loss?
- What is the success rate of tamoxifen?
- What is the major side effect of tamoxifen?
- Does tamoxifen change your appearance?
- What happens if you don't take tamoxifen?
- What is the biggest risk with tamoxifen?
- Does tamoxifen cause teeth problems?
- Does tamoxifen make you tired?
- Is tamoxifen a chemo pill?
- What vitamins should not be taken with tamoxifen?
- Can tamoxifen damage your heart?
- Does tamoxifen cause brain fog?
- What is the best time of day to take tamoxifen?
- What is the black box warning on tamoxifen?
- How common are blood clots with tamoxifen?
- Why do doctors push tamoxifen?
- What are the positive effects of tamoxifen?
- Can I have one drink on tamoxifen?
- What herbs not to take with tamoxifen?
- Why does tamoxifen fail?
- How long can a patient be on tamoxifen?
- Does tamoxifen make hair thin?
- What are the side effects of the drug Tamodex?
- Can tamoxifen cause weight gain?
- How long can you take tamoxifen?
- What can I take instead of tamoxifen?
- What organs does tamoxifen affect?
- Is tamoxifen expensive?
- Can tamoxifen damage your heart?
- Does tamoxifen cause brain fog?
What is tamodex used for?
It treats breast cancer.
Are tamodex and tamoxifen the same?
Tamodex 20 Tablet includes Tamoxifen as an ingredient—a medication known for its oestrogen properties used in treating breast cancer that has metastasized to other areas of the body, in both men and women.
Is tamodex 10 mg a steroid?
No
Is a prescription needed for Tamodex 10 mg?
Yes
Can I drink alcohol with Tamodex 10 mg?
No
What are the side effects of the drug Tamodex?
- Hot flushes
- Night sweats
- Insomnia
- Vaginal Irritation
- Decreased libido
- Mood swings
What is the use of Tamodex 10 mg tablet?
The 10 mg Tamodex tablet is prescribed for treating types of breast cancer in both men and women.
Is Tamodex 20 a steroid?
No
What is the drug tamoxifen used for?
Tamoxifen is prescribed for both men and women with breast cancer that has metastasized to areas of the body, as well as for women with early-stage breast cancer who have undergone surgery and other treatments, like radiation or chemotherapy
What is the most alarming side effect of tamoxifen?
- Bone loss
- Uterine cancer
- Cataracts
- Deep vein thrombosis
- Pulmonary emboli
- Stroke
What to avoid when taking tamoxifen?
- Grapefruits
- Tangerines
- Alcohol
What is the difference between tamoxifen and letrozole?
It has been found that Letrozole tends to be more effective than tamoxifen for women with hormone receptor HR+) breast cancer in terms of reducing recurrence rates and enhancing disease-free survival rates. Letrozole functions by suppressing estrogen production, whereas tamoxifen is an estrogen receptor modulator ( SERM ) that impedes estrogen receptors on cancer cells.
Can tamoxifen cause weight gain?
Yes
How long can you take tamoxifen?
5 years
What can I take instead of tamoxifen?
Raloxifene (Evista)
What organs does tamoxifen affect?
Breast Tissue
Is tamoxifen expensive?
Yes
Who cannot take tamoxifen?
- Have blood clot disorders
- Pregnant or trying to become pregnant
- Breastfeeding
Can I drink coffee while taking tamoxifen?
Coffee might increase the treatment effects of tamoxifen
What is the new drug replacing tamoxifen?
Anastrozole, exemestane and letrozole
Does tamoxifen cause hair loss?
Yes
What is the success rate of tamoxifen?
67%
What is the major side effect of tamoxifen?
- Hot flashes
- Night sweats
- Nausea
- Mood swings
- Depression
- Decreased libido
Does tamoxifen change your appearance?
It can cause hyperpigmentation.
What happens if you don't take tamoxifen?
Studies indicate that failing to adhere to therapy as directed (such as taking medication as prescribed or missing doses altogether) can increase the likelihood of breast cancer returning or spreading to other parts of the body and may also elevate the risk of cancer-related mortality.
What is the biggest risk with tamoxifen?
Since tamoxifen mimics estrogen in the uterus area of the body, it may raise the chances of developing cancers, such as endometrial cancer and uterine sarcoma. It is also associated with a likelihood of developing pre-cancers in the endometrium.
Does tamoxifen cause teeth problems?
Yes
Does tamoxifen make you tired?
Yes
Is tamoxifen a chemo pill?
No
What vitamins should not be taken with tamoxifen?
- Vitamin E
- Soy supplement
- St. John's wort
- Red clover
Can tamoxifen damage your heart?
No
Does tamoxifen cause brain fog?
Yes
What is the best time of day to take tamoxifen?
Bedtime
What is the black box warning on tamoxifen?
It may cause uterine cancer.
How common are blood clots with tamoxifen?
2% chance
Why do doctors push tamoxifen?
To stop breast cancer from spreading
What are the positive effects of tamoxifen?
Besides reducing the chances of breast cancer and its recurrence, tamoxifen also helps in preventing bone loss (osteoporosis) post menopause and decreasing cholesterol levels.
Can I have one drink on tamoxifen?
No
What herbs not to take with tamoxifen?
Turmeric and curcumin
Why does tamoxifen fail?
Increased crosstalk between ER and HER2 coupled with high expression of coactivator SRC3
How long can a patient be on tamoxifen?
10 years
Does tamoxifen make hair thin?
Yes
What are the side effects of the drug Tamodex?
- Hot flushes
- Insomnia
- Decreased libido
- Mood swings
Can tamoxifen cause weight gain?
Yes
How long can you take tamoxifen?
5 years
What can I take instead of tamoxifen?
Raloxifene (Evista)
What organs does tamoxifen affect?
Breast
Is tamoxifen expensive?
Yes
Can tamoxifen damage your heart?
No
Does tamoxifen cause brain fog?
Yes