Citicoline/ Piracetam
- 1. Introduction to Citicoline and Piracetam
- 2. Composition and Pharmaceutical Formulation
- 3. Mechanism of Action: How Citicoline and Piracetam Work in the Brain
- 4. Approved and Off-label Uses of Citicoline / Piracetam
- 5. Dosage and Administration Guidelines
- 6. Potential Side Effects and Adverse Reactions
- 7. Drug Interactions and Compatibility Considerations
- 8. Warnings, Contraindications, and Black Box Alerts
- 9. Special Precautions and Careful Administration
- 10. Use in Special Populations
- 11. Overdose Risks and Emergency Management
- 12. Clinical Research and Evidence Base
1. Introduction to Citicoline and Piracetam
Overview of Citicoline and Piracetam Combination Therapy
Citicoline and Piracetam, when combined, represent a powerful neuroenhancement duo widely recognized for their synergistic effects in promoting cognitive function. This combination therapy is especially utilized in managing conditions involving neuronal degeneration, trauma, or cerebrovascular deficits.
Historical Background and Development
Citicoline (CDP-Choline) was first developed in Japan and gained prominence for its neuroregenerative properties, particularly post-stroke. Piracetam, synthesized in the 1960s by Belgian pharmacologist Corneliu Giurgea, is hailed as the prototype nootropic. The combination has gained clinical interest for dual-action support in brain metabolism and neurotransmission.
Approval Status in Different Countries
