Furic, Febuxostat
- Introduction to Furic, Febuxostat
- Composition and Formulation of Furic Febuxostat
- Febuxostat Mechanism of Action
- Febuxostat Uses
- Off-Label Uses of Furic Febuxostat
- Febuxostat Dosage and Administration Guidelines
- Administration of Furic Febuxostat to Special Populations
- Side Effects of Febuxostat
- Serious and Rare Side Effects of Furic Febuxostat
- Febuxostat Interactions
- Warnings and Important Precautions When Using Furic (Febuxostat)
- Contraindications for Furic Febuxostat
- Careful Administration and Monitoring Requirements
- Handling Precautions for Furic Febuxostat
- Overdosage and Management of Furic (Febuxostat) Toxicity
Introduction to Furic, Febuxostat
The medication Furic is an advanced way to manage levels of uric acid in the body for a long time, effectively and safely, to reduce gout flare-ups compared to older treatments, like xanthine oxidase inhibitors. It has been approved by health organizations such, as the FDA and EMA. Has now become a common choice for handling individuals with persistent gout issues who do not respond well to allopurinol treatment.
Doctors acknowledge Furic not only for its ability to lower acid levels but also for its effectiveness, in addressing related health issues, like;
- Gout.
- Renal uric acid lithiasis
- Hyperuricemia is caused by cancer therapy treatments.
Frequently confused with a substance, furic acid is actually a misinterpretation of the product name Furic, with feboxostat being the key ingredient, under the brand name.
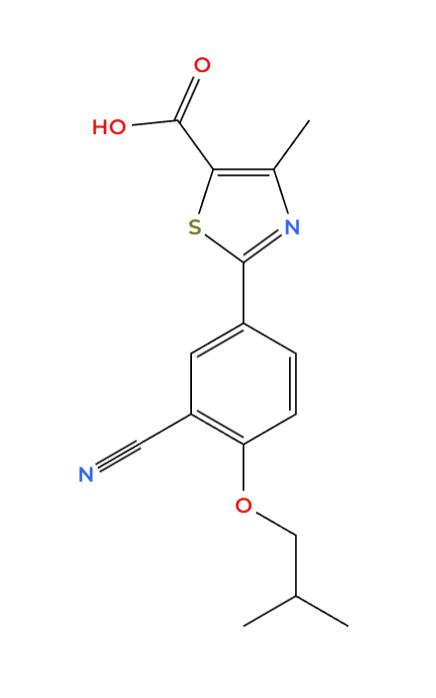
Composition and Formulation of Furic Febuxostat
At the heart of Furic is febuxostat, which is an inhibitor of xanthine oxidase that is not derived from purines. Chemically known as 2 (3-cyanophenyl) 6 methylthiazole. 7 Carboxylate possesses a thiazole ring structure that provides specificity towards the active site of xanthine oxidase and reduces the chances of cross-reaction. Furic can be purchased in potencies such, as;
- 40 milligram tablets.
- 80 milligram tablets.
Each tablet includes substances, like lactose monohydrate and microcrystalline cellulose, to aid in absorption and stability within the body's digestive system process, with consistent availability, for patients needing different treatment options being taken into account.
- Allopurinol is a medication that has been found to be effective but may have restrictions, to allergic reactions.
- Colchicine is not specifically aimed at reducing acid levels. It is commonly given alongside other medications to prevent acute gout attacks.
- Probenecid is a medication that helps the kidneys remove acid from the body and is often recommended for individuals with hyperuricemia caused by decreased excretion.
When making comparisons;
- When comparing Febuxostat to Allopurinol, it is noted that Febuxostat demonstrates selectivity and effectiveness when uric acid levels are elevated. It also faces heightened cardiovascular evaluation scrutiny.
- Febuxostat and Colchicine work differently. Febuxostat is used for long term management, while colchicine is more suitable for relief during short-term episodes
- When deciding between Probenecid and Febuxostat, it's important to consider how Probenecid boosts the excretion of acid while Febuxostat works by blocking its production process, based on each patient's kidney function and other health conditions they may have.
Febuxostat Mechanism of Action
Febuxostat works by blocking the xanthine oxidase enzyme, a component, in the purine breakdown process that transforms hypoxanthine into xanthine and xanthine into uric acid. By interrupting this enzymatic activity chain, feboxustat successfully reduces the production of acid. This biochemical inhibition leads to;
- Lowering the levels of uric acid in the bloodstream
- Inhibiting the development of crystals made from monosodium urate
- Improving the symptoms of gout related inflammation.
Febuxostat shows attachment, to xanthine oxidase compared to allopurinol and remains effective for patients with to moderately impaired kidneys. It's structure, being purine, helps avoid the immune response commonly linked with allopurinol.
Febuxostat also proves reliable in keeping acid levels below 6 mg/dL consistently than traditional treatments essential for gout management. However, due to outcome studies it is advised to use caution in patients with existing heart conditions.
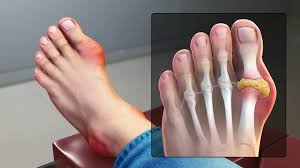
Febuxostat Uses
Management of Chronic Hyperuricemia in Gout Patients
Febuxostat plays a role in treating chronic hyperuricemia. It is especially helpful, for those dealing with gout symptoms. It works by inhibiting xanthine oxidase to reduce the production of acid at a level. This targeted approach helps address the cause of urate crystal buildup in joints and soft tissues. It's often recommended for adult patients, with uric acid levels above 7 mg/dL despite lifestyle changes. Febuxostat is typically prescribed in situations;
- Recurrent episodes of gout accompanied by levels of acid
- Dealing with gout necessitates the breakdown of urate accumulations.
- Renal problems where allopurinol cannot be used due, to issues that can occur.
Keeping urate levels below 6 mg/dL with the help of medication can help in decreasing flare-ups and reducing the long-term effects of uncontrolled high levels of uric acid, in the body.
Prevention of Gout Flares During Urate-Lowering Therapy Initiation
When starting treatment, acid levels in the body can sometimes lead to sudden gout flare-ups due to changes in urate levels and crystal movement. The use of Febuxostat at the beginning of treatment may unexpectedly cause these attacks to occur.
Nevertheless, with measures in place, this situation can be effectively controlled. To address these flare-ups, Febuxostat is usually given alongside inflammatory medications, like ;
- Colchicine is often recommended in doses for its ability to inhibit crystal formation.
- NSAIDs, like naproxen or indomethacin, can be used if there are no issues with the system or kidneys.
- Reserved for individuals with contraindications to NSAIDs and colchicine, corticosteroids are considered as an option.
Continuing the use of febuxostat during a flare is actually considered a beneficial practice as it helps in keeping uric acid levels stable, over time, and ensures long-term stability in health conditions like gout management.
Doctors usually advise a treatment plan of prophylactic for six months after starting the medication or for three months after reaching the desired uric acid levels. Whichever duration proves to be longer based on individual response, to the treatment.
