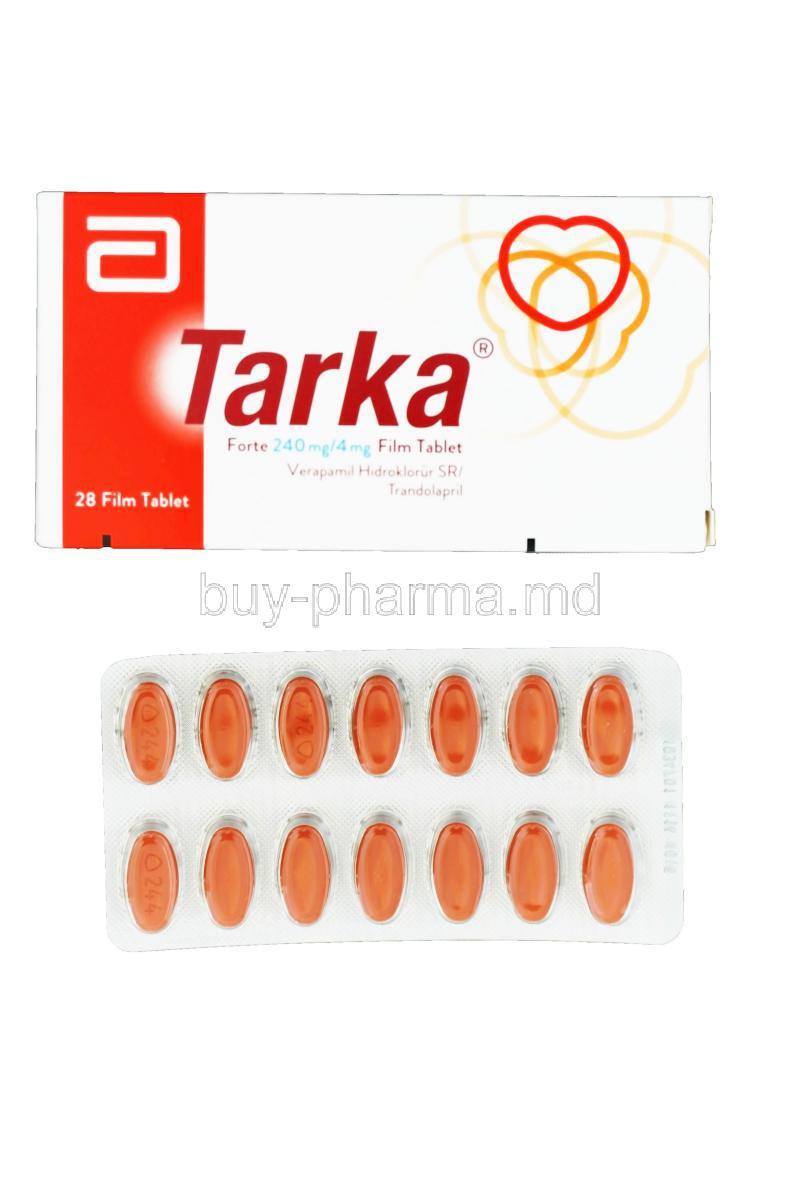
1. Introduction to Tarka Forte
Tarka Forte is a prescription combination medication designed for the management of high blood pressure, falling within the class of antihypertensive agents. By merging two potent cardiovascular agents, it provides a comprehensive solution for individuals with complex hypertension that does not respond well to monotherapy.
This fixed-dose formulation contains verapamil hydrochloride, a calcium channel blocker, and trandolapril, an angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitor. Together, they deliver dual-action cardiovascular control. Tarka Forte is manufactured by reputable pharmaceutical companies and is also available in generic formulations, making it accessible across various markets.
Its relevance in modern cardiology stems from its ability to reduce the workload on the heart, enhance vascular compliance, and lower the risk of long-term complications such as stroke and heart failure.
2. Composition and Formulation Details
- Active ingredients: Verapamil hydrochloride and Trandolapril.
- Available strengths: Typically found in combinations such as verapamil 240 mg with trandolapril 4 mg.
- Dosage forms: Extended-release oral tablets.
The pharmacokinetic profile of this combination ensures that both agents are released in a synchronized manner, optimizing blood pressure control over a 24-hour period. Verapamil offers sustained calcium channel blockade, while trandolapril is hydrolyzed into its active metabolite to maintain ACE inhibition.
Inactive ingredients include lactose, magnesium stearate, and hypromellose, which support the tablet’s extended-release mechanism and ensure stability and tolerability.
3. How Tarka Forte Works: Mechanism of Action
Verapamil acts by inhibiting L-type calcium channels in vascular smooth muscle and myocardium, leading to decreased myocardial contractility, vasodilation, and slower atrioventricular conduction. This results in lowered systolic and diastolic pressures and improved oxygen supply to the myocardium.
