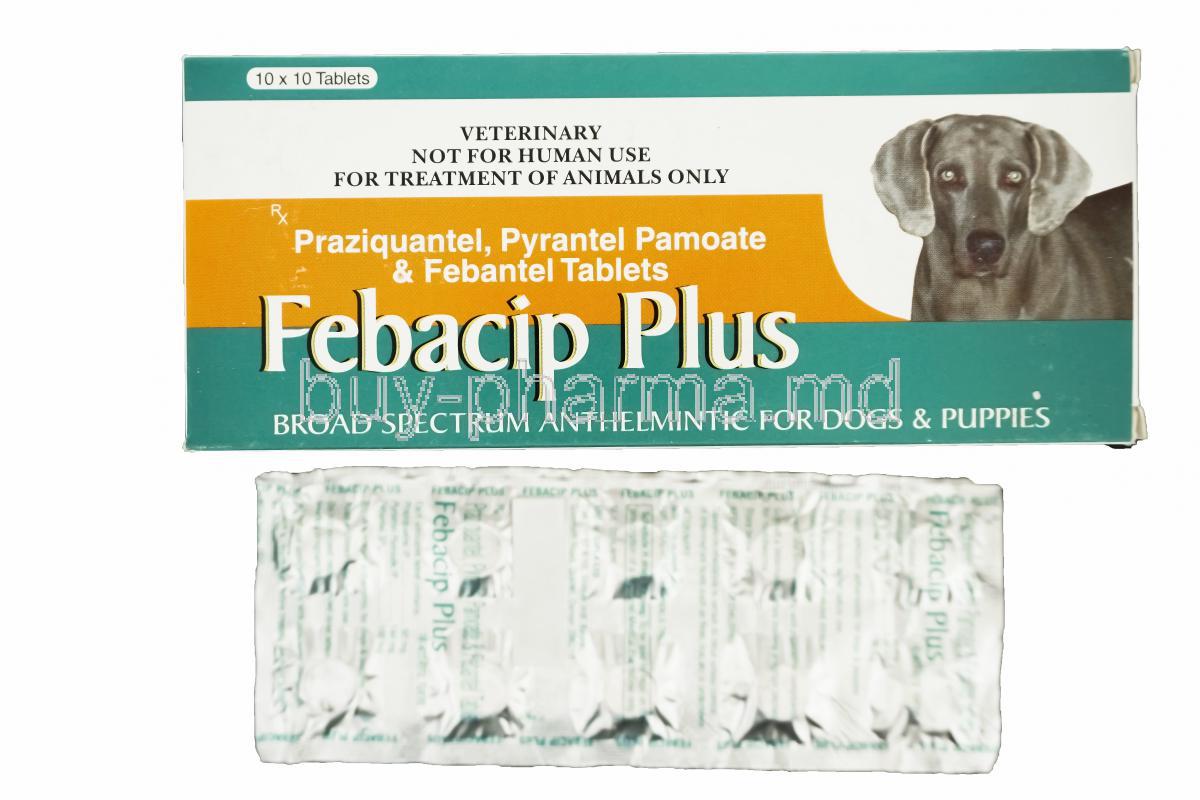
Febacip Plus
Introduction to Febacip Plus
What is Febacip Plus? An Overview
Febacip Plus is an antibiotic cream often recommended for healing bacterial skin infections, such as impetigo and folliculitis, or for treating infected cuts and wounds effectively. This special cream contains a combination of Clindamycin phosphate and Nicotinamide, which work together to address the reasons for infection and redness on the skin surface.
- Clindamycin phosphate is an antibiotic from the class of medications known as Lincosamides that works by inhibiting the production of proteins in bacteria, thereby stopping the growth of microorganisms effectively.
- Nicotinamide is a type of vitamin B that has anti-inflammatory and sebum-regulating properties, which help reduce redness and swelling while also controlling excessive sebum production on the skin.
The combination of these two elements makes Febacip Plus an excellent option for treating acne vulgaris, while also addressing skin infections that arise from scratching or weakened barriers.
The Evolution and Development of Febacip Plus in Medical Practice
The combination of Clindamycin and Nicotinamide, in an action treatment, represents a notable progression in the field of dermatological medication therapy. Initially, these substances were used separately, with Clindamycin used to manage overgrowth and Nicotinamide suggested as an adjunct due to its anti-inflammatory properties. The creation of Febacip Plus, a solution that combines ingredients, was inspired by medical field studies that demonstrated the effectiveness of using multiple treatments together compared to using just one for stubborn acne and infected skin issues.
Dermatologists and regular doctors embraced this product due to its effectiveness and benefits, such as;
- A two-pronged approach targeting both the activity of microbes and the body's inflammatory response. The convenience of an application has improved adherence.
- The safety record is positive. It has a targeted impact, with absorption into the bloodstream.
Over the years, Febacip Plus has become a preferred treatment option in areas where antibiotic-resistant strains of Cutibacterium acnes and Staphylococcus aureus are prevalent. Its effectiveness goes beyond treating acne; it is also relied upon as a go-to solution for types of surface skin infections that worsen the visible symptoms due to inflammation. Modern advancements in healthcare are shifting towards treatments that specifically target issues without requiring intervention, resulting in improved overall skin health outcomes. The ongoing enhancement of these combined products ensures that Febacip Plus will continue to be a go-to option for care.
