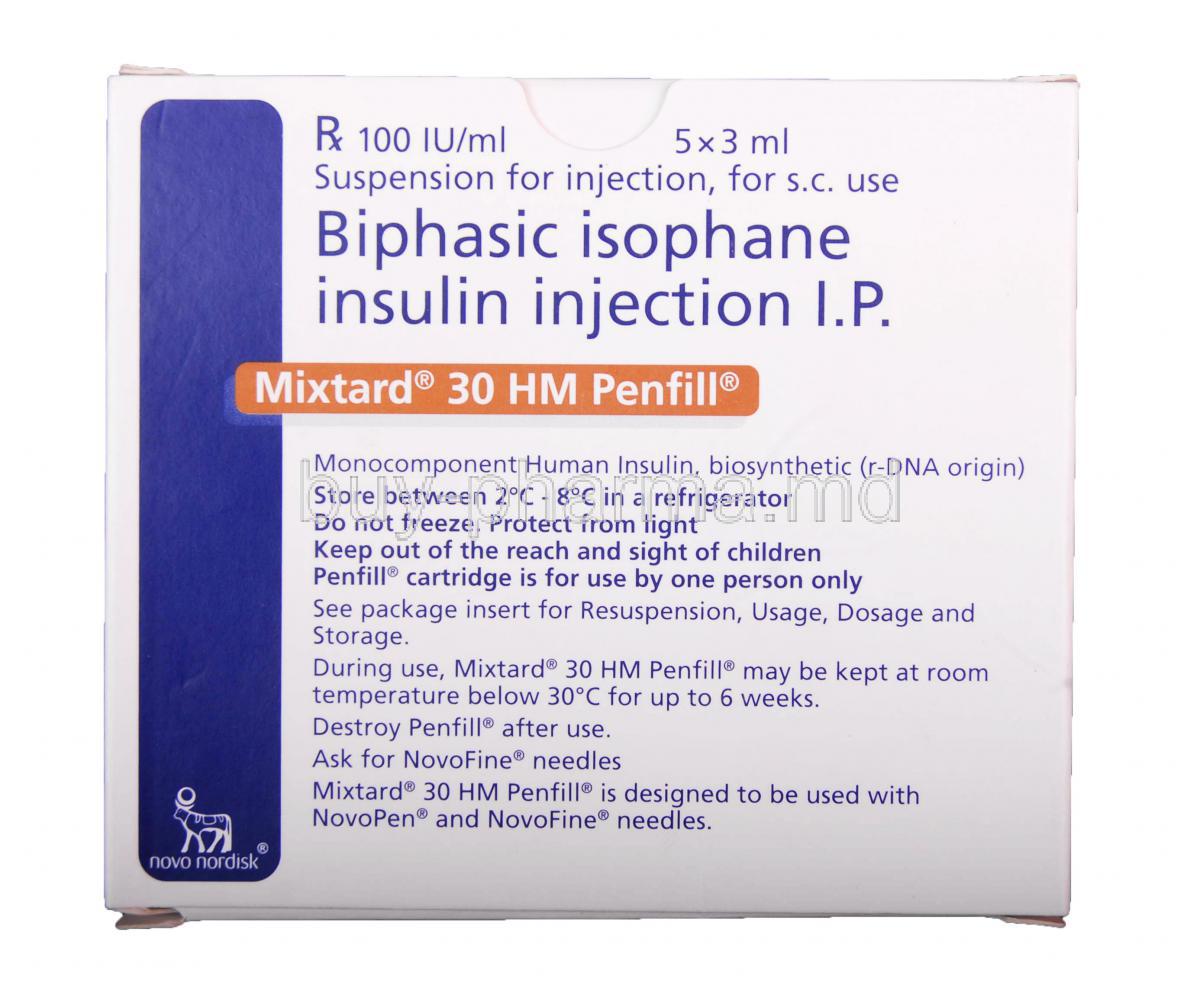
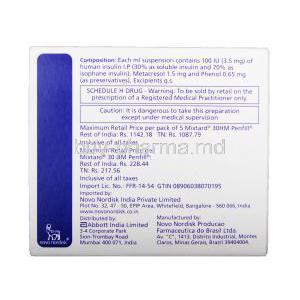
Mixtard 30 HM Pen-filled Injection
- Introduction to Mixtard 30 HM Pen-filled Injection
- Composition and Formulation Details
- Mechanism of Action: How Mixtard 30 HM Pen-filled Injection Works
- Approved Uses and Indications
- Off-label Uses of Mixtard 30 HM Pen-filled Injection
- Dosage and Administration Guidelines
- Special Population Administration
- Storage Instructions for Mixtard 30 HM Pen-filled Injection
- Common Side Effects of Mixtard 30 HM Pen-filled Injection
- Other Possible Side Effects
- Drug Interactions Involving Mixtard 30 HM Pen-filled Injection
- Warnings and Important Precautions
- Contraindications for Mixtard 30 HM Pen-filled Injection
- Careful Administration Considerations
- Handling and Administration Precautions
- Overdose and Emergency Management
Introduction to Mixtard 30 HM Pen-filled Injection
Overview of Mixtard 30 HM Pen
Mixtard 30 HM Pen Filled Injection is an insulin delivery device designed for accurate diabetes mellitus management, allowing individuals to administer insulin on their own terms with ease and reliability.