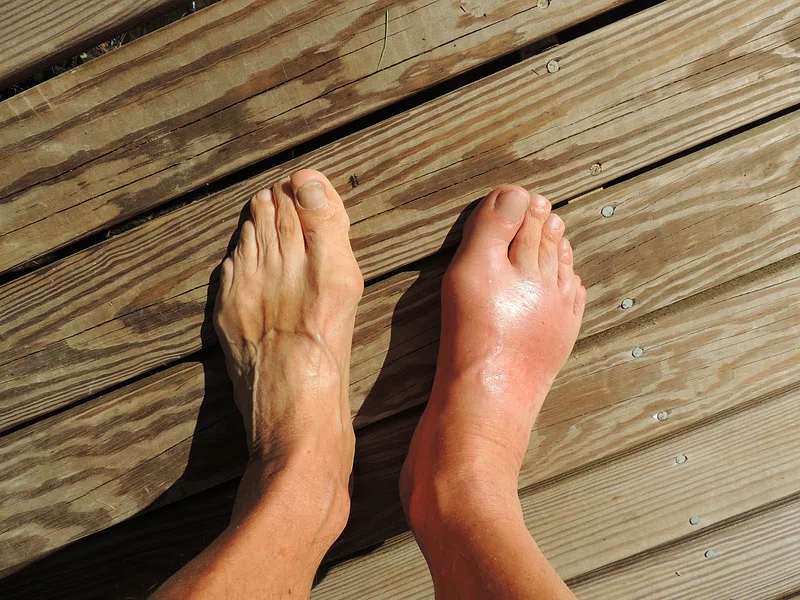
Febuxostat for Gout
Febuxostat provides a highly effective choice for individuals suffering from gout conditions who may find it challenging to use allopurinol due to sensitivity issues and kidney related problems. Its accuracy in decreasing the production of acid by inhibiting xanthine oxidase without affecting purines results in better control of uric acid levels for many patients.
Research studies like CONFIRMS and FACT have shown that febuxostat is successful in reaching target levels of acid when compared to allopurinol treatment. For those with slight, to moderate kidney impairment. Febuxostat is unique in that it is not broken down by xanthine oxidase directly. This property enables control over time without the need for dosage modifications in cases of renal insufficiency.
Noteworthy benefits of using febuxostat for treating gout are;
- Successfully lowering acid levels in instances.
- Limited dependence on pathways for excretion by the kidneys.
- Taking a pill once a day can help you remember to stick to your medication routine.
While it is effective, in practice usage of this treatment should be approached with care in individuals who already suffer from heart conditions due to reports suggesting an increase, in the risk of heart related deaths after the medication has been introduced to the market; hence healthcare providers should tailor treatment decisions based on each patients risk factors.
Off-Label Uses of Furic Febuxostat
Management of Tumor Lysis Syndrome
Febuxostat is known under the brand name Furic. Has drawn attention for its use in treating tumor lysis syndrome (TLS), a serious condition in cancer patients characterized by sudden cell breakdown and high levels of purine release in the body. When starting chemotherapy for patients with blood cancers such as leukemia and lymphoma, TLS can cause an increase in uric acid levels, leading to kidney damage and dysfunction in multiple organs.
Furic works by blocking xanthine oxidase activity, which helps reduce the production of acid from purine metabolites. This method offers both treatment advantages, in TLS by lowering the chance of urate-triggered acute kidney damage. Situations in practice that call for the use of febuxostat, for TLS prevention include;
A significant number of cancer cells, with a rate of growth.
- Baseline high levels of acid or kidney problems.
- Struggling to tolerate or respond to allopurinol
- While rasburicase continues to be accepted as the option, for treating TLS (tumor lysis syndrome)
Furic has also gained recognition as a suitable substitute—particularly beneficial for individuals with glucose 6 phosphate dehydrogenase deficiency or in situations where cost plays a significant role. The convenient dosing. Favorable pharmacokinetic properties of Furic offered advantages, for managing oncology patients in various care settings.
Use in Kidney Transplant Patients to Prevent Urate Nephropathy
Elevated levels of acid are often seen in individuals who have received a kidney transplant because of the combined impact of medications that suppress the system and changes, in kidney function caused by drugs like cyclosporine that lead to higher levels of urate in the body's circulation.
If uric acid remains consistently high in the blood over time after a kidney transplant surgery it could result in damage to the kidneys known as urate nephropathy, which can harm how the kidney functions and its overall longevity.
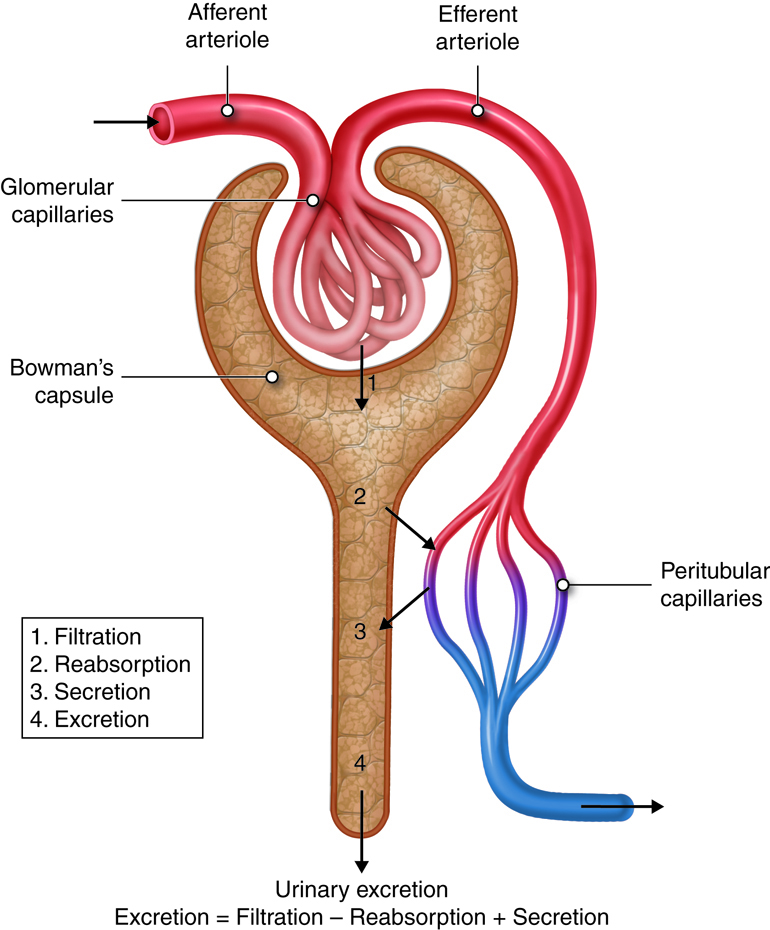
Doctors have looked into using Furic, off-label, as a treatment to manage levels of uric acid following kidney transplants and their associated issues. The safety record of the kidneys is not primarily dependent on the filtration in the glomeruli.
