1. Introduction to Previcox for Dogs
Previcox is a prescription-only non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) specifically formulated for canine use. It plays a pivotal role in modern veterinary medicine by offering targeted relief from pain and inflammation, particularly in cases involving musculoskeletal conditions.
Initially approved by the FDA’s Center for Veterinary Medicine (CVM), Previcox gained popularity due to its selective inhibition of the cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) enzyme. Unlike older NSAIDs that non-selectively target both COX-1 and COX-2, Previcox minimizes damage to the gastrointestinal lining while providing effective analgesia.
Veterinarians commonly prescribe Previcox in a range of clinical scenarios, including osteoarthritis management, post-surgical recovery, and chronic orthopedic conditions that impair mobility and quality of life.
2. Understanding Firocoxib: The Active Ingredient
Firocoxib is a synthetic compound classified as a selective COX-2 inhibitor. Structurally, it belongs to the coxib family, a subclass of NSAIDs developed to reduce inflammation while sparing the gastrointestinal tract and kidneys from adverse effects.
By selectively inhibiting COX-2, Firocoxib blocks the production of prostaglandins that mediate inflammation and pain, without significantly affecting the protective COX-1 pathways.
- Highly selective for COX-2 over COX-1
- Faster onset and longer half-life than many traditional NSAIDs
- Reduced risk of gastrointestinal ulceration and renal compromise
Compared to older agents like carprofen and meloxicam, Firocoxib offers a more refined therapeutic profile with a lower incidence of adverse events in many canine patients.
3. Approved Veterinary Uses of Previcox in Dogs
Previcox is officially approved for the following veterinary indications:
- Osteoarthritis: Long-term pain and inflammation management in dogs with joint degeneration and stiffness.
- Post-operative pain: Short-term analgesia following orthopedic surgeries or soft tissue operations, aiding smoother recovery.
- Degenerative joint diseases: Relief from chronic mobility impairment and lameness due to age-related conditions.
The drug enhances comfort and encourages physical activity in affected animals, ultimately supporting musculoskeletal health and vitality.
4. Off-Label and Investigational Uses of Previcox in Dogs
While not officially endorsed, Previcox has shown promise in a variety of off-label and investigational settings:
- Dental inflammation: Alleviation of pain following extractions or periodontal procedures.
- Cancer-associated pain: Adjunctive management in palliative oncology care to improve comfort.
- Geriatric pain management: Use in elderly dogs with chronic discomfort not strictly limited to arthritis.
Some practitioners also report positive experiences using Previcox in horses for orthopedic pain. However, off-label prescribing requires thorough clinical judgment and awareness of species-specific pharmacokinetics and regulatory boundaries.
5. How Previcox Works: Mechanism of Action of Firocoxib
Firocoxib exerts its therapeutic effects by inhibiting the COX-2 enzyme, which is upregulated in inflammation. This inhibition reduces the synthesis of prostaglandins responsible for pain, swelling, and fever.
- Anti-inflammatory: Blocks pathways that cause tissue swelling and heat.
- Analgesic: Reduces peripheral and central pain sensitization.
- Antipyretic: Lowers elevated body temperature in febrile states.
Its COX-2 selectivity provides a protective margin against the gastrointestinal and renal side effects typically seen with non-selective NSAIDs.
6. Dosage and Administration Guidelines for Dogs
Previcox dosage is weight-specific and should always follow veterinary guidance:
- Recommended dose: 5 mg/kg body weight once daily.
- Available formats: 57 mg or 227 mg chewable tablets.
- With or without food: Previcox may be administered on an empty stomach or with meals to ease GI tolerance.
In chronic cases, treatment duration may be long-term. Dogs should be reassessed periodically to evaluate efficacy and monitor for side effects. If a dose is missed, it should be given as soon as remembered unless it's close to the next scheduled dose.
