Introduction to Terbinafine
Overview of Terbinafine as an Antifungal Medication
Terbinafine is a widely prescribed antifungal agent used to eradicate superficial fungal infections of the skin, hair, and nails. Belonging to the class of allylamine antifungals, it is known for its high efficacy and fungicidal activity against dermatophytes. Unlike many antifungals that merely inhibit fungal proliferation, terbinafine actively destroys fungal cells, leading to faster and more definitive outcomes.
Historical Development and Medical Significance
Introduced in the early 1990s, terbinafine represented a breakthrough in antifungal therapy. Before its arrival, prolonged treatments with limited efficacy were the norm. Its ability to shorten treatment courses for nail and skin infections made it an essential therapeutic option. Today, terbinafine continues to be a cornerstone of dermatological and podiatric medicine.
Therapeutic Classification and Brand Names
Pharmacologically, terbinafine is classified as an allylamine antifungal. It is available under multiple brand names globally, including Lamisil, Terbisil, and various generic equivalents. Its broad accessibility ensures that patients across different regions can benefit from its proven antifungal properties.
Composition and Formulations
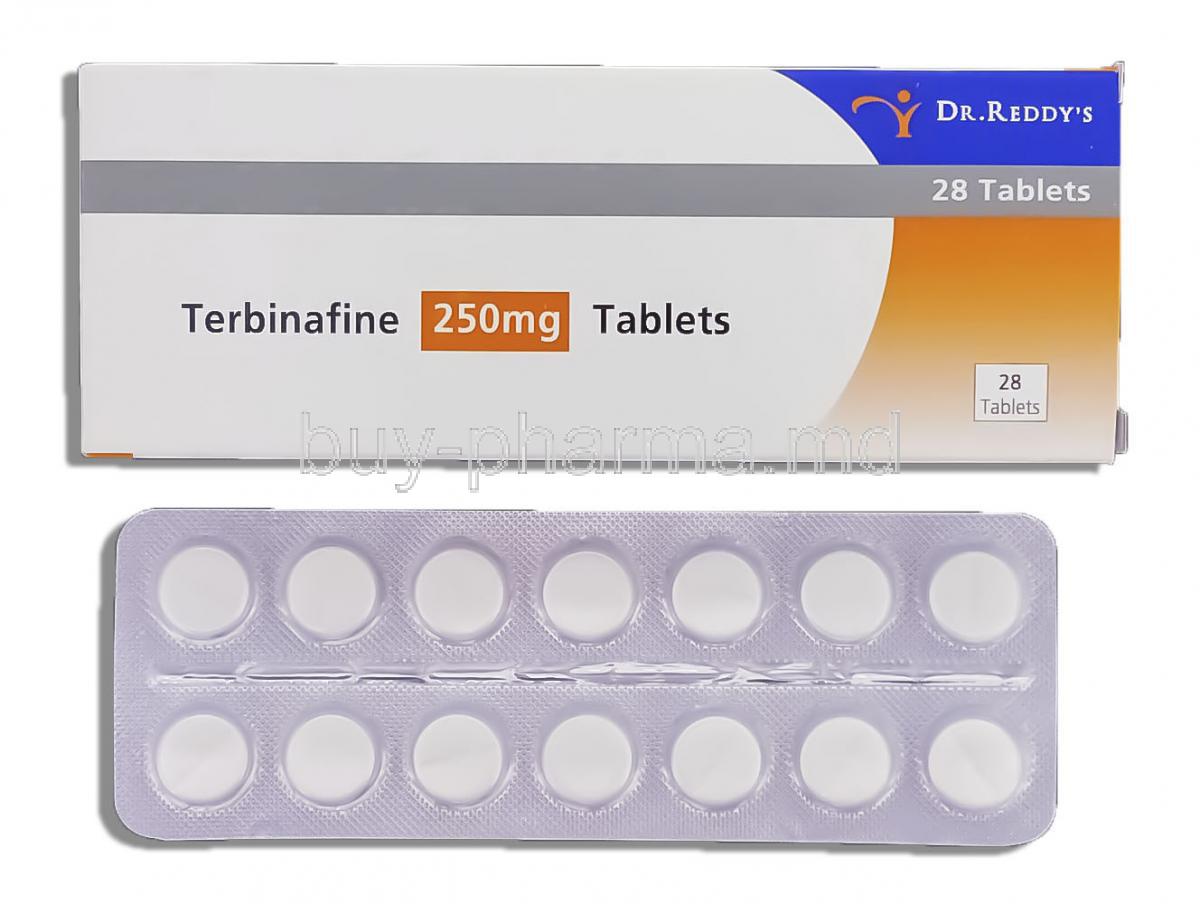
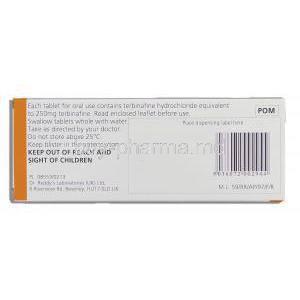
Active Pharmaceutical Ingredient: Terbinafine Hydrochloride
The primary active substance is terbinafine hydrochloride, a salt form that enhances solubility and stability. This compound targets fungal cell membranes, ultimately leading to cell death.
Available Dosage Forms
To address varying infection sites and severities, terbinafine is produced in multiple formulations:
- Oral Tablets – for systemic fungal infections, particularly of the nails.