It doesn't seem like there's any impact, on inhibitors. Consistent control of acid levels, without changes. Preliminary data shows that febuxostat could help maintain the estimated filtration rate (eGFR) in transplant recipients as opposed to allopurinol usage.
Therefore, it's use in transplant care should be decided based on collaborative agreement and personalized risk assessment.
Potential Use in Cardiovascular Disease Management (Controversial)
Lately, there has been a growing fascination and skepticism surrounding the impact of febuxostat, on cardiovascular disease (CVD). Hyperuricemia is now seen as a risk factor in the development of hypertension, atherosclerosis, and heart failure.
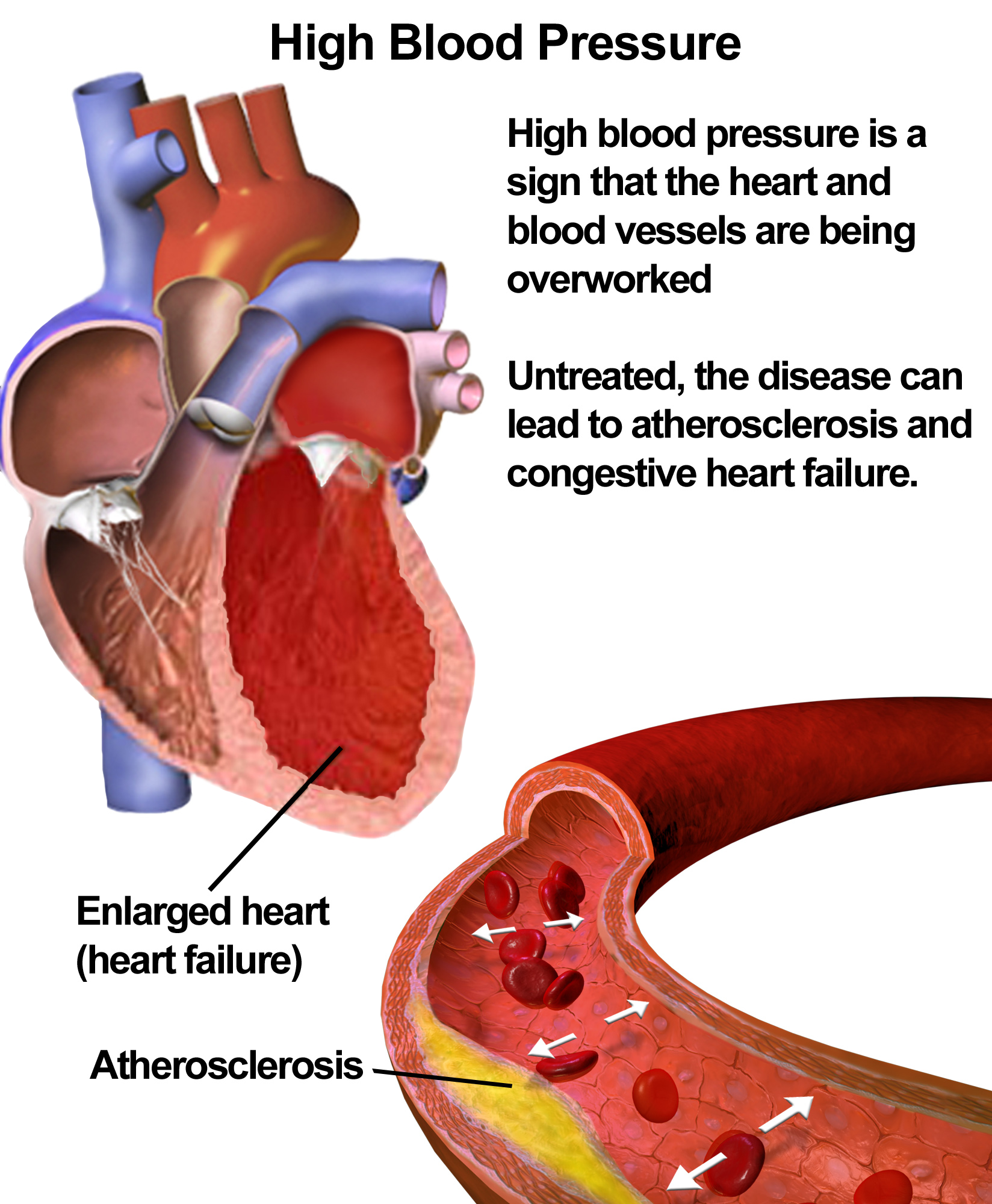
Aside from its role in producing acid, the xanthine oxidase enzyme also contributes to oxidative stress by producing oxygen species known to be involved in endothelial dysfunction and vascular inflammation. In theory blocking xanthine oxidase with Furic could potentially offer protection against issues such as;
- Reducing stress and damage to blood vessels.
- Enhanced availability of oxide in cells
- Reducing the rigidity of arteries
However, this possible advantage is still uncertain. The CARES study and other research studies have expressed worries about safety by showing an occurrence of heart-related deaths in patients treated with febuxostat compared to allopurinol
This discovery has led bodies to issue warnings, particularly for patients with known heart disease As a result the use of Furic, for heart-related purposes is still debated. Current studies are trying to determine whether certain subgroups could benefit from its antioxidant effects without facing unnecessary heart risks
Febuxostat Dosage and Administration Guidelines
Febuxostat Dose
Febuxostat is usually taken by mouth. It is commonly started at a dose of 40 mg, per day initially. If patients do not achieve the desired serum urate levels (< 6 mg/dL) within two to four weeks the dosage may be increased to 80 mg daily. In some cases where patients do not respond well to treatment, doses as high as 120 mg have been examined; however, this exceeds the dosage recommendations in most areas. Determining the dosage is. Based on individual factors such as;
- Baseline levels of uric acid
- The Intensity of gout attacks.
- Detection of tophi or erosion in the joints
Peak plasma concentrations are typically reached about 60 to 90 minutes after taking the medication, and steady-state levels are usually achieved within two weeks of starting treatment. Food intake does not impact the effectiveness of the medication as its bioavailability remains consistent regardless of meals.
Dose Adjustments Based on Renal or Hepatic Impairment
Febuxostat provides a benefit in terms of how it moves through the body for patients, with kidney issues because it is cleared less by the kidneys. This means that people with a bit to moderate kidney problems (with an eGFR of 30 mL/min, per 1.73 m2 or above) do not need to adjust their starting dose. In cases of liver problems;
- For individuals with mild impairment (Child Pugh A), there is no need for any adjustment in dosage.
- Approach with care when dealing with moderate impairment (Child Pugh B).
- Severe liver damage (Child Pugh C); Avoided if possible.
Regularly checking the levels of liver enzymes and kidney functions is recommended for individuals at risk of health issues within the six months of treatment.
Guidelines for Initiating and Maintaining Therapy
Therapy should start once any ongoing gout flare-up subsides, since starting it soon might actually lead to flare-ups occurring later on in the treatment process. It is advised to administer measures against inflammation—like taking low-dose colchicine or NSAIDs, for a minimum of 6 months, at the beginning of therapy.