Therapeutic class and classification
This medication falls under the category of drugs used to treat diabetes, as a mix of fast and slow human insulin types.
General indications and patient populations
Mixtard 30 HM Pen is recommended for use by adults and children diagnosed with Type 1 or Type 2 diabetes who need insulin to manage their blood sugar levels effectively.
Composition and Formulation Details
Active ingredients and their concentrations
Each milliliter of the solution contains 100 units of insulin, with a composition of 30% soluble insulin and 70% isophane insulin suspension.
Type of insulin (biphasic insulin)
Mixtard 30 HM falls under the category of insulin as it provides a quick sugar reduction and sustained glucose-lowering impact.
Mechanism of biphasic formulation (30% soluble insulin, 70% isophane insulin)
The working part keeps your blood sugar in check after the injection, and the slow-release part helps maintain stable glucose levels all day long.
Excipients and preservatives included
- Metacresol (preservative)
- Zinc chloride (stabilizer)
- Glycerol (tonicity regulator)
- Sodium phosphate buffers
- Water for injection
Mechanism of Action: How Mixtard 30 HM Pen-filled Injection Works
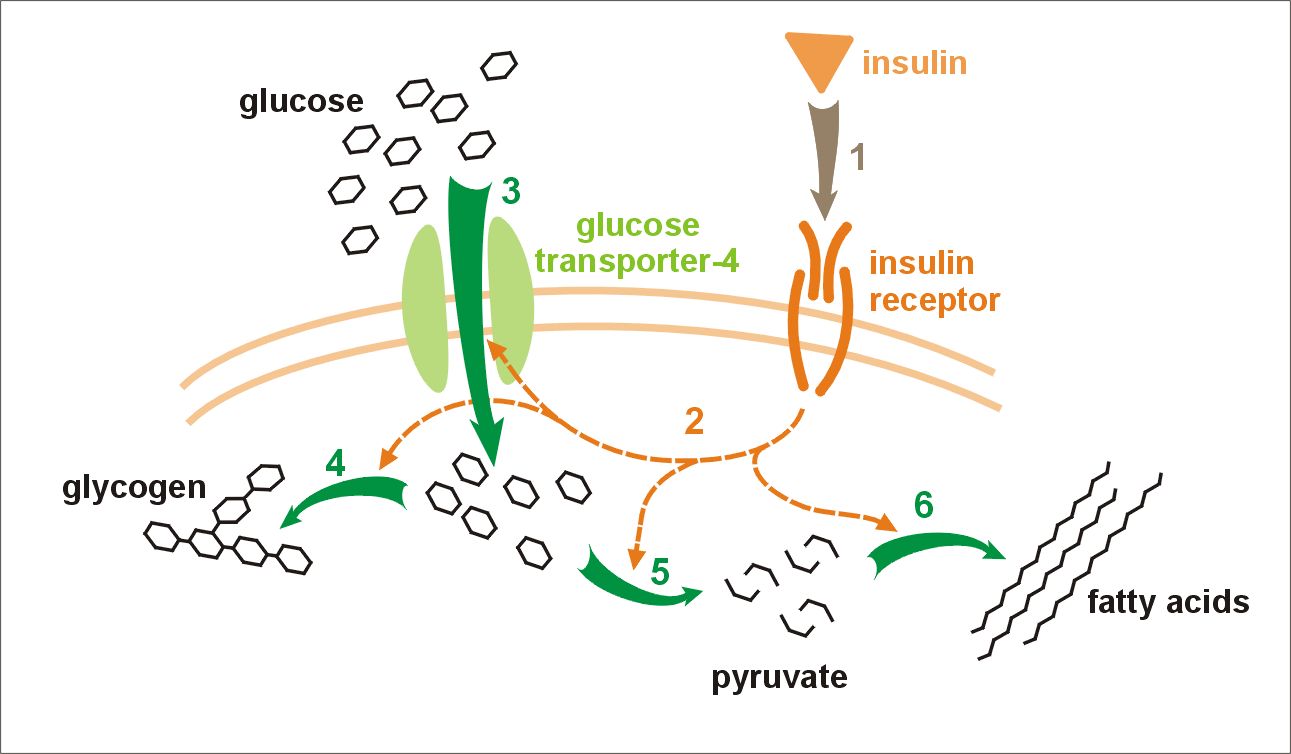
Insulin action on glucose metabolism
Mixtard 30 HM helps muscles and fat cells absorb glucose effectively, while also preventing the liver from producing glucose, thereby maintaining stable and normal blood sugar levels.
Onset, peak, and duration of action
- Onset: 30 minutes post-injection
- Peak action: 2-8 hours
- Duration: Up to 24 hours
Pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic profile
The way glucose control works can be affected by where you inject it and how active you are, since it balances long-term effects.
Approved Uses and Indications
Management of Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus
Management of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
Perioperative glycemic control
Use in gestational diabetes (if applicable)
Off-label Uses of Mixtard 30 HM Pen-filled Injection
Treatment of steroid-induced hyperglycemia
Management of diabetes secondary to pancreatitis
Transitional therapy during insulin pump interruption
Serves as a temporary insulin delivery method when insulin pump therapy is paused due to device failure or surgery.

Dosage and Administration Guidelines
Standard dosing regimens for adults