While Citicoline and Piracetam are approved in several European, Asian, and Latin American countries, their regulatory status varies. In the U.S., Citicoline is often sold as a dietary supplement, whereas Piracetam remains unapproved by the FDA but is available in other jurisdictions under prescription.
Therapeutic Categories
- Cognitive enhancers
- Stroke and trauma recovery support
2. Composition and Pharmaceutical Formulation
Active Ingredients and Their Respective Concentrations
The combination generally contains:
- Citicoline sodium (250-500 mg per dose)
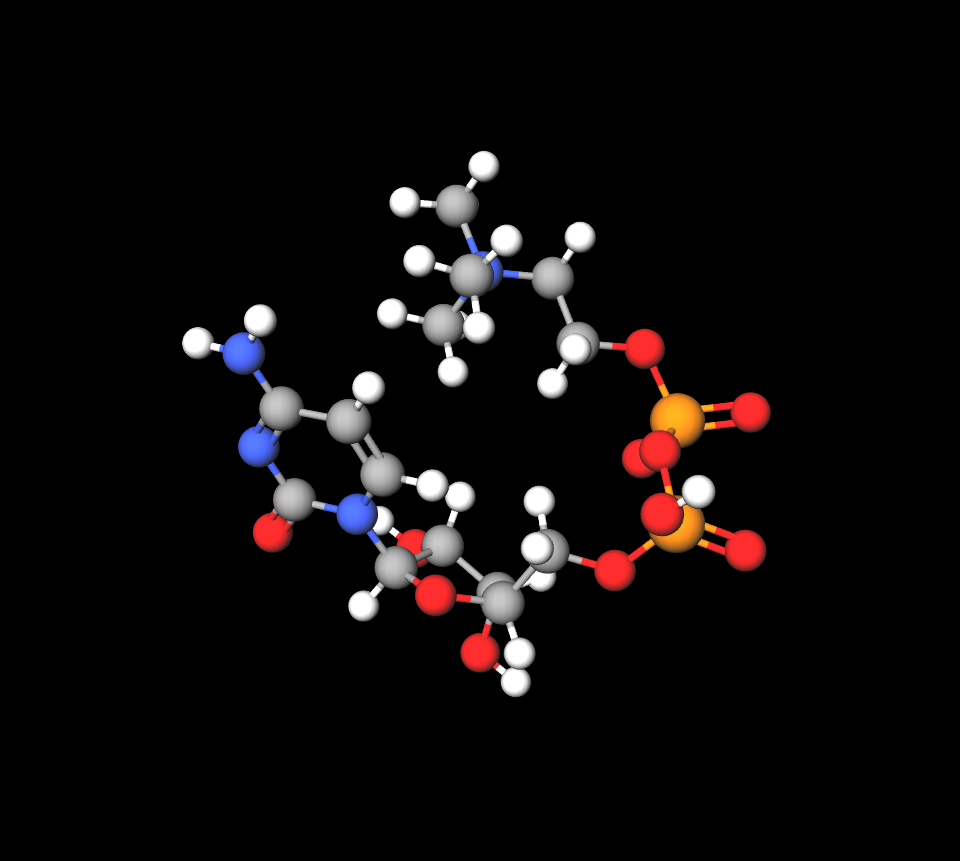
- Piracetam (400-800 mg per dose)
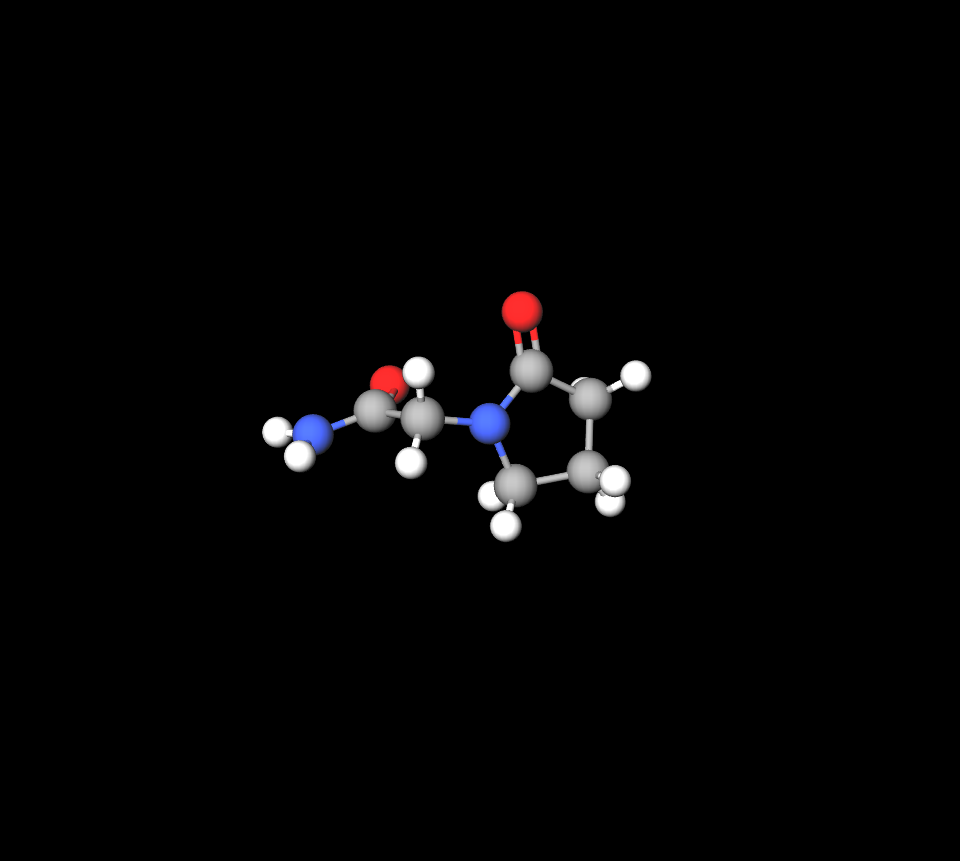
Available Dosage Forms
- Oral tablets and capsules
- Injectable ampoules for intravenous or intramuscular use
- Oral liquid solutions or syrups
Citicoline and adderall
Citicoline and Adderall are both thought to affect cognitive function, but they do so through different mechanisms and have different potential effects. Citicoline is a nootropic that may enhance focus and memory by supporting brain cell health and neurotransmitter function. Adderall, a stimulant medication, primarily affects dopamine and norepinephrine levels in the brain, leading to increased alertness and focus, but it can also have side effects. While some studies suggest citicoline may be helpful in certain situations, such as in some neurodegenerative disorders or for cognitive enhancement, it is not a substitute for Adderall for ADHD.
