Introduction to Fungotek (Terbinafine)
Overview of Fungotek Brand
Fungotek is a well-recognized antifungal medication containing terbinafine, a compound widely prescribed for the treatment of superficial and nail fungal infections. Known for its efficacy and safety, Fungotek has become a trusted option for both dermatological and systemic fungal conditions.
History and Medical Significance of Terbinafine
Introduced in the late 20th century, terbinafine marked a breakthrough in antifungal therapy. Unlike earlier agents with limited activity, terbinafine demonstrated powerful fungicidal properties, particularly against dermatophytes. Its development contributed significantly to improved outcomes in chronic nail and skin fungal infections.
Therapeutic Classification as an Antifungal Medication
Terbinafine belongs to the allylamine class of antifungal agents. Unlike azoles that primarily inhibit fungal growth, allylamines directly disrupt fungal cell membrane formation, making terbinafine fungicidal rather than fungistatic.
FDA Approvals and Global Regulatory Status
Approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) and various international health authorities, terbinafine is recognized globally as a first-line antifungal treatment. It is included in many essential medicines lists due to its wide therapeutic relevance.
Composition and Formulations
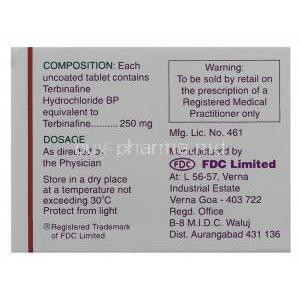
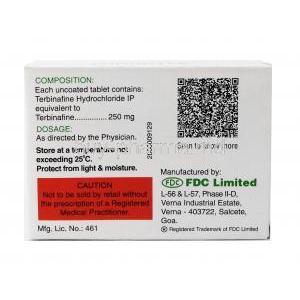
Active Ingredient: Terbinafine Hydrochloride
The core active pharmaceutical ingredient in Fungotek is terbinafine hydrochloride, designed to deliver potent antifungal activity with favorable pharmacokinetics.
Available Dosage Forms
- Tablets for systemic therapy
- Topical creams and gels for localized infections
- Sprays for large surface coverage
- Oral granules for pediatric administration
Inactive Ingredients and Excipients
Formulations may contain lactose, starch, magnesium stearate, or preservatives, varying slightly between oral and topical forms. These excipients help stabilize the active ingredient and optimize absorption.
Generic vs. Branded Formulations
Fungotek is available as a branded preparation, but generic terbinafine formulations offer similar therapeutic efficacy and are often more affordable. Both comply with international pharmaceutical quality standards.
Mechanism of Action: How Fungotek Works
Terbinafine as an Allylamine Antifungal
Belonging to the allylamine group, terbinafine functions differently from azole antifungals, giving it a unique advantage in resistant infections.
Inhibition of Squalene Epoxidase Enzyme
Terbinafine inhibits the fungal enzyme squalene epoxidase, a critical catalyst in the ergosterol biosynthesis pathway. This leads to toxic accumulation of squalene within fungal cells.
Effects on Fungal Cell Membrane Synthesis
By disrupting ergosterol production, terbinafine weakens and destabilizes the fungal cell membrane, resulting in cell death. This fungicidal action differentiates it from agents that merely inhibit growth.
Spectrum of Antifungal Activity
Fungotek is effective against dermatophytes, yeasts such as Candida species, and certain molds. Its broad activity makes it a versatile treatment for various cutaneous and nail infections.
Approved Medical Uses
Treatment of Onychomycosis
Fungotek is widely prescribed for fungal nail infections, where prolonged therapy ensures clearance of stubborn pathogens.
Dermatophytosis
Effective against ringworm infections affecting the scalp, groin, and other skin areas.
Tinea Pedis (Athlete’s Foot)
A common fungal infection of the feet, terbinafine provides rapid symptom relief and eradication of the causative fungi.
Tinea Cruris (Jock Itch)
Fungotek alleviates itching, redness, and scaling associated with groin infections.
Tinea Corporis (Ringworm of the Body)
Topical formulations are especially effective for treating localized patches of ringworm on the body.
Off-Label and Investigational Uses
Use in Severe Systemic Fungal Infections
In certain cases, terbinafine may be considered as part of combination therapy for systemic mycoses, though this is not routine.
Adjunct Therapy for Resistant Candidiasis
Some clinical studies suggest its use in resistant Candida infections when conventional therapies fail.
Prophylaxis in Immunocompromised Patients
Investigational protocols have examined terbinafine as prophylaxis in immunocompromised individuals, though results are limited.
Pediatric Use Beyond Labeled Indications
Though not always approved, terbinafine granules have been utilized in children with scalp infections under specialist supervision.