The dosage is individualized, generally initiated at 0.3 to 1.0 units/kg/day, divided according to patient needs and meal patterns.
Dosage adjustments based on blood glucose monitoring
Regular self-monitoring of blood glucose (SMBG) informs dosage adjustments, ensuring optimal control while minimizing the risk of hypoglycemia.

Titration strategies and individualized therapy
- Weekly dose adjustments based on fasting plasma glucose levels
- Incremental changes of 2-4 units recommended
Switching from other insulin regimens
Switching from basal combined insulin treatment plans necessitates adjustments, including dosage changes, to prevent sudden changes in blood sugar levels.
Administration technique and injection sites
Subcutaneous injections should be administered in the abdomen, thigh, upper arm, or buttocks, with rotation of injection sites to prevent lipodystrophy.
Timing of administration relative to meals
Typically injected approximately 30 minutes before meals to align insulin activity with postprandial glucose elevations.

Special Population Administration
Administration to Elderly Patients
Dose adjustments considering renal function
To start treatment cautiously, due to decreased kidney function, and adjust the dosage carefully by monitoring health closely is important.
Hypoglycemia risk management
Older people are more prone, to experiencing blood sugar levels so its crucial for them to monitor their glucose levels regularly.
Administration to Pregnant Women and Nursing Mothers
Insulin requirements during pregnancy
Insulin demands fluctuate significantly during pregnancy, often increasing during the second and third trimesters.
Safety profile during breastfeeding
Human insulin is considered safe for use while breastfeeding, as the amounts passed into breast milk have no harmful effects on the baby being nursed.

Administration to Pediatric Patients
Dosage considerations in children and adolescents
Pediatric dosing requires meticulous calculation based on body weight and dynamic metabolic demands during growth periods.
Monitoring and adjustment protocols
Children should undergo close supervision to adjust dosing for changes in physical activity, diet, and illness episodes.

Storage Instructions for Mixtard 30 HM Pen-filled Injection
Recommended storage conditions before and after first use
Pens that have not been used yet should be stored in a refrigerator, between 2°C and 6 °C. Once they are used, you can keep them at room temperature below 30°C for a maximum of 6 weeks.