Citicoline vs choline
One notable contrast between citicoline and choline lies in the fact that choline is a substance present in the body while citicoline is frequently included in dietary supplements.
Citicoline vs alpha gpc
Both Citicoline and Alpha GPC are types of brain supplements known as nootropics that have the potential to improve abilities; however, they work in ways and offer distinct benefits to individuals seeking cognitive enhancement. While Citicoline is often recommended for promoting long term brain health and memory function while also boosting dopamine levels for motivation purposes, over a period of time; Alpha GPC is generally preferred for its cognitive enhancing effects specifically related to focus and physical performance, in the short term.
Noopept vs piracetam
Noopept is a cognitive enhancer than piracetam and requires much smaller doses to produce similar effects compared to piracetam; Noopept is actually structurally related to it but believed to possess extra neuroprotective qualities as well. Both are intended to enhance brain function with Noopept potentially offering a wider range of benefits at lower doses
Piracetam vs phenylpiracetam
Phenylpiracetam differs from piracetam as it contains a phenyl group that enhances its potency and provides effects similar to those not seen in piracetam alone. Moreover, phenylpiracetam offers a range of benefits such as improved stamina and resilience to cold conditions, alongside cognitive enhancements.
Piracetam vs aniracetam
Piracetam and Aniracetam are both nootropics in the racetam class, sharing some structural similarities. Aniracetam is generally considered more potent than piracetam due to its lipid solubility and has a broader impact, affecting AMPA receptors and potentially modulating anxiety and mood in addition to cognition. While piracetam primarily focuses on improving brain function, especially in individuals with cognitive impairment or certain neurological conditions, aniracetam may offer more pronounced effects on memory, concentration, and emotional well-being.
Piracetam vs oxiracetam
Piracetam is the original nootropic and is thought to primarily improve cell membrane fluidity and neurotransmission, potentially aiding general cognitive function, particularly in those with cognitive decline. Oxiracetam is a derivative of piracetam, often considered more potent, with additional benefits in enhancing the release of neurotransmitters like acetylcholine and glutamate, leading to improvements in memory, learning, and focus. While both belong to the racetam family and aim to boost cognition, oxiracetam is generally seen as having a mild stimulating effect and a more direct impact on specific cognitive processes.
Piracetam vs modafinil
Piracetam and Modafinil are both considered nootropics, but they function differently. Piracetam, a racetam, is believed to enhance brain function by improving membrane fluidity and neurotransmission, and is often used to treat cognitive impairment and enhance memory. Modafinil, a wakefulness-promoting agent, primarily increases dopamine and orexin levels, leading to increased alertness and improved focus, and is commonly used to treat sleep disorders such as narcolepsy. While both may enhance cognition, piracetam's effects are generally subtle and aimed at overall brain health, whereas modafinil provides a more direct stimulant-like effect on wakefulness and attention.
3. Mechanism of Action: How Citicoline and Piracetam Work in the Brain
Citicoline: Precursor of Phosphatidylcholine and Neuronal Membrane Repair
Piracetam: Modulation of AMPA and NMDA Receptors, Membrane Fluidity
Piracetam is believed to modulate glutamatergic receptors, including AMPA and NMDA subtypes, thereby improving synaptic plasticity. It also enhances membrane fluidity, promoting efficient neurotransmitter release and signal transduction.
Synergistic Cognitive Enhancement Effects of Combined Therapy
Together, Citicoline and Piracetam improve cholinergic transmission, increase cerebral blood flow, and accelerate repair of damaged neural circuits, especially following injury or age-related decline.