- Topical Cream and Gel – designed for cutaneous infections such as ringworm or jock itch.
- Spray and Solution – useful for larger surface areas and scalp involvement.
Strengths and Common Packaging
Oral tablets are typically available in 250 mg strength, supplied in blister packs or bottles. Topical forms are provided in tubes, usually ranging from 10 g to 30 g, while sprays and solutions are packaged in applicator bottles for ease of use.
Mechanism of Action: How Terbinafine Works
Inhibition of Squalene Epoxidase in Fungal Cells
Terbinafine acts by inhibiting the enzyme squalene epoxidase, a crucial catalyst in the ergosterol biosynthesis pathway. Ergosterol is a vital component of fungal cell membranes, and its depletion leads to cellular vulnerability.
Disruption of Ergosterol Synthesis and Fungal Cell Membrane Integrity
By blocking ergosterol production, terbinafine causes toxic accumulation of squalene within fungal cells. This dual effect both damages the membrane and interferes with cellular survival, ultimately causing fungal cell death.
Fungicidal vs. Fungistatic Effects
Unlike fungistatic drugs that merely halt fungal growth, terbinafine exerts fungicidal activity against dermatophytes. This distinction contributes to shorter treatment durations and higher cure rates for nail and skin infections.
Specificity for Dermatophytes, Yeasts, and Molds
Terbinafine exhibits high specificity against dermatophytes such as Trichophyton species. It also demonstrates activity against certain yeasts, including Candida, and molds, although its efficacy may vary depending on the organism.
Approved Medical Uses
Onychomycosis (Fungal Nail Infection)
One of the most common indications, terbinafine tablets are highly effective in treating nail fungus. Treatment courses typically last several weeks to months, depending on the nail growth rate and severity of infection.
Tinea Infections (Athlete’s Foot, Jock Itch, Ringworm)
Topical terbinafine is frequently prescribed for dermatophyte infections of the skin. Its rapid onset of action provides symptomatic relief from itching, redness, and scaling within days.
Cutaneous Candidiasis
Though not its primary target, terbinafine demonstrates activity against certain Candida infections of the skin. It may be considered in patients intolerant to azole antifungals.
Pityriasis (Tinea) Versicolor
Terbinafine topical formulations can be used to treat this superficial infection caused by Malassezia species. Treatment helps restore normal skin pigmentation and reduces recurrence rates.
Off-Label and Investigational Uses
Treatment of Sporotrichosis
Terbinafine has shown efficacy in treating sporotrichosis, a chronic fungal infection often acquired through plant material. Though itraconazole remains the drug of choice, terbinafine serves as an alternative in selected cases.
Adjunct Therapy in Chromoblastomycosis
In difficult-to-treat fungal diseases such as chromoblastomycosis, terbinafine has been utilized in combination regimens. This approach enhances overall treatment outcomes in resistant cases.
Rare Dermatophyte Infections in Immunocompromised Patients
Immunocompromised individuals may develop unusual or persistent fungal infections. Terbinafine’s fungicidal activity makes it a valuable tool for managing such cases under careful medical supervision.
Potential Use in Pediatric Onychomycosis and Difficult-to-Treat Cases
Although not universally approved for pediatric use, terbinafine is increasingly studied in children with nail infections. Evidence suggests it may offer a safe and effective solution for refractory fungal infections in this group.
Dosage and Administration Guidelines
Oral Tablet Dosing for Onychomycosis
Oral terbinafine tablets are generally prescribed at a standard dose of 250 mg once daily. This regimen targets fungal nail infections that are often resistant to topical treatments. Continuous daily use ensures therapeutic levels in the nail bed, where fungi reside and proliferate.
Topical Dosing Schedules for Skin Infections
Topical formulations, including creams, gels, and sprays, are applied directly to the affected skin. Common schedules involve:
- Once or twice daily application depending on severity.
- Thorough cleansing and drying of the affected area before use.
- Extending application to surrounding healthy skin to prevent reinfection.
Duration of Therapy for Nails, Skin, and Scalp Infections
The duration of treatment depends on the site and severity of infection:
- Nail infections: typically 6 weeks for fingernails and 12 weeks or longer for toenails.
- Skin infections: usually 1 to 4 weeks, depending on the type of tinea.
- Scalp infections: often require systemic therapy for several weeks due to hair follicle involvement.
Special Dosing Considerations in Renal and Hepatic Impairment
In patients with kidney or liver dysfunction, dosage adjustments may be necessary. Reduced clearance of terbinafine can lead to increased systemic exposure, heightening the risk of toxicity. Clinical monitoring and individualized treatment schedules are recommended.
Missed Dose and Discontinuation Advice
If a dose is missed, patients should take it as soon as possible unless it is nearly time for the next dose. Double dosing should be avoided. Sudden discontinuation without medical consultation is discouraged, as incomplete therapy may lead to recurrence of infection.
Administration in Special Populations
Elderly Patients: Metabolic Considerations and Monitoring
Older adults may metabolize terbinafine differently due to reduced hepatic or renal function. Careful monitoring of liver enzymes and kidney function is recommended during therapy to minimize adverse events.
Pregnant Women and Nursing Mothers: Safety Data and Recommendations
Limited human data exist on the use of terbinafine during pregnancy. It should