Key recommendations comprise;
- Commence with 40 milligrams once, per day.
- Remember to check the acid levels, in the blood after 2 to 3 weeks.
- Adjust the dosage to 80 milligrams if the desired outcome is not reached.
Make sure to keep up with your therapy even after your urate levels return to normal. Stopping suddenly or unexpectedly may cause a rebound in acid levels. Raise the chances of another flare-up occurring.
Missed Dose Instructions
If a patient forgets to take a dose of medication and remembers on, but it's almost time for the dose anyway then it's best to skip the missed dose to prevent taking too much medicine at once. Patients shouldn't double up on doses unless a healthcare provider tells them to do.
Keeping a schedule helps patients stick to their medication routine and keeps the levels of medicine in their body steady to avoid fluctuations, in treatment effectiveness don't take two doses in one day without the doctor's guidance.
Administration of Furic Febuxostat to Special Populations
Use in Elderly Patients: Dosage Considerations and Monitoring
As people get changes, in how medications work and how the body clears these drugs can happen. In research studies it has been found that most of the time older patients don't need to have their doses changed. However, it's recommended to keep an eye and check regularly for those who are above 75 years old or have more than one health condition. Suggested steps include;
- Evaluating the kidney and liver functions.
- Routine checks-on the levels of acid in the blood and liver enzymes
- Reducing the use of medications to lower the risks of drug interactions.
Administration to Pregnant Women: Risks and Current Recommendations
Febuxostat is often labeled as category C for pregnancy in regions due to findings from animal studies showing impacts on fetal development, such as skeletal abnormalities and lower fetal weight; however human data remains scarce in this area.
It is advised to avoid using febuxostat during pregnancy unless it is deemed essential and the benefits, for the mother are deemed to outweigh any risks to the fetus. Doctors are encouraged to consider ways of managing in pregnant women that do not involve medication.

Use During Lactation: Potential Transfer to Breast Milk and Precautions
The elimination of feboxustat, through human breast milk remains uncertain at this time. Understanding its characteristics of being lightweight and lipid soluble suggests that a potential transfer, to breast milk may occur.
Caution is advised for nursing mothers when considering its administration. Guidelines recommend the following precautions;
- Balancing the need for care with the risk of exposing infants.
- Pondering the possibility of pausing breastfeeding while undergoing treatment.
- If you suspect exposure, make sure to keep an eye on infants for any changes, in their kidney or liver function.
Administration to Pediatric Patients: Safety and Efficacy Considerations
The effectiveness and safety of febuxostat in children have not been confirmed yet. It is not permitted for use by those under 18 years. Due to clinical information available for children’s usage of febuxostat and the lack of official approval for pediatric applications officially, its off-label administration should only be done in a controlled research setup. When dealing with gout triggered by genetic metabolic disorders or blood-related issues; it is vital to follow a specialized treatment plan focusing on alternative medications proven safe for children.

Side Effects of Febuxostat
Gastrointestinal Symptoms (Nausea, Diarrhea)
Digestive issues are commonly noted as side effects linked to febxostat use, by people who take it. Medication users might encounter a range of symptoms from stomach discomfort to ongoing queasiness. Some individuals may have diarrhea in the initial stages of treatment, though it usually resolves without intervention. Noteworthy signs include;
- Feeling queasy without throwing up.
- Having loose stools. Experiencing more frequent bowel movements.
- Experiencing discomfort in the abdomen
The impact of these effects usually lasts for a time. Varies based on the dosage taken. To reduce stomach discomfort in those who are sensitive to it, taking this with food can help.

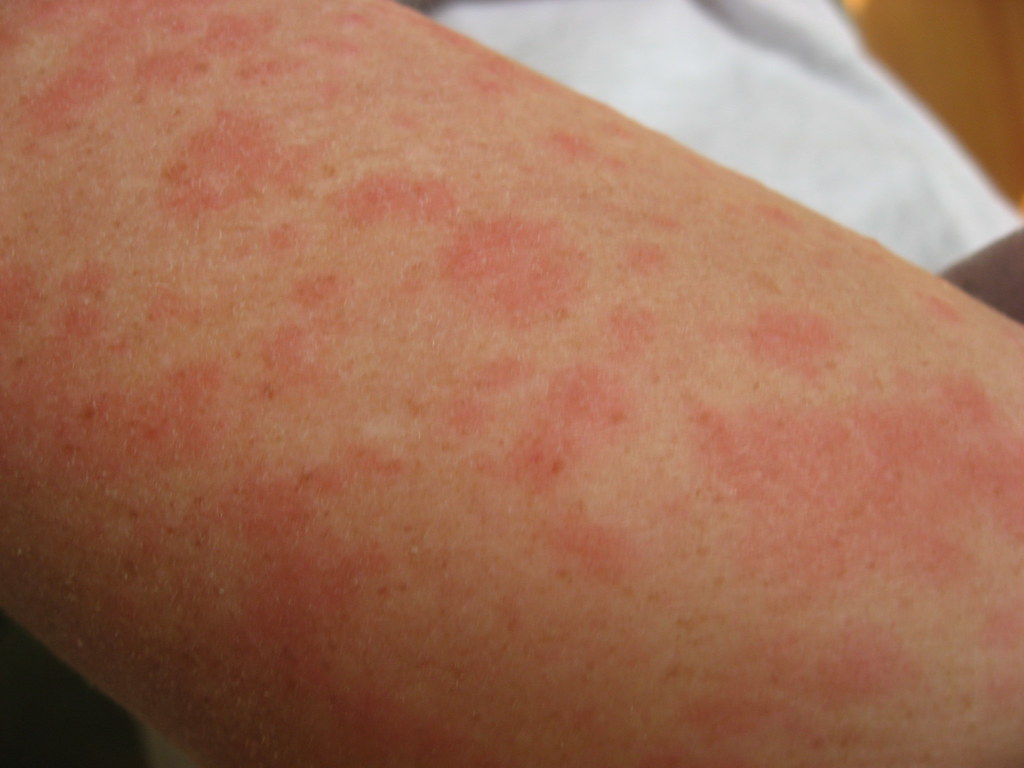
Rash and Skin Reactions
Skin reactions to feboxustat might show up as rashes, with raised bumps or hives and general skin irritation that's not specific in nature; typically harmless, but important to keep an eye out for as they could signal serious allergic reactions developing later.
Clinical factors to consider are:
- Symptoms usually start appearing in the weeks of treatment.
- Upon cessation or when using antihistamines a decision will be made.
- Looking out for indications of advancing towards skin reactions.
Liver Function Abnormalities
Febuxostat has been linked to slight increases in liver enzymes called hepatic transaminases, which may not show symptoms and can be reversed by stopping or adjusting the dosage of the medication. Parameters to monitor include;
- Alanine aminotransferase (ALT)
- AST stands for aspartate transaminase.
- The enzyme known as phosphatase (ALPs).