Temperature sensitivity and protection from freezing
Freezing destroys the insulin formulation, rendering it ineffective. Exposure to direct heat and sunlight should also be avoided.
Shelf-life and expiry considerations
Ensure you inspect the expiration date before using it and dispose of any pen that has not been stored properly or has expired.
Handling opened pens
Remember to put the cap back on the pen after use to prevent contamination or damage over time.
Common Side Effects of Mixtard 30 HM Pen-filled Injection
Hypoglycemia and its symptoms
- Shakiness
- Palpitations
- Confusion
- Seizures in severe cases
Local injection site reactions
You might experience redness, swelling, or itching at the injection spot. It usually goes away on its own.
Weight gain
Insulin's increased muscle-building effects could result in weight gain. May require adjustments in diet and exercise routines.
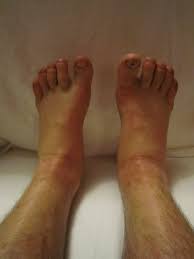
Edema and fluid retention
Other Possible Side Effects
Lipodystrophy at injection sites
Prolonged use of Mixtard 30 HM Pen-filled Injection at the same anatomical site can lead to lipodystrophy, characterized by localized atrophy or hypertrophy of adipose tissue. This phenomenon can affect insulin absorption, leading to unpredictable glycemic control. Rotating injection sites systematically mitigates this risk.
Allergic reactions (rash, pruritus)
Minor allergic reactions, such as erythematous rash, localized urticaria, and pruritus, may manifest at or near the injection site. These reactions are typically transient but warrant monitoring for progression.
Visual disturbances upon initiation
Rare systemic allergic reactions
Hypersensitivity reactions, like angioedema, can sometimes occur rarely with insulin therapy. May need medical attention for safety reasons.
Drug Interactions Involving Mixtard 30 HM Pen-filled Injection
Interaction with oral antidiabetic drugs
Concurrent use with sulfonylureas, meglitinides, or DPP-4 inhibitors can potentiate the hypoglycemic effect, necessitating careful dosage adjustment and enhanced glucose monitoring protocols.
Effects of beta-blockers, ACE inhibitors, and corticosteroids
- Beta-blockers can obscure typical hypoglycemia warning signs, such as tachycardia and tremor.
- ACE inhibitors may enhance insulin sensitivity, increasing hypoglycemia risk.
- Corticosteroids antagonize insulin action, often requiring insulin dose escalation during co-administration.
Interactions with diuretics and sympathomimetics
Thiazide diuretics and sympathomimetic agents can elevate blood glucose levels by impairing insulin action, mandating careful glycemic monitoring and potential insulin dose adjustment.
Alcohol interaction and glycemic control variability
Alcohol consumption can exacerbate the risk of delayed hypoglycemia, particularly during fasting states. It also impairs hepatic gluconeogenesis, compromising the body's counter-regulatory response to low blood glucose.
Warnings and Important Precautions
Risk of hypoglycemia and recognition strategies
Patients must be educated on recognizing early symptoms of hypoglycemia, including dizziness, sweating, palpitations, and confusion. Carrying rapid-acting carbohydrates is essential to manage sudden episodes effectively.
Importance of regular blood glucose monitoring
Regularly checking blood sugar levels using blood is crucial for keeping your blood sugar levels in check and preventing low blood sugar levels.
Adjustments during infection, surgery, or stress
Stressful conditions such as infections, trauma, or surgery can significantly alter insulin requirements. Temporary dose modifications and intensified glucose monitoring are critical during these periods.
Impact of travel, meal changes, and physical activity
- Time zone changes may necessitate adjustment of insulin dosing schedules.
- Alterations in meal patterns or composition require proactive insulin dose recalibration.
- Increased physical activity typically heightens insulin sensitivity, reducing insulin requirements and increasing hypoglycemia risk.
Contraindications for Mixtard 30 HM Pen-filled Injection
Hypersensitivity to insulin human or any excipients
Patients who have experienced reactions to insulin or any ingredient in Mixtard 30 HM should avoid using it and consult with a medical professional for alternative treatment options.