Effects on Neurotransmitters, Cerebral Metabolism, and Neuroplasticity
- Boosts acetylcholine and dopamine levels
- Enhances glucose and oxygen utilization in neurons
- Supports neuroplasticity and synaptic connectivity
4. Approved and Off-label Uses of Citicoline / Piracetam
4.1 Medically Approved Uses
- Stroke Rehabilitation: Facilitates recovery of motor and cognitive function after ischemic events.
- Cognitive Impairment: Used in Alzheimer's disease and other dementias to slow decline.
- Traumatic Brain Injury (TBI): Enhances neuroregeneration and memory recall post-injury.
- Vascular Dementia: Improves attention, mental clarity, and overall cognitive performance.
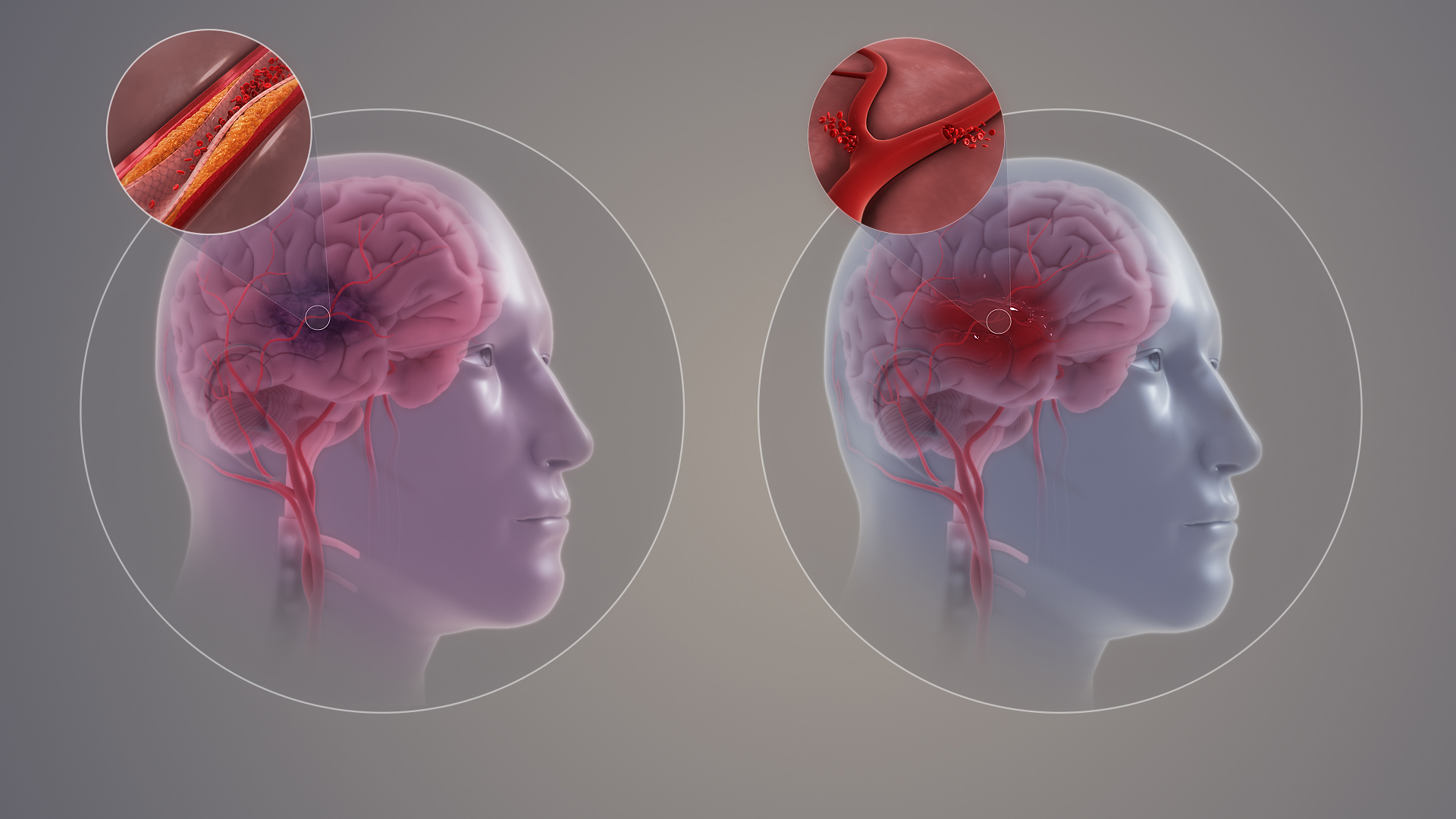
4.2 Off-label and Emerging Uses
- ADHD: Investigated for enhancing attention span and working memory.