Before starting and, at intervals during treatment, it is advised to conduct routine liver function tests to assess for any abnormalities or issues with the liver function of patients.
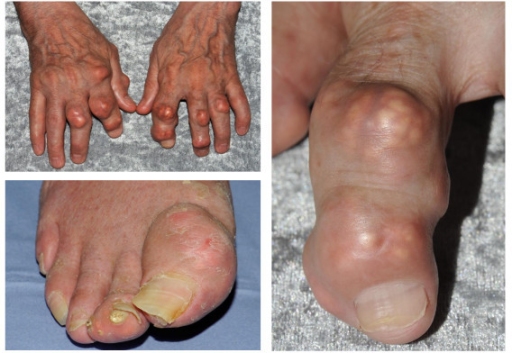
Joint Pain and Musculoskeletal Issues
Starting feboxostat treatment may actually cause a worsening of gout symptoms as it helps release acid deposits in the body—a surprising twist that can lead to sudden pain in the joints as well, as inflammation and limited movement. Other issues related to muscles and bones that could arise are;
- Muscle aches
- Joint pains are not associated with gout attacks.
- Muscle tightness, without any signs of inflammation.
It's important to take colchicine or NSAIDs in the few months of treatment to reduce the chance of experiencing flare-ups and improve how well you stick to your treatment plan.
Febuxostat Side Effects on the Kidney
While febuxostat is mostly broken down by the liver as its primary route of metabolism, in the body can result in issues as well as reported cases of renal adverse events occurring occasionally even though they are usually mild in nature it is important to remain vigilant especially when dealing with patients who already have kidney issues or are taking other medications that might be harmful, to their kidneys. Potential effects related to the kidneys may include;
- Increase in the level of creatinine, in the blood serum.
- Reduction of creatinine clearance in susceptible individuals
- Decreased kidney injury, in people who are prone to it.
It is recommended to monitor kidney function. eGFR and serum creatinine. Particularly, for older individuals and those with underlying health issues, like diabetes or hypertension.
Serious and Rare Side Effects of Furic Febuxostat
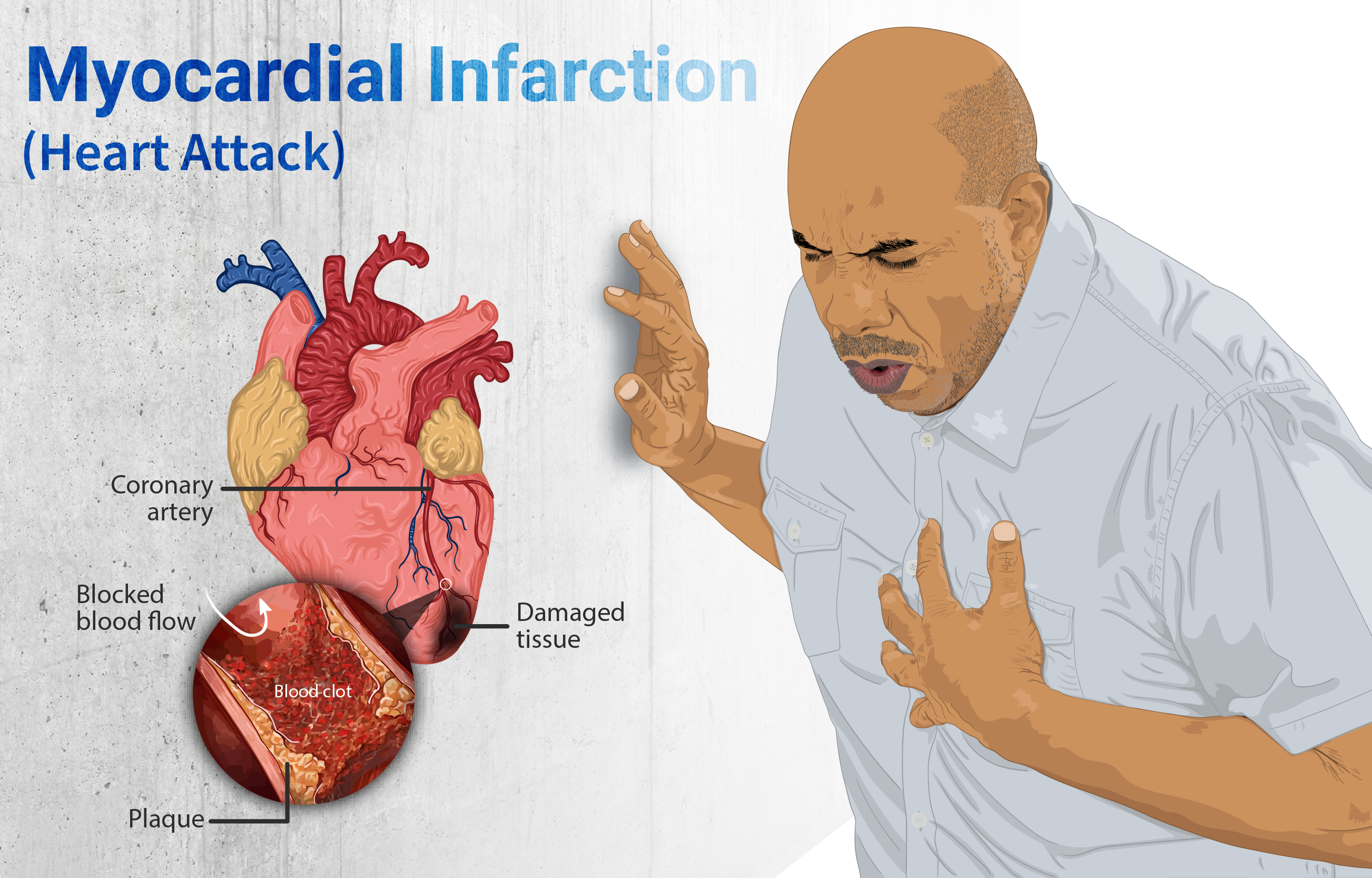
Cardiovascular Risks, Including Heart Attack and Stroke
The Cardiovascular safety of Febuxostat has come under examination after the CARES trial was released to the public. The research showed a chance of heart-related death, among individuals taking febuxostat compared to allopurinol users— those already suffering from cardiovascular conditions. Some possible outcomes are;
- Heart attack.
- A blockage in blood flow to the brain, known as a Stroke.
- Unexpected passing due to heart failure.
Regulatory bodies have alerted individuals to use caution when treating high-risk patients and stress the importance of assessing risks and benefits on a case-by-case basis before starting any treatment.
Severe Hypersensitivity Reactions
Rare instances of hypersensitivity reactions can be triggered by Febuxostat but occur infrequently in practice. One may observe signs indicating the onset of conditions, like Drug Reaction, with Eosinophilia and Systemic Symptoms (DRESS), alongside syndromes affecting multiple organs.
- Fever accompanied by a skin rash of intensity.
- Swollen lymph nodes
- Involvement in the liver or kidneys
It is crucial to stop using it if you show any signs of sensitivity and seek immediate medical attention for organ issues.