Hypoglycemic episodes without adequate monitoring
The medication should not be used by those who cannot regularly check their blood sugar levels, as it increases the chances of blood sugar and serious issues going unnoticed.
Careful Administration Considerations
Situations requiring close monitoring
Particular vigilance is warranted in patients undergoing significant lifestyle changes, illness, or medication adjustments that can influence insulin sensitivity and glucose metabolism.
Handling in patients with renal or hepatic impairment
Impairment, in both kidney and liver functions, can affect how the body processes insulin and removes it from the system, which could lead to a risk of hypoglycemia occurring. It is recommended to use caution when dosing medications and to regularly monitor blood sugar levels.
Cardiovascular risk factors and insulin therapy
Patients who already have heart conditions should be carefully treated to prevent weight gain and low blood sugar from insulin therapy which could potentially worsen their heart health outcomes.
Handling and Administration Precautions
Pen handling guidelines to prevent contamination
Make sure to use a needle every time you give an injection and refrain, from sharing pens to avoid any risk of cross contamination or spreading infections, between people.
Safe needle disposal practices
Be sure to dispose of used needles in an approved sharps disposal container authorized by the FDA. Avoid trying to recap or reuse needles to reduce the risk of injury.
Use of new needles for each injection
Using the needle multiple times can result in tips that might cause harm at the injection site and make the process more painful, while also adversely affecting how insulin is absorbed in the body's system. It is recommended to use a needle every time to maintain sterility and ensure proper administration techniques are employed for results.
Overdose and Emergency Management
Clinical manifestations of insulin overdose
Administered insulin in amounts mainly leads to blood sugar levels and is characterized by signs, like mental confusion, feeling physically weak, rapid heartbeat, profuse sweating, seizures, and passing out.
Immediate steps in managing severe hypoglycemia
- If the patient is conscious: administer oral glucose or a carbohydrate-rich snack.
- If unconscious or unable to swallow: administer glucagon intramuscularly or seek emergency medical assistance for intravenous dextrose administration.
Role of glucagon and intravenous glucose
Glucagon acts by stimulating hepatic glycogenolysis, rapidly raising blood glucose levels. In severe or prolonged hypoglycemia, intravenous dextrose infusion provides an immediate and controlled glucose source to restore normalcy.
Mixtard 30 HM Pen-filled Injection FAQ
- Which pen is used for Mixtard 30?
- How do you inject Mixtard 30?
- How do you use an insulin pen injection?
- Is mixtard 30 FlexPen reusable?
- When is the best time to give mixtard?
- Do insulin pens need to be refrigerated?
- What if I get blood in my insulin pen?
- How do you use a 30 HM Mixtard?
- What type of insulin is mixtard 30?
- What are the side effects of Mixtard 30 hm?
- How long does Mixtard 30 last?
- What is the difference between human insulin and mixtard?
Which pen is used for Mixtard 30?
(Penfill) or pre-filled pens
How do you inject Mixtard 30?
Subcutaneously
How do you use an insulin pen injection?
Grasp the insulin pen firmly in your hand with your thumb positioned on the injection site.
Is mixtard 30 FlexPen reusable?
Mixtard Penfill should only be used for injecting under the skin with a pen.
When is the best time to give mixtard?
30 minutes before a meal
Do insulin pens need to be refrigerated?
Yes
What if I get blood in my insulin pen?
There is a risk of transmitting bloodborne and bacterial pathogens to patients if the pen is shared among individuals, even after changing the needle.
How do you use a 30 HM Mixtard?
When giving yourself a dose of Mixtard insulin via injection, into your skin ( remember to avoid injecting it into a vein or muscle as it can be harmful and inefficient for absorption into your system, it's important to switch up injection sites, within a region, each time to prevent any issues like lump formation or skin indentations from occurring over time.
What type of insulin is mixtard 30?
Mixtard is a dual-acting insulin.
What are the side effects of Mixtard 30 hm?
Some possible side effects include a reaction at the injection site, low blood sugar levels (hypoglycemia), itching, skin thickening or pits at the injection site (lipodystrophy), swelling (edema), rashes, and weight gain.
How long does Mixtard 30 last?
24 hrs
What is the difference between human insulin and mixtard?
Mixtard is an injection suspension that contains insulin as its primary ingredient.