Trandolapril inhibits the conversion of angiotensin I to angiotensin II, a potent vasoconstrictor. This action reduces peripheral resistance, lowers aldosterone secretion, and promotes natriuresis. It also blunts sympathetic activity, aiding in long-term blood pressure regulation.
The combined pharmacodynamics result in:
- Enhanced control of vascular tone
- Reduced cardiac workload
- Improved left ventricular function in hypertensive patients
The onset of action is typically observed within 2–4 hours post-ingestion, with peak effects sustained through extended release.
4. Approved Medical Uses of Tarka Forte
Tarka Forte is primarily approved for the treatment of essential hypertension. Its use is especially valuable in patients who have not achieved adequate control with either ACE inhibitors or calcium channel blockers alone.
In addition to blood pressure regulation, this combination has been shown to reduce cardiovascular morbidity in high-risk individuals by:
- Decreasing arterial stiffness
- Lowering pulse pressure
- Reducing left ventricular hypertrophy
It is typically prescribed when combination therapy is preferred to improve adherence and streamline treatment.
5. Off-Label Uses and Emerging Research
Though not FDA-approved for these conditions, Tarka Forte or its components are used off-label for:
- Chronic heart failure: Especially in patients intolerant to beta-blockers, though data remains limited.
- Diabetic nephropathy: Due to trandolapril’s renal protective properties via decreased intraglomerular pressure.
- Migraine prophylaxis: The verapamil component has demonstrated moderate efficacy in reducing migraine frequency in select cases.
Preclinical and clinical trials are also evaluating its impact on endothelial function, oxidative stress reduction, and long-term kidney outcomes in hypertensive individuals.
6. Dosage and Administration Guidelines
For adults, the usual starting dose is one tablet of Tarka Forte once daily. Dosage strength is chosen based on prior exposure to either verapamil or trandolapril and adjusted according to blood pressure response.
- Titration: May be adjusted every 1–2 weeks to achieve target BP.
- Renal impairment: Use with caution. Lower doses recommended for patients with creatinine clearance <30 mL/min.
- Hepatic impairment: Dose adjustment may be necessary due to reduced metabolism of verapamil.
Tablets should be swallowed whole with food to enhance absorption and reduce gastrointestinal discomfort. If a dose is missed, patients should take it as soon as remembered unless it is near the time for the next dose. Abrupt discontinuation should be avoided to prevent rebound hypertension.
7. Common and Serious Side Effects of Tarka Forte
7.1 Common Side Effects
- Dizziness and postural hypotension, especially during the initial days of therapy
- Headache and fatigue due to vasodilation and mild CNS effects
- Constipation, attributed to verapamil’s effect on intestinal smooth muscle
- Dry cough and hypotension, related to trandolapril’s ACE inhibition
7.2 Serious and Rare Adverse Reactions
- Angioedema: A rare but serious allergic reaction requiring immediate discontinuation
- Bradycardia and heart block: Seen in patients with preexisting conduction abnormalities
- Hepatic enzyme elevation: Rare hepatotoxicity has been reported
- Renal dysfunction: Particularly in those with bilateral renal artery stenosis or severe CHF
8. Drug Interactions and Combination Risks
Tarka Forte may interact with several classes of medications, necessitating careful monitoring:
- Beta-blockers: Additive effects may increase the risk of AV block and bradycardia
- NSAIDs: May reduce antihypertensive effect and increase renal impairment risk
- Potassium-sparing diuretics and supplements: Risk of hyperkalemia with trandolapril
- CYP3A4 inhibitors (e.g., ketoconazole, erythromycin): May elevate verapamil levels, leading to toxicity
- Lithium: Increased serum lithium levels and neurotoxicity risk
- Alcohol and hypoglycemics: Enhanced hypotensive effect and blood glucose alterations
9. Contraindications to Tarka Forte Use
- History of angioedema: Particularly from prior use of ACE inhibitors
- Severe hypotension: Especially in volume-depleted patients
- Cardiogenic shock or advanced AV block: Verapamil can exacerbate bradyarrhythmias unless a pacemaker is in place
- Known hypersensitivity: Allergy to verapamil, trandolapril, or other ACE inhibitors
In such cases, alternative antihypertensive regimens should be considered under the guidance of a medical professional.
10. Important Warnings and Safety Information
Tarka Forte contains trandolapril, an ACE inhibitor, which has been associated with significant fetal toxicity when administered during the second and third trimesters of pregnancy. Exposure can lead to neonatal renal dysfunction, skull hypoplasia, and even fetal death. It is imperative to discontinue the drug immediately upon detection of pregnancy.