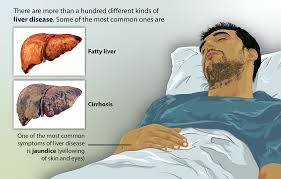
Hepatotoxicity and Liver Failure
While rare occurrences have linked febuxostat to damage and even severe cases of acute liver failure believed to result from immune responses rather than dosage levels; signs, in clinical settings include;
- Yellowing of the skin and eyes is often caused by liver issues.
- Pain, in the right upper quadrant.
- A significant increase, in transaminases and bilirubin levels was observed.
In situations where liver damage is suspected it is important to stop taking the medication and seek advice, from a liver specialist.
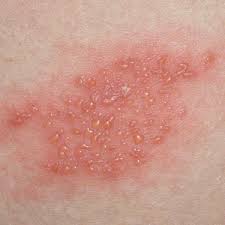
Serious Skin Reactions (Stevens-Johnson Syndrome)
One dermatologic event that causes concern is Stevens-Johnson syndrome (also known as SJS), a serious mucocutaneous condition characterized by severe epidermal necrosis. Febuxostat has been occasionally associated with SJS. Mostly, in individuals who have a tendency for drug allergies. Some key features include;
- A widespread rash causing discomfort, with blisters.
- Ulceration, in membranes (mouths and genitals).
- Skin Symptoms affecting the body.
Recognizing the issue early and promptly transferring the patient to a burn unit or intensive care facility is vital to reduce the impact and improve the chances of recovery, for those affected.
Febuxostat Interactions
Interaction with Azathioprine and Mercaptopurine
Febuxostat shows an interaction in how it works with purine analogs like azathioprine and 6 MP as they both go through the xanthine oxidase pathway, which febuxostat strongly blocks. This combination can lead to a buildup of these system suppressants, causing serious blood-related issues, like bone marrow suppression and low blood cell count. Therefore, it's advised not to use them. Key things to remember in practice are;
- The risk of myelosuppression includes the possibility of infections that could be life-threatening.
- If exposure happens by accident, it's recommended to keep an eye on the blood counts.
- Whenever possible, replace with representatives.
In situations involving transplants or autoimmune conditions where the use of azathioprine or mercaptopurine is essential, for treatment success, febuxostat should be carefully avoided.
Effects When Combined with Theophylline
Even though febxostat doesn't interact much with cytochrome P450 enzymes, as per in vitro studies it might slightly raise the levels of theophylline in the bloodstream by interfering with its liver metabolism. Theophylline is a bronchodilator with a range, and this interaction could potentially lead to increased risks of toxicity, such as;
- Tachycardia
- Difficulty sleeping and shakiness.
- In situations, seizures may occur.
It's important to keep an eye on patients who are taking medications for any signs of theophylline toxicity when starting feboxostat treatment. It might be an idea to check their theophylline levels, in the blood and make dose adjustments as needed.

Interactions with Other Medications Affecting Uric Acid Levels
Many different factors can impact the levels of acid in the blood. Should be taken into consideration when taking feboxustat medication.
- Thiazide and loop diuretics can lead to increased reabsorption of urate, potentially reducing the effectiveness of feboxustat.
- Low-dose aspirin can paradoxically increase acid levels through its effects, on the kidneys.
- Cyclosporine can affect the excretion of urate, requiring monitoring.
- Probenecid enhances the effects of acid excretion. Should be used with care when combined with other medications.
Adaptations might be necessary based upon the approach, to reducing acid levels and considering each person's kidney function individualy important reviews of medications are crucial to prevent adverse reactions or unforeseen interactions.
Warnings and Important Precautions When Using Furic (Febuxostat)
Cardiovascular Risk Management
A major concern linked to Furic (febuxostat) is its risk to heart health, as shown in the CARES trial findings, which indicated rates of all cause and cardiovascular deaths among patients with prior heart disease using febuxostat instead of allopurinol. Tips, for caution include;
- Before starting any treatment, it's important to conduct an evaluation of the cardiovascular risks, to health.
- Regularly check for signs of heart issues while undergoing treatment.
- It is advisable to steer clear of high-risk patients unless there are no options available.
When it comes to prescribing feboxustat to patients, with existing heart conditions it's crucial to involve them in the decision making process.
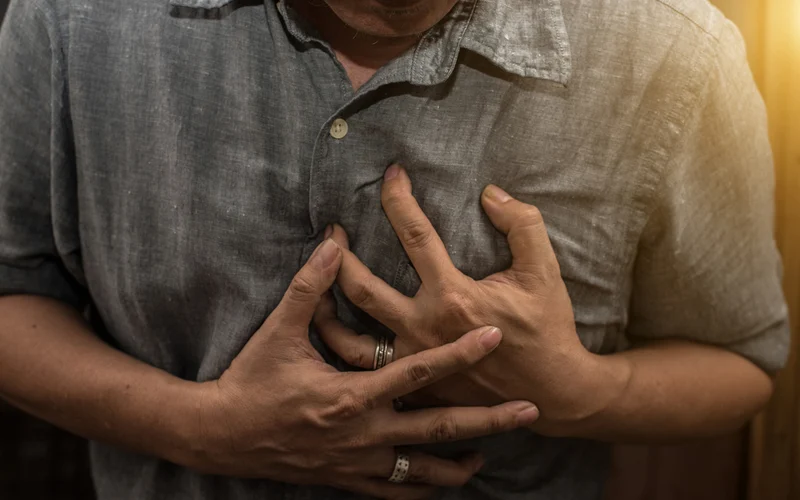

Monitoring Liver Function During Treatment
Elevations in liver enzymes can sometimes occur when using feboxustat. It may not always show symptoms, but it could lead to liver issues over time. The suggested monitoring plan is as follows;
- Before starting treatment it is recommended to conduct liver function tests (referred to as LFTs).
- Regular evaluations, within a half year period.
- If you notice any signs, like yellowing of the skin or feeling unusually tired it's important to seek assessment.
When liver function test levels remain high for a period of time it might be necessary to lower the dosage or stop the medication altogether, especially if there are symptoms affecting the whole body.
Risk of Gout Flares During Therapy Initiation
Enough starting treatment to reduce acid levels can trigger sudden gout attacks as uric acid is released from tissues unexpectedly. It's widely known that there is a rise, in the frequency of gout flares in the months of taking feboxostat. Suggestions, for prevention include;
- Low dose of colchicine ranging from 500 micrograms, to 10000 micrograms, per day.
- If colchicine cannot be used, consider NSAIDs.
- Continuing preventive measures, for a minimum of six months, after starting treatment.
It's crucial to inform patients not to stop taking feboxostat when experiencing a flare up since it could delay recovery and disrupt urate levels.