- Age-related Memory Decline: Helps combat forgetfulness and cognitive fog.
- Cognitive Enhancement: Used by students and professionals for performance improvement.
- Amblyopia: Especially in pediatric cases to improve visual processing and acuity.
- Post-Anesthesia Recovery: Potential benefit in reducing postoperative cognitive dysfunction.
5. Dosage and Administration Guidelines
5.1 Standard Dosage Recommendations
Typical regimens include:
- Citicoline: 500-1000 mg per day
- Piracetam: 1200-2400 mg per day, in divided doses
These are usually administered orally for chronic use, or via injection during acute management.

5.2 Patient-specific Dose Adjustments
- Renal Impairment: Piracetam dosage may need reduction.
- Hepatic Impairment: Monitor for altered metabolism or accumulation.
- Long-term Use: Consider cycling therapy (e.g., 2 months on, 1 month off) to prevent tolerance or desensitization.
6. Potential Side Effects and Adverse Reactions
6.1 Common Side Effects
- Mild gastrointestinal discomfort
- Headache and lightheadedness
- Restlessness or insomnia, especially with evening dosing
6.2 Serious and Rare Adverse Events
- Hypersensitivity reactions including rash, urticaria
- Behavioral agitation or anxiety, especially in susceptible individuals
- Increased bleeding risk in patients using anticoagulants (Piracetam effect on platelet aggregation)
7. Drug Interactions and Compatibility Considerations
Interaction with Antiplatelets and Anticoagulants
Piracetam has been shown to inhibit platelet aggregation, which may potentiate the effects of antiplatelet and anticoagulant medications such as aspirin, clopidogrel, and warfarin. This interaction raises the risk of bleeding events, particularly in elderly patients or those with cerebrovascular vulnerability. Co-administration requires close hematologic monitoring and INR evaluation where applicable.
CNS Stimulant or Depressant Interaction Risks
The cognitive-enhancing properties of Citicoline/Piracetam may be modulated when combined with central nervous system (CNS) stimulants (e.g., methylphenidate) or depressants (e.g., benzodiazepines). This can lead to unpredictable effects, including overstimulation or increased sedation. Patients should be monitored for altered mental status, sleep disruption, or paradoxical mood shifts.

Interactions with Cholinergic or Glutamatergic Agents
Both agents influence neurotransmitter dynamics. Citicoline enhances acetylcholine synthesis, and Piracetam modulates glutamate receptors. When combined with cholinergic agonists or glutamatergic drugs, there may be an additive effect, increasing the risk of excitotoxicity or overstimulation. Clinical vigilance is necessary when used with agents like donepezil or memantine.
Considerations When Used Alongside Antidepressants or Antipsychotics
Concomitant use with SSRIs, SNRIs, or atypical antipsychotics may influence mood or cognitive processing. While Citicoline may offer neuroprotective synergy, Piracetam's neuroactive modulation could potentiate or dampen psychiatric medication effects. Periodic psychiatric evaluation is advised to preempt adverse mood or behavioral alterations.
8. Warnings, Contraindications, and Black Box Alerts
8.1 Absolute Contraindications
- Hypersensitivity: Individuals with a known allergy to Citicoline or Piracetam should avoid use due to risk of anaphylaxis or severe dermatologic reactions.