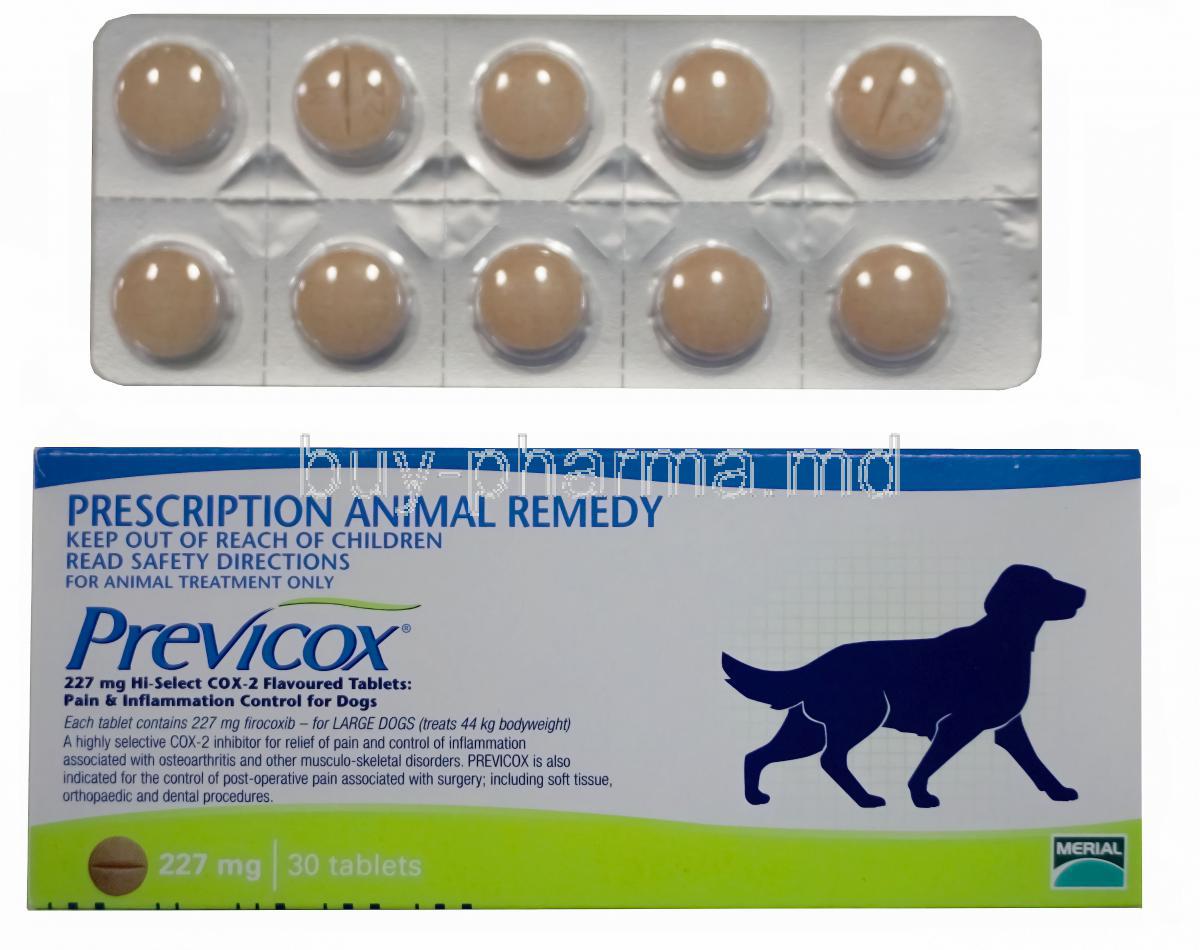
7. Composition and Available Strengths of Previcox
Previcox is formulated as a chewable, palatable tablet, making administration easier in canines.
- Active ingredient: Firocoxib
- Excipients: Lactose monohydrate, croscarmellose sodium, artificial beef flavoring, microcrystalline cellulose
- Strengths: 57 mg for small to medium dogs; 227 mg for large breed dogs
The scored tablets allow for more flexible dosing in intermediate weight categories.
8. Proper Storage and Handling Instructions
To maintain drug integrity, Previcox should be stored under optimal environmental conditions:
- Store at 15°C to 30°C (59°F to 86°F)
- Keep in original packaging to protect from moisture and light
- Do not refrigerate or freeze
Pet owners should avoid touching tablets with wet hands and keep all medications out of the reach of children and animals.
9. Drug and Food Interactions with Previcox
Previcox may interact with other pharmaceuticals and should be used cautiously in polypharmacy scenarios:
- Contraindicated: Concurrent use with other NSAIDs or corticosteroids due to increased risk of gastrointestinal ulcers and renal injury
- Use with caution: Diuretics, ACE inhibitors, nephrotoxic drugs
- Generally safe: Joint health supplements (glucosamine, chondroitin), antibiotics, most commercial dog foods
Veterinary consultation is essential to ensure safe combination therapy.
10. Common Side Effects of Previcox in Dogs
Although Previcox is well-tolerated by most dogs, some may exhibit mild to moderate side effects:
- Gastrointestinal: Vomiting, soft stools, diarrhea, appetite loss
- Systemic: Lethargy, behavioral changes, restlessness
- Clinical monitoring: Elevations in kidney or liver enzymes may be detected on routine bloodwork
Most side effects are transient and resolve upon dose adjustment or discontinuation. Persistent or severe symptoms warrant immediate veterinary evaluation.
11. Serious Adverse Effects and Long-Term Safety Risks
While Previcox is generally safe when administered under veterinary supervision, serious adverse reactions can occur in some dogs, particularly during prolonged use or at higher-than-recommended dosages.
- Gastrointestinal ulceration or bleeding: Manifesting as dark tarry stools, vomiting with blood (hematemesis), abdominal pain, and reluctance to eat. This condition requires immediate discontinuation and supportive care.
- Renal dysfunction: Signs include increased thirst and urination, lethargy, and elevated blood urea nitrogen (BUN) and creatinine levels.
- Hepatic enzyme elevation: Elevated ALT and AST levels may be seen in periodic blood tests. Symptoms may include jaundice, anorexia, and vomiting.
- Hypersensitivity reactions: These may present as facial swelling, urticaria (hives), respiratory distress, or anaphylaxis. These events are rare but potentially life-threatening.