Avoidance in Patients with Severe Ischemic Heart Disease
Patients, with heart disease or recent heart attacks should avoid using feboxustat due to the increased chance of major cardiovascular issues (known as MACE). In this group of patients, the balance between the risks and benefits of this medication is not favorable. Other options for reducing acid levels, like allopurinol and uricosurics should be looked into if possible, from a standpoint. If the use of feboxustat cannot be avoided, closely monitoring the patient’s health during treatment is crucial.
Contraindications for Furic Febuxostat
Known Hypersensitivity to Febuxostat
People who have experienced a response to febxostat should avoid using it again as it can lead to severe skin rash or other anaphylaxis, indicating an immune system intolerance. It is crucial to avoid re-exposure in cases where symptoms of hypersensitivity are evident.
- Struggling to breathe or experiencing a bronchospasm
- Generalized urticaria or angioedema
- Instances of multiorgan hypersensitivity reactions, like Drug Reaction, with Eosinophilia and Systemic Symptoms (DRESS)
Use in Patients Being Treated with Azathioprine or Mercaptopurine
Co-administering febuxostat, with either azathioprine or 6 MP is not recommended because it can lead to blood cell deficiencies due to drug buildup in the body. This interaction is expected based on how the drugs work and can have consequences for patients who are immunosuppressed and taking these purine analog medications. Alternative treatments, for gout should be considered for these individuals.
Contraindications Related to Pre-existing Cardiovascular Disease
Individuals who have recently experienced syndrome or unstable angina or cerebrovascular events face elevated risks when using febuxostat due to its link, to higher cardiovascular mortality rates. In high-risk groups it is advised to avoid using the drug unless alternative treatments are ineffective or not well tolerated. Specific situations where febuxostat should not be used include;
- Myocardial infarction within the last 6 months
- Irregular heart rhythms
- Recent Ischemic stroke
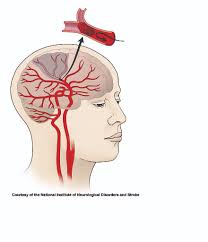
When dealing with patients it's important to consult a cardiologist and explore options, for reducing uric acid levels.
Careful Administration and Monitoring Requirements
Regular Monitoring of Uric Acid Levels
Managing hyperuricemia effectively with Furic (febuxostat) requires checking serum urate levels to adjust treatment and track adherence accurately. Targeting urate levels below 6 mg/dL is typically recommended, with a goal of 5 mg/dL, for individuals, with gout or advanced joint issues. Recommended monitoring schedules include;
- Before starting treatment we need to establish a measurement.
- After starting or adjusting the dosage, it's recommended to reevaluate progress within 2 to 4 weeks.
- Routine checks every 3 to 5 months while, on maintenance treatment.
Prolonged high levels of acid could lead to increasing the dosage of medication or making changes, to ones lifestyle habits or re-assessing potential underlying causes of hyperuricemia.
Liver Function Testing Schedule
Liver damage is still a known risk of taking febuxostat medication as a side effect. A regular check-up of liver function is essential, for monitoring its effects in medical safety. The drug is broken down in the liver, and occasional increases, in enzymes are quite typical, though often go unnoticed. A detailed examination plan involves;
- Baseline liver function tests include ALT (alanine aminotransferase), AST (aspartate aminotransferase), ALP (alkaline phosphatase), and bilirubin levels.
- Be sure to conduct follow-up evaluations at the 2-week and 4-week marks during the treatment period.
- Yearly assessment, throughout management.
If the enzyme levels show an increase— more than three times the normal range—it is important to reconsider the dosage or stop the medication altogether if there are signs of jaundice or digestive issues along, with feeling unwell.
Cardiovascular Risk Evaluation During Long-Term Therapy
Considering the link between febuxostat. Heightened fatalities in individuals, with prior ischemic heart conditions.
Handling Precautions for Furic Febuxostat
Safe Handling Guidelines for Patients and Caregivers
When dealing with Furic (febuxostat), it's important to handle it to ensure its effectiveness and prevent any exposure. Though it's not considered hazardous, in use situations it's advisable to take precautions, especially when working with children, individuals, or those, with weakened immune systems. Some key precautions to keep in mind are;
- Remember to wash your hands and after handling the tablet.

- Remember to store tablets in their original blister packaging until you're ready to use them.
- Please refrain from crushing or splitting unless specifically instructed.
- Remember to wear gloves or use dispensing tools when touching tablets for someone.
Make sure to keep the medicine in a place where children and pets can't access it easily as accidental consumption can cause harm to those who are not supposed to take it according to their prescription.
Proper Disposal of Unused or Expired Medication
Unused or expired febuxostat should be carefully discarded to avoid any misuse or environmental harm, to prevent any ingestion risks as well as contamination of the surrounding. The medication should not be flushed down the toilet or thrown in regular household trash unless local regulations explicitly allow it. The suggested ways of disposal include;
- Engaging in programs, for the disposal of medication.
- Back, to the drugstores that have places to return medications.
- Adhering to guidelines for disposing of waste at the local level.
If you can't return the tablets and need to dispose of them at home as a resort, with permission to do so; mix them with something, like old coffee grounds or cat litter, in a sealed plastic bag before throwing them in the trash.
Overdosage and Management of Furic (Febuxostat) Toxicity
Symptoms of Febuxostat Overdose
Medical information about febuxostat overdose is not widely available; however taking much of it can lead to negative effects ranging from mild to severe reactions have been observed in reported instances of overdose cases where high doses were taken intentionally or accidentally. Some signs and symptoms that may occur include symptoms such, as;
- Feeling extremely nauseous and throwing up uncontrollably.
- Feeling a headache or dizziness and experiencing disturbances

- High levels of liver enzymes were detected.
- Worsening of gout symptoms caused by the movement of acid.
Rare instances of instability should not be disregarded entirely; in patients, with existing comorbidities or those taking multiple medications concurrently.
Immediate Steps and Supportive Treatment Strategies
In case of a suspected situation arises with usage prompt medical assistance is crucial. There is no antidote designated for feboxustat treatment involves primarily addressing symptoms. Providing support accordingly. Key steps to take include ;
- Assessing the airway and breathing while also checking circulation (ABC).
- Administering charcoal is effective if done within an hour of ingestion.
- Monitoring signs, like heart rate and liver, and kidney health.
- Administering fluids through an IV to help the kidneys remove waste products.
It's important to keep an eye, on the heart function for patients with a past of heart problems and to also assess the brain for any issues like seizures or changes in mental state.
Role of Dialysis and Intensive Care in Severe Cases
Febuxostat has an attachment to plasma proteins. Is processed by the liver, which makes dialysis ineffective for removing the drug from the body efficiently. However in cases of toxicity leading to system failure or persistent low blood pressure, supportive care in an intensive care unit may be necessary. Some reasons for admission, to the ICU could be;
- The sudden onset of liver failure is accompanied by blood clotting issues
- Serious irregular notable abnormalities, in an electrocardiogram
- A change, in condition necessitating the safeguarding of the airway.
In these situations management requires collaboration, across fields like nephrology and cardiology alongside care experts to achieve a successful recovery through timely and suitable treatment measures, with the outcome heavily influenced by the quantity consumed and how quickly treatment is administered.