- Severe Renal Impairment: Piracetam is renally excreted and may accumulate in cases of significant renal dysfunction, increasing the potential for toxicity.
- Huntington's Disease: Caution is advised due to reports of exacerbated symptoms with Piracetam in patients with this neurodegenerative disorder.
8.2 Warnings and Use Limitations
- Lowered Seizure Threshold: Piracetam may reduce the threshold for seizures in susceptible individuals; caution is warranted in those with epilepsy.
- Intracranial Bleeding Risk: Post-stroke patients, especially those on anticoagulants, may face increased bleeding risk. Regular imaging and neurological assessments are recommended.
- Neuropsychiatric Monitoring: Agitation, anxiety, or mood swings should prompt reevaluation of therapy. Regular mental health screenings may be necessary during long-term use.

9. Special Precautions and Careful Administration
9.1 Important Precautions During Use
- Avoid sudden discontinuation, particularly in patients undergoing post-stroke rehabilitation, as abrupt withdrawal may lead to cognitive regression.
- Exercise caution in patients with a prior history of depression, schizophrenia, or mania, as neuroactive modulation may worsen underlying symptoms.
- Baseline cognitive and neurological assessments are recommended to evaluate therapeutic efficacy and detect adverse effects early.
9.2 Handling and Storage Precautions
- Store the product in a cool, dry environment, ideally between 15°C and 25C.
- Protect the medication from direct light and excessive humidity to maintain stability.
- Dispose of expired or unused products according to pharmaceutical safety protocols. Do not flush or throw into household waste.
10. Use in Special Populations
10.1 Administration in Elderly Patients
Elderly individuals often exhibit altered pharmacokinetics due to decreased renal clearance. Dose adjustments should be made based on creatinine clearance values. Regular cognitive assessments are crucial to evaluate ongoing benefits and avoid cognitive overactivation or sedation.
10.2 Use in Pregnant and Nursing Women
- No conclusive human data exists regarding safety during pregnancy. Animal studies have shown mixed outcomes regarding fetal development, thus Citicoline/Piracetam use during pregnancy is only recommended when the potential benefits outweigh potential fetal risks. It is not known whether these compounds are excreted in human breast milk. Caution is advised during lactation; temporary discontinuation of breastfeeding may be considered.

10.3 Use in Pediatric Populations
- Evidence supports its use in amblyopia and learning difficulties in children above 7 years of age. Safety in children under 5 years has not been well established. Growth parameters and neurodevelopmental milestones should be closely monitored during prolonged therapy.
11. Overdose Risks and Emergency Management
Symptoms of Overdose
- Neurological: tremors, irritability, vertigo, or agitation
- Gastrointestinal: nausea, vomiting, abdominal discomfort
- Psychiatric: confusion, anxiety, or acute disorientation
Recommended Supportive Treatment Strategies
There is no specific antidote for Citicoline/Piracetam overdose. Management is symptomatic:
- Activated charcoal may be administered if ingestion is recent.
- Hydration and renal monitoring are essential due to Piracetam's renal excretion.
- Seizure precautions should be instituted in high-risk individuals.

Hospitalization and Detox Protocol
Patients presenting with severe symptoms may require hospitalization for:
- Continuous cardiac and neurological monitoring
- Intravenous fluid administration
- Psychiatric evaluation for altered behavior or mood
12. Clinical Research and Evidence Base
Key Randomized Controlled Trials and Meta-analyses
Multiple studies have demonstrated the efficacy of Citicoline and Piracetam in post-stroke recovery, cognitive enhancement in dementia, and amblyopia in children. Meta-analyses suggest statistically significant improvements in memory, attention, and processing speed.
Efficacy Comparison with Other Nootropics
Compared to agents like modafinil or aniracetam, the Citicoline/Piracetam combination offers a favorable safety profile and broader applications in neurodegenerative and cerebrovascular disorders. However, onset of effect may be more gradual.
Real-world clinical use has confirmed its tolerability and cognitive benefits across diverse populations, including elderly, pediatric, and neurologically impaired groups. Ongoing studies are assessing its utility in depression-related cognitive dysfunction and post-COVID cognitive fatigue.
Citicoline/ Piracetam FAQ
- What is the use of Neurocetam Plus tablets?
- What is Neurocetam used for?
- What is Piracetam and citicoline used for?
- What is the drug Piracetam used for?
- What is the purpose of citicoline?
- Does Piracetam help memory?
- Is citicoline safe to take daily?
- When is the best time to take piracetam?
- Is piracetam safe for kidneys?
- Is piracetam good for stroke?
- Who takes piracetam?
- What is citicoline in neurology?
- What to avoid when taking citicoline?
- Is piracetam safe to use?
- Does piracetam make you sleepy?
- What are the side effects of citicoline and piracetam tablets?
- Does citicoline improve vision?
- Does citicoline lower BP?
- How long should Citicoline be taken?
- Can piracetam prevent stroke?
What is the use of Neurocetam Plus tablets?
The Neurocelam Plus tablet is a medication utilized for stroke recovery and cognitive improvement purposes, protecting the brain's nerve cells from harm, while also aiding in the restoration of nerve cells and potentially assisting in brain trauma management as well.
What is Neurocetam used for?
Treatment for memory loss in individuals with Alzheimer's disease. It can also address memory decline associated with aging and post-traumatic experiences. It functions by enhancing communication among nerve cells while safeguarding the brain's well-being.
What is Piracetam and citicoline used for?
Citicoline aids in creating brain neurotransmitters to mend harmed nerve cells, and Piracetam enhances blood flow to the brain for oxygen and nutrient delivery. When used together, they enhance brain function and cognition while promoting focus.
What is the drug Piracetam used for?
Piracetam is prescribed for managing Alzheimer's disease symptoms, for addressing stroke effects and memory loss associated with aging or head injury in individuals with Parkinson's disease and other conditions.
What is the purpose of citicoline?
Citizens often turn to citicoline to combat memory loss associated with aging and cognitive decline. It is also utilized for addressing issues, like glaucoma, stroke recovery, Alzheimer's disease, bipolar disorder, depression, and a variety of health concerns.
Does Piracetam help memory?
By enhancing the impact of acetylcholine on the receptors, piracetam helps enhance learning and memory.
Is citicoline safe to take daily?
Yes
When is the best time to take piracetam?
Before or after meals
Is piracetam safe for kidneys?
No
Is piracetam good for stroke?
Piracetam possesses thrombotic properties that could potentially lower mortality rates and decrease disability among individuals experiencing an acute stroke.
Who takes piracetam?
Piracetam is a medication known for its effectiveness in treating disorders and conditions such as vertigo, dyslexia, cortical myoclonus, and sickle cell anemia. Although there are varying opinions on its benefits, it is used for dementia treatment.
What is citicoline in neurology?
Acetylcholine (referred to as ACh) serves as a neurotransmitter, impacting various brain activities, such as memory retention and physical functions like facilitating muscle movements for mobility.
What to avoid when taking citicoline?
Antiparkinsonian medications, like levodopa and carbidopa, along with enhancers such as centrophenoxine and meclofenoxate.
Is piracetam safe to use?
Piracetam is considered safe when taken in amounts of up to 24 grams per day for a maximum of 2 weeks or 20 grams per day for a duration of up to 18 months.
Does piracetam make you sleepy?
Yes
What are the side effects of citicoline and piracetam tablets?
- Insomnia
- Diarrhea
- Stomach pain
- Hypoglycemia
- Arrythmia
Does citicoline improve vision?
Yes
Does citicoline lower BP?
Yes
How long should Citicoline be taken?
12 months
Can piracetam prevent stroke?
Piracetam exhibits antithrombotic properties that could potentially lower the risk of mortality and disability in individuals experiencing a stroke.