If any of these adverse signs emerge, Previcox should be immediately discontinued. Supportive therapy may include fluid resuscitation, gastroprotectants, and liver or kidney function support depending on the affected organ system.
12. Contraindications for Previcox Use in Dogs
Previcox is contraindicated in several canine populations due to the elevated risk of severe adverse reactions:
- Hypersensitivity: Dogs known to be allergic to firocoxib or other NSAIDs should never be prescribed Previcox.
- Pre-existing gastrointestinal ulcers: COX-2 inhibitors may exacerbate ulcerative lesions, leading to bleeding or perforation.
- Renal or hepatic dysfunction: Dogs with impaired kidney or liver function are at higher risk for toxic accumulation of the drug.
- Concurrent use with other NSAIDs or corticosteroids: This increases the risk of gastrointestinal hemorrhage and renal toxicity through additive or synergistic effects.
13. Warnings and Black Box Alerts for Veterinarians and Owners
Veterinarians and pet owners must observe several critical warnings before initiating Previcox therapy:
- Pre-treatment testing: A baseline complete blood count (CBC), liver panel, and renal profile are recommended before initiating therapy to identify any underlying dysfunction.
- Masking of clinical signs: NSAIDs, including Previcox, can obscure symptoms of infection or underlying systemic illness, delaying diagnosis.
- Long-term use monitoring: Regular follow-up exams and periodic bloodwork are crucial to detect potential organ toxicity or adverse effects early in the treatment course.
14. Guidelines for Careful Administration in At-Risk Dogs
In dogs with increased vulnerability, careful consideration must guide the use of Previcox:
- Dehydration or hypotension: These conditions increase the risk of NSAID-induced renal ischemia. Ensuring adequate hydration is essential before and during therapy.
- Cardiac disease: Dogs with heart conditions may require modified dosing or alternative therapies due to altered hemodynamics and drug clearance.
- Sensitive breeds: Breeds predisposed to drug sensitivities (e.g., Collies, Greyhounds) may require lower dosages and closer monitoring.
15. Important Precautions Before and During Treatment
To minimize risks, several precautionary measures should be followed:
- Veterinary evaluation: A full physical examination, health history, and diagnostic screening are essential prior to initiating treatment.
- Owner education: Guardians should be thoroughly briefed on potential side effects and the importance of adherence to dosing schedules and follow-ups.
- Avoiding human NSAIDs: Owners must be cautioned never to substitute Previcox with over-the-counter human pain relievers such as ibuprofen or aspirin, which can be toxic to dogs.
16. Administration of Previcox to Senior Dogs
Elderly dogs often benefit from Previcox for managing age-related conditions like arthritis, but special considerations apply:
- Adjusted dosage: Age-related decline in liver and kidney function may necessitate reduced doses or less frequent administration.
- Increased monitoring: Senior dogs should undergo more frequent laboratory testing and clinical evaluations to monitor for toxicity.
- Supportive use: Previcox may significantly improve mobility and comfort in older dogs, enhancing quality of life when used judiciously.
17. Use of Previcox in Pregnant, Breeding, and Lactating Dogs
Previcox has not been extensively studied in pregnant, breeding, or nursing dogs, and its safety profile in these populations remains uncertain.
- Pregnancy: Use during gestation may pose risks to fetal development due to potential effects on prostaglandin pathways.
- Lactation: It is unclear whether firocoxib is excreted in canine milk; hence, use is generally discouraged in nursing mothers.
- Veterinary discretion: Alternative pain management strategies are typically recommended unless no safer options exist.
18. Safety and Guidelines for Use in Puppies and Young Dogs
The safety of Previcox in young dogs is also limited by age and body weight thresholds:
- Minimum age and weight: Previcox is not recommended for puppies under 7 months of age or below 5 kg (11 lbs) unless explicitly directed by a veterinarian.
- Organ immaturity: Developing renal and hepatic systems in young dogs may not efficiently metabolize and eliminate the drug.
- Alternative treatments: For orthopedic conditions in growing dogs, physical therapy and non-NSAID pain control may be safer options.
19. Overdose Symptoms and Emergency Management
In cases of accidental overdose, prompt recognition and intervention are crucial:
- Symptoms: Lethargy, vomiting, bloody stool, loss of coordination, muscle tremors, and seizures.
- Initial steps: Inducing emesis if ingestion was recent, followed by administration of activated charcoal to limit absorption.
- Veterinary intervention: Hospitalization with IV fluids, gastrointestinal protectants, anti-seizure medications, and organ support as needed.
Overdose outcomes depend on dose ingested, time to treatment, and the general health status of the animal.
20. Safe Handling and Disposal of Previcox Tablets
Proper handling and disposal of Previcox help protect both human and animal health:
- Storage safety: Store in a secure, dry place away from direct sunlight and out of reach of children and pets.
- Tablet division: Only split tablets if scored and instructed by a veterinarian, as uneven dosing can lead to toxicity.
- Environmental disposal: Do not flush unused medication. Instead, return it to a veterinary clinic or follow local pharmaceutical disposal guidelines.
Responsible use and storage ensure Previcox remains a safe and effective tool in canine pain management.