Comprehensive Composition of Febacip Plus
Active Ingredients and Their Functions
Febacip Plus Cream includes two ingredients, for pharmaceutical purposes, namely Clindamycin phosphate and Nicotinamide.
- Clindamycin Phosphate (1%) is an antibiotic that works by attaching to the 50S ribosomal subunit of bacteria to stop protein production and reduce bacterial growth effectively targeting Gram positive cocci and specific anaerobic bacteria that cause skin infections and inflammation linked to acne.
- Nicotinamide (4%) is a form of vitamin B3 recognized for its anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties, as well as its ability to regulate sebum production effectively in the context of skin care. It helps decrease the release of cytokines and promotes balance in sebum secretion levels making it a valuable asset, for addressing acne vulgaris and skin conditions characterized by redness and swelling.
The combination of these elements works to combat microbes and improve skin health simultaneously, leading to the healing of lesions and reducing the likelihood of them recurring.
Inactive Components and Their Roles in Drug Efficacy
The effectiveness of medication is influenced by its components; however, supplementary materials and foundational elements play roles in preserving the stability, absorption rate, and tolerance of the formulation. These commonly consist of;
- Isopropyl Myristate is known to improve the skin's absorption of ingredients by changing its permeability.
- Propylene Glycol serves as both a humectant and a solvent, helping the cream spread evenly on the skin.
- Carbomer is used as a thickening agent to stabilize the emulsion and maintain a texture.
- Disodium EDTA functions, as a chelating agent binding to divalent metal ions that could potentially disrupt the formulation stability.
- Purified water and emulsifying wax are used as the foundation for the application, preventing any separation of components.
These inactive components help maintain the effectiveness of the ingredients in medications for an extended period without irritation, ensuring they are suitable for the skin.
Praziquantel vs Fenbendazole
While Febacip Plus does not contain the elements specifically discussed in comparisons among agents, it can offer insights for both dermatological and veterinary fields on a broader scale.
- Praziquantel is a type of medication that effectively treats a range of infections, specifically targeting flatworms like trematodes and cestodes by causing muscle spasms and paralysis through changes in calcium ion levels within the worms' bodies.
- Fenbenzadole works differently, as it belongs to a class of medications that target nematodes and specific protozoa by interfering with microtubule formation through binding to the β-tubulin protein and disrupting vital functions in parasitic creatures.
Both of them work well; however, they have different ranges of effectiveness and mechanisms of action, which makes them better suited for particular infections and types of hosts.
Febantel vs Fenbendazole
Febantel is a type of compound known as a benzimidazole, which transforms into fenbenzadole and oxfendazole through metabolic processes in the liver, resulting in its effectiveness after this conversion occurs. Fenbenzadole is already effective on its own. Directly stops parasites by blocking tubulin formation. Both are useful for treating parasites; however, febantel's prodrug characteristics enable it to be combined with pyrantel or praziquantel to produce synergistic effects.
Pyrantel vs Praziquantel
Pyrantel is a type of medication that works by causing muscle stiffness in parasites, nematodes, through its action on specific receptors in their nervous system called nicotinic acetylcholine receptors. Praziquantel works on tapeworms and flukes by making their cell walls more porous, allowing calcium ions to enter. This causes muscle spasms. Eventually, it makes them separate from the host tissues. These agents have variations in target organisms and methods of operation that complement each other well when managing infections in animals using veterinary polytherapy protocols.
Therapeutic Uses of Febacip Plus
Primary Indications: Managing Pain and Fever
Contrary to popular belief, Febacip Plus is not primarily used for treating pain or fever. Instead, it is a skincare product designed to combat skin infections and reduce inflammation. However, it may indirectly alleviate some discomfort, such as pain or warmth associated with inflamed skin areas, by targeting the root cause of the infection and inflammatory factors. Febacip Plus helps reduce skin inflammation in the regions that can cause a feeling of warmth or discomfort, as well as symptoms of a general fever. The product helps alleviate pain and redness caused by skin infections or acne by lowering bacterial levels on your skin. Febacip Plus functions on the skin's surface, targeting pain or fever directly; therefore, it is not recommended as the primary treatment for general body pain or fever-related issues.
Secondary Therapeutic Uses in Clinical Settings
Febacip Plus has gained importance in settings, beyond its use for treating acne concerns—particularly in dermatology and minor surgical settings due to its wide ranging antimicrobial and anti inflammatory characteristics that make it suitable, for various skin related issues.
- After surgery skin infections are treated with medicine to stop infections, in skin surgery procedures.
- Folrulitis and furunculosis focus, on inflamed hair follicles and abscesses around the hair follicles due, to infection.
- In cases of eczema or psoriasis, secondary bacterial infections can be helpful when scratching causes the skin barrier to be broken and allows microbes to enter.
- Pityrosporum folliculitis (a type of acne caused by yeast); While it is mainly fungal, in nature additional bacterial issues can be addressed with Febacip Plus medication.
- Periorificial dermatitis should be treated with care under the guidance of a dermatologist, especially when bacterial factors worsen the condition.
In places with limited resources. Febacip Plus has been used in real world situations for skin infections when specific treatments are not easily accessible Its ability to treat both inflammation and bacterial infections at the same time makes it a valuable option for dermatological care, outside of hospitals and clinics Febacip Plus is known for its strategy, in tackling skin conditions that involve both infection and inflammation making it a practical option, for treatment.
Off-Label Applications of Febacip Plus
Exploring Unapproved Uses in Different Medical Fields
Febacip Plus is mainly used to treat acne vulgaris and bacterial skin infections in areas. It has been utilized in various clinical situations, as well as for unapproved purposes, due to its ability to fight microbes and reduce inflammation simultaneously. In the field of dermatology and other areas, variations of use that are not officially approved have been observed.
- Perianal dermatitis and intertrigo are treated with this application to reduce inflammation and bacterial growth in areas of moisture and friction.
- Minor skin abrasions caused by trauma are often treated to prevent infections and speed up the healing process of cuts and scrapes.
- Rosacea, although it is not formally recommended for treatment, may benefit from its components in cases, and has been studied in rosacea subtypes with bacterial presence.
- Applying the solution to insect bites can help reduce issues and ease inflammation on the skin. In the stages of decubitus ulcers treatment involves occasionally using methods to lessen the microbial load and redness in pressure induced skin lesions; however it is not recommended for open or deep wounds.
In these cases, the programs rely heavily upon the expertise of healthcare professionals. They are typically used when alternative therapies have proven ineffective or are not readily available.
Evaluating the Efficacy and Safety of Off-Label Uses
The effectiveness of Febacip Plus in standard use is primarily based on personal accounts and small observational studies, rather than solid evidence-backed research findings. In environments where it is not permitted for clinical use, noted enhancements include decreased redness in skin appearance and fewer skin lesions, leading to reduced discomfort for the patient. This is credited to the potent antibacterial properties of Clindamycin and the anti-inflammatory abilities of Nicotinamide.
- Febacip Plus is generally safe for people when applied to the skin; however, its long-term safety on mucous membrane areas or large skin surfaces has not been thoroughly confirmed yet.
- Skin rash can occur from contact. Prolonged use may lead to the emergence of resistance. In populations such as infants or older people with compromised skin, there is a risk of systemic absorption to consider.
Due, to a lack of studies supporting these alternative uses for Febacip Plus medication label changes should be approached with care while keeping a close eye and monitoring of patients at a priority level is key to ensuring safety and effectiveness in treatment decisions It is advised to obtain informed consent conduct a thorough risk benefit analysis and restrict usage duration when considering prescribing Febacip Plus for purposes, outside its officially approved medical conditions In some situations where there is potential for progress to be made in the possibilities that are being explored emphasize the need, for studies and established procedures to guarantee safety and maintain therapeutic effectiveness consistently.
Mechanism of Action: Understanding How Febacip Plus Works
The Pharmacological Basis of Febacip Plus
Febacip Plus works by combining two components. Clindamycin phosphate and Nicotinamide. In a way that enhances their effects thanks to their unique pharmacological characteristics. Clindamycin phosphate is a modified version of lincomycin that falls into the lincosamide category of antibiotics. It works by stopping replication and reducing the number of bacteria on the skin through its action on the 50S subunit of the bacterial ribosome during protein synthesis. Nicotinamide is another term, for niacinamide. Is a type of vitamin B3 that dissolves in water of oil like other anti infectives do primarily through immune regulation and reducing inflammation mechanisms as its main effects, on the body It works by decreasing the presence of pro inflammatory cytokines and decreasing oil production in the sebaceous glands while also aiding in repairing the skin barriers integrity. The reason for using these medications is that they can address both the infection and inflammation aspects of skin lesions that have causes.
How Febacip Plus Affects the Body at the Molecular Level
At a basic level, Febacip Plus triggers a series of reactions that inhibit the growth of bacteria and reduce swelling simultaneously.
- Clindamycin phosphate penetrates the skin layer. Accumulates in hair follicles and oil producing glands to inhibit bacterial protein production there specifically targeting Cutibacterium acnes and Staphylococcus bacteria which are frequently associated with acne and folliculitis infections.
- It stops the process of RNA peptide elongation.
- Positive bacteria are inhibited in their exotoxin production by the treatment. Helps stop the buildup of biofilm in lasting wounds.
- Nicotinamide functions at both the cellular membrane levels to achieve its effects.
- By blocking the activity of polymerase (PARP), oxidative stress is decreased. Regulating toll receptors and reducing the activation of nuclear factor kappa B (NF-κB) can help reduce inflammation caused by cytokines.
- Encourage the production of ceramides to help moisturize and heal the skin's layer.
The unique dual action of Febacip Plus not only eradicates surface-level infections but also addresses the root cause of skin inflammation and barrier issues, speeding up healing and reducing scarring. This combination of medications results in a targeted treatment that affects specific areas without impacting the entire body. Perfect for addressing inflammatory skin conditions, such as acne and minor skin infections, in a precise manner.