Patients with bilateral renal artery stenosis or those with a single functioning kidney are at heightened risk of renal impairment. In these populations, Tarka Forte can further compromise glomerular filtration, necessitating cautious use under strict medical supervision.
Ongoing monitoring is critical:
- Blood pressure: Regular checks to detect hypotensive episodes, especially in volume-depleted individuals
- Renal function: Periodic evaluation of serum creatinine and glomerular filtration rate (GFR)
- Electrolytes: Monitoring of serum potassium to prevent life-threatening hyperkalemia
Abrupt discontinuation of Tarka Forte may provoke rebound hypertension. Gradual tapering, accompanied by clinical supervision, is advisable to avoid cardiovascular instability.
11. Precautions for Safe and Effective Use
Prior to initiating Tarka Forte therapy, a thorough cardiovascular assessment should be conducted, including a baseline electrocardiogram (ECG) to identify pre-existing conduction abnormalities that may be exacerbated by verapamil.
Periodic laboratory evaluations are essential for safe administration:
- Serum potassium: To detect and address hyperkalemia, particularly in patients on concomitant potassium-sparing agents
- Serum creatinine: To assess renal clearance and avoid drug accumulation
Dose titration should be performed gradually to minimize adverse effects such as orthostatic hypotension or bradycardia. Patients should be counseled thoroughly regarding the importance of adherence, potential side effects, and when to seek medical attention.
Education about daily administration, lifestyle modifications, and avoidance of self-discontinuation enhances long-term efficacy and safety.
12. Careful Administration in Special Populations
12.1 Use in Elderly Patients
Elderly individuals often exhibit increased pharmacodynamic sensitivity and decreased physiological reserve, which may amplify the effects of Tarka Forte. Hypotension and bradycardia are more pronounced in this group, contributing to a higher incidence of falls and syncopal episodes.
Lower initial dosages and slower upward titration are strongly recommended. Renal function should be monitored closely, as age-related decline may not be evident through serum creatinine alone due to reduced muscle mass.
12.2 Use in Pregnant and Breastfeeding Women
Trandolapril poses significant teratogenic risks, particularly during the second and third trimesters. ACE inhibitor exposure during fetal development has been linked to oligohydramnios, neonatal renal failure, and skeletal deformities. As such, Tarka Forte is contraindicated during pregnancy unless no safer alternatives exist.
Verapamil is known to be excreted in human breast milk. Though clinical significance is uncertain, caution is advised, especially in neonates with immature renal and hepatic systems. Close monitoring of infants for bradycardia, hypotension, or feeding issues is prudent if maternal therapy is continued during lactation.
12.3 Use in Pediatric Patients
The safety and efficacy of Tarka Forte have not been established in the pediatric population. Clinical trials are limited, and regulatory approval does not currently support its use in individuals under 18 years of age.
Due to the lack of robust data and potential for serious adverse reactions, alternative therapies with established pediatric safety profiles are recommended when treating hypertension in children.
13. Overdose Management and Emergency Measures
An overdose of Tarka Forte may manifest with severe hypotension, profound bradycardia, dizziness, syncope, and electrolyte imbalances such as hyperkalemia. Immediate identification and intervention are vital to prevent cardiovascular collapse.
Recommended emergency measures include:
- Supportive care: Supine positioning, IV fluids, and vasopressors to maintain perfusion
- Activated charcoal: Effective if administered within 1–2 hours of ingestion
- Intravenous calcium: Used to counteract the myocardial depressant effects of verapamil
Patients must be transferred to an emergency facility without delay, as close cardiac monitoring and resuscitative measures may be necessary.
14. Storage Instructions for Tarka Forte
To preserve the efficacy and integrity of Tarka Forte, it should be stored at a controlled room temperature between 15°C and 25°C (59°F to 77°F). Deviations outside this range, especially exposure to excessive heat or humidity, may compromise the stability of the formulation.
- Keep the medication away from direct light and moisture
- Store in the original, tightly closed container to prevent contamination
- Always use child-resistant packaging and keep out of reach of children
Expired or unused medication should be disposed of safely, following local pharmaceutical waste guidelines. Do not flush tablets down the toilet unless instructed by a pharmacist.
15. Handling and Dispensing Precautions
Pharmacies should ensure that Tarka Forte tablets are dispensed in intact, tamper-evident blister packs or sealed containers to maintain product safety. Any broken, chipped, or discolored tablets should not be used.
Pharmacists must provide clear instructions on:
- Proper storage conditions at home
- The importance of taking the medication at the same time each day
- The risks of missing doses or abrupt cessation
Unless explicitly approved by the manufacturer, tablets should not be crushed or split, as this may disrupt the extended-release mechanism.
Tarka Forte is classified as a prescription-only medication (Rx), and its dispensing should always follow proper regulatory protocols and documentation.