Dosage and Administration
Standard Adult Dosage for Oral Tablets
Typical dosing involves 250 mg once daily for 6 to 12 weeks, depending on the site of infection.
Topical Application Guidelines
Apply thinly to the affected area once or twice daily, ensuring coverage of surrounding skin.
Duration of Treatment by Condition
- Nail infections: 6–12 weeks
- Athlete’s foot: 2–4 weeks
- Jock itch: 2–4 weeks
- Ringworm: 2–4 weeks
Dose Adjustments for Hepatic and Renal Impairment
Patients with liver or kidney dysfunction require adjusted dosing or alternative therapy due to altered drug clearance.
Monitoring During Long-Term Therapy
Regular monitoring of liver enzymes is advised for prolonged use to minimize hepatotoxicity risks.
Administration in Special Populations
Elderly Patients
While generally well tolerated, elderly patients may require careful assessment of liver and kidney function before initiating therapy.
Pregnant Women
Terbinafine is not routinely recommended during pregnancy. Limited data suggest caution, particularly during the first trimester.
Nursing Mothers
Terbinafine may be excreted in breast milk. Avoidance is generally advised during lactation unless benefits outweigh risks.
Children
Approved for certain pediatric indications, especially tinea capitis. Dosing is weight-adjusted, and safety has been established in specific age groups.
Side Effects of Fungotek
Common Side Effects
Fungotek (terbinafine) is generally well tolerated, yet some individuals may experience mild to moderate reactions. These effects are typically transient but should be acknowledged.
- Gastrointestinal disturbances – including nausea, diarrhea, dyspepsia, and abdominal pain, often occurring during the first days of therapy.
- Headache and dizziness – neurological discomforts that may interfere with concentration but usually resolve without intervention.
- Taste disturbances (dysgeusia) – a unique side effect characterized by altered or diminished taste perception, occasionally leading to reduced appetite.
- Skin rashes and mild pruritus – localized itching or erythematous patches, particularly with topical formulations.
Serious Adverse Reactions
Although rare, severe reactions demand prompt recognition and immediate medical attention. These complications underscore the importance of careful monitoring during prolonged treatment.
- Hepatotoxicity and liver enzyme abnormalities – manifested as jaundice, dark urine, fatigue, and elevated liver transaminases.
- Severe cutaneous adverse reactions (SCARs) – such as Stevens-Johnson syndrome or toxic epidermal necrolysis, requiring urgent discontinuation of therapy.
- Hematological effects – including neutropenia, agranulocytosis, or thrombocytopenia, leading to increased risk of infection or bleeding.
- Anaphylactic reactions – acute hypersensitivity presenting with airway compromise, urticaria, and circulatory collapse.
Drug Interactions
Fungotek engages in significant pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic interactions. These may alter drug metabolism, potentiate toxicities, or diminish therapeutic efficacy.
- CYP2D6 substrates – terbinafine inhibits this enzyme, potentially increasing serum levels of antidepressants, beta-blockers, and certain antiarrhythmics.
- Anticoagulants – co-administration with warfarin may interfere with INR stability, necessitating enhanced monitoring.
- Hepatotoxic drugs and alcohol – additive risk of hepatic injury when combined with agents such as isoniazid or chronic ethanol consumption.
- Immunosuppressants – altered plasma levels of cyclosporine may occur, requiring dose recalibration.
Warnings and Contraindications
Fungotek must be prescribed judiciously, with strict adherence to contraindications and warnings that safeguard patient safety.
- Hypersensitivity to terbinafine – absolute contraindication in patients with known allergic reactions.
- Active or chronic liver disease – high risk of hepatic decompensation.
- Severe renal impairment – reduced clearance necessitates avoidance or careful dose modification.
- Risk of liver failure – prolonged or high-dose use may precipitate fulminant hepatic injury.
- Importance of monitoring – routine assessment of liver function tests is recommended throughout therapy.
Careful Administration and Important Precautions
Preventive strategies ensure optimal outcomes and mitigate risks associated with systemic antifungal therapy.
- Pre-treatment screening – comprehensive hepatic and renal evaluation prior to initiation.
- Periodic monitoring – scheduled laboratory testing during extended courses.
- Avoidance of alcohol – reduces hepatic burden and synergistic toxicity.
- Recognition of warning signs – early jaundice, unexplained rash, or persistent gastrointestinal discomfort should trigger reassessment.
- Discontinuation criteria – immediate cessation in the presence of significant liver dysfunction, hematological abnormalities, or severe skin reactions.
Overdose and Emergency Management
Terbinafine overdose is uncommon but can manifest with systemic disturbances requiring urgent care.
- Symptoms – include nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, dizziness, headache, and possible dermatologic eruptions.
- Supportive treatment – maintenance of hydration, correction of electrolyte imbalance, and symptomatic management form the cornerstone of care.