Furic, Febuxostat FAQ
- When to stop Febuxostat?
- What is Febuxostat?
- What is Febuxostat used for?
- Why is Febuxostat so expensive?
- Which is safer Febuxostat or Allopurinol?
- Which is better Colchicine vs Febuxostat?
- What is Febuxostat used to treat?
- What is the most common side effect of Febuxostat?
- How long should I take Febuxostat?
- Does Febuxostat damage liver?
- How do you know if Febuxostat is working?
- Can I stop Febuxostat suddenly?
- Can Febuxostat damage kidneys?
- What drugs should not be taken with Febuxostat?
- Are Allopurinol and Febuxostat the same?
- Can Febuxostat be taken at night?
- Can Febuxostat cause gout?
- Can Febuxostat be taken without food?
- Can Febuxostat be cut in half?
- How Febuxostat works?
- Where is Febuxostat metabolized?
- When to take Febuxostat?
- When to stop Febuxostat?
- Febuxostat which class of drug?
- Will Febuxostat raise blood sugar?
- How long will Febuxostat take to work?
- How to take Febuxostat?
- Febuxostat 40 mg how many times a day
- What is Febuxostat used to treat?
- How fast does Febuxostat work?
- How does Febuxostat work for gout?
- What are the side effects of Febuxostat?
When to stop Febuxostat?
If you experience liver damage or allergic reactions to Febuxostat or have heart-related issues while taking it, it is advisable to discontinue its use as a precautionary measure and consult your doctor promptly for guidance on next steps, for managing your condition effectively.
What is Febuxostat?
Febuxostat functions as a xanthine oxidase inhibitor, working to decrease the production of acid within the body. It is typically prescribed for treating gout and hyperuricemia conditions.
What is Febuxostat used for?
Febuxostat is prescribed to reduce the levels of acid in the blood of individuals suffering from long-term gout, aiding in preventing gout flare-ups and protecting joints from damage caused by the accumulation of urate crystals.
Why is Febuxostat so expensive?
The high cost of Febuxostat can be attributed to factors such, as patent protections and the complexities involved in manufacturing it well as its limited availability in generic form and the expenses tied to research and development, along with regulatory approval processes.
Which is safer Febuxostat or Allopurinol?
Allopurinol is typically viewed as an option for the majority of patients when it comes to risk factors, rather than Febuxostat, which might be more suitable for individuals with slight to moderate kidney issues but has a greater concern for heart-related complications.
Which is better Colchicine vs Febuxostat?
Colchicine is typically prescribed to address sudden gout flare-ups, and Febuxostat is commonly prescribed for managing acid levels over a period of time. They have their own roles and are frequently utilized together instead of being seen as mutually exclusive options.
What is Febuxostat used to treat?
Febuxostat is commonly prescribed to manage levels of acid in individuals suffering from gout when Allopurinol is not well tolerated or fails to provide sufficient relief.
What is the most common side effect of Febuxostat?
One of the issues with Febuxostat is that it can cause results, in liver function tests commonly seen among users experiencing rash or nausea and joint pain as well.
How long should I take Febuxostat?
Febuxostat is commonly used for a period to regulate acid levels, in the body and the length of treatment varies based on individual health status and reaction; it is important not to discontinue its use without proper medical advice.
Does Febuxostat damage liver?
Febuxostat has the potential to increase liver enzyme levels and occasionally lead to liver damage, in situations; hence it is advised to undergo monitoring of liver function while undergoing treatment.
How do you know if Febuxostat is working?
The way we determine if the treatment is working involves checking the levels of acid in the blood and tracking how gout flare-ups occur as time goes on.
Can I stop Febuxostat suddenly?
Stopping Febuxostat suddenly can lead to gout flares caused by changes, in acid levels in the body so it's essential to have a healthcare provider oversee any decision to discontinue the medication.
Can Febuxostat damage kidneys?
Febuxostat is generally considered safe for the kidneys. It is recommended to be cautious when prescribing it to patients, with existing kidney issues and to regularly check their kidney function.
What drugs should not be taken with Febuxostat?
It's important to avoid using Azathioprine and Mercaptopurine along, with Theophylline when taking Febuxostat as there could be interaction risks involved in doing so. Remember to discuss your medications with your doctor for an effective treatment plan.
Are Allopurinol and Febuxostat the same?
They are not the medications as they have chemical structures and ways in which they work in the body to reduce uric acid levels—each with its own set of potential side effects and how they are broken down in the body.
Can Febuxostat be taken at night?
Febuxostat can be taken in the evening or, at the time each day regardless of meals.
Can Febuxostat cause gout?
Paradoxically and interestingly enough,when taking Febuxostat there's a possibility that it might cause gout flares due, to the changes, in acid levels. It's practice to consider anti-inflammatory medication at the beginning stages.
Can Febuxostat be taken without food?
You can take Febuxostat with or without food because food doesn't really impact how it's absorbed by the body.
Can Febuxostat be cut in half?
It's usually best not to break or split Febuxostat tablets unless your doctor tells you to do.
How Febuxostat works?
Febuxostat prevents xanthine oxidase from converting purines into acid by inhibiting the enzymes activity in the bodys metabolic processes This helps reduce the levels of uric acid present, in the bloodstream.
Where is Febuxostat metabolized?
Febuxostat is mainly broken down in the liver through processes involving conjugation and oxidation.
When to take Febuxostat?
Febuxostat is usually consumed a day at a time daily to ensure stable blood levels.
When to stop Febuxostat?
If you experience side effects from Febuxostat, it should be stopped. If it does not provide any therapeutic benefits as determined by your doctors recommendation.
Febuxostat which class of drug?
Febuxostat is classified as a type of medication known as xanthine oxidase inhibitors.
Will Febuxostat raise blood sugar?
Febuxostat typically doesn't lead to blood sugar levels often; however its recommended to keep an eye on individuals.
How long will Febuxostat take to work?
Reducing acid levels and alleviating gout flare-ups with Febuxostat can require a week to a couple of months to show noticeable improvements.
How to take Febuxostat?
You should take Febuxostat by mouth a day either with or, without food at the time every day as directed by your doctor.
Febuxostat 40 mg how many times a day
Usually, the usual dose of Febuxostat 40 mg is to be taken once a day unless instructed differently by a healthcare professional.
What is Febuxostat used to treat?
Febuxostat is commonly prescribed for managing levels of uric acid in individuals suffering from gout.
How fast does Febuxostat work?
The levels of acid start to decrease in a matter of days; however; noticeable relief, from gout symptoms may not be experienced until after a week.
How does Febuxostat work for gout?
Febuxostat works by lowering the production of acid in the body to prevent the formation of crystals, in the joints and reduce the frequency and intensity of gout flare-ups.
What are the side effects of Febuxostat?
Typical adverse reactions may involve levels of liver enzymes, skin rashes, feelings of nausea and discomfort, in the joints. Common but severe potential dangers encompass heart related incidents and harm to the liver.