- Activated charcoal and gastric lavage – considered in recent ingestions to reduce systemic absorption.
- Emergency intervention – immediate medical evaluation is essential, particularly in patients with pre-existing hepatic or renal compromise.
Storage and Handling Precautions
Proper storage and handling of Fungotek maintain its potency and safeguard user safety.
- Storage conditions – keep at controlled room temperature, away from excessive humidity or direct sunlight.
- Protection – tablets and topical preparations should remain sealed in original packaging until use.
- Safe handling – avoid contamination of topical products by ensuring hands and applicators are clean.
- Disposal – discard expired or unused medication responsibly, following pharmaceutical waste guidelines to prevent environmental contamination.
Fungotek, Terbinafine FAQ
- What is the use of Fungotek Tablet?
- What fungus is terbinafine used for?
- What should I avoid while taking terbinafine?
- Is terbinafine a high risk medication?
- How long does treatment take with terbinafine?
- What are the worst side effects of terbinafine?
- How to tell if terbinafine is working?
- What organ can terbinafine affect?
- Does terbinafine affect sleep?
- Can terbinafine cause weight gain?
- Can terbinafine damage kidneys?
- Can terbinafine cause hair loss?
- Can terbinafine affect your heart?
- Who cannot use terbinafine?
- Can terbinafine cause tiredness?
- How do I know if terbinafine is affecting my liver?
- Can terbinafine cause anxiety?
- How many days does terbinafine stay in your system?
- Is terbinafine the strongest antifungal?
- Does terbinafine make you pee a lot?
- Is it better to take terbinafine in the morning or at night?
- Can I take vitamin C with terbinafine?
- Does terbinafine stop itching?
- Can I buy terbinafine tablets over the counter?
- What are the bad side effects of terbinafine?
- Can terbinafine cause high cholesterol?
- Does terbinafine affect gut bacteria?
- Can I exercise while taking terbinafine?
- Can your liver recover from terbinafine?
- Can terbinafine weaken your immune system?
- Can terbinafine cause depression?
- What are the worst side effects of terbinafine?
- Which is stronger, fluconazole or terbinafine?
- Is terbinafine 100% effective?
What is the use of Fungotek Tablet?
The Fungotek Tablet is a medication designed to combat infections that affect the nails. It's also effective in treating a condition known as tinea capitis, an infection of the scalp commonly referred to as ringworm.
What fungus is terbinafine used for?
Terbinafine is a type of medicine known as an antifungal. It's used to tackle infections caused by fungi.
What should I avoid while taking terbinafine?
Too much caffeine
Is terbinafine a high risk medication?
Terbinafine has been associated with a number of cases of liver damage, which, in some instances has been severe enough to be life threatening.
How long does treatment take with terbinafine?
2-6 weeks
What are the worst side effects of terbinafine?
- Liver problems
- Blood Disorders
- Severe skin reactions
How to tell if terbinafine is working?
As the itching, scaling and flaking start to subside
What organ can terbinafine affect?
Liver
Does terbinafine affect sleep?
Yes
Can terbinafine cause weight gain?
Yes
Can terbinafine damage kidneys?
Yes
Can terbinafine cause hair loss?
Yes
Can terbinafine affect your heart?
Yes
Who cannot use terbinafine?
- People with kideny or liver problems
- Pregnant or trying to become pregnant
Can terbinafine cause tiredness?
Yes
How do I know if terbinafine is affecting my liver?
Symptoms include
- Abdominal pain
- Malaise
- Scleral icterus
- Severe jaundice
Can terbinafine cause anxiety?
Yes
How many days does terbinafine stay in your system?
At least 30 weeks
Is terbinafine the strongest antifungal?
Itraconazole
Does terbinafine make you pee a lot?
Yes
Is it better to take terbinafine in the morning or at night?
To get the most out of tablets, take them at the same time every day.
Can I take vitamin C with terbinafine?
Yes
Does terbinafine stop itching?
Yes
Can I buy terbinafine tablets over the counter?
Yes
What are the bad side effects of terbinafine?
- Stomach cramps
- Nausea
- Vomiting
- Headache
Can terbinafine cause high cholesterol?
Yes
Does terbinafine affect gut bacteria?
No
Can I exercise while taking terbinafine?
No Intense exercises
Can your liver recover from terbinafine?
In all instances, the liver damage caused by terbinafine is temporary, with most people recovering within 3-6 months.
Can terbinafine weaken your immune system?
When you take this medicine, it can cause a drop in the number of white blood cells.
Can terbinafine cause depression?
Yes
What are the worst side effects of terbinafine?
- Liver problems
- Blood Disorders
Which is stronger, fluconazole or terbinafine?
Terbinafine
Is terbinafine 100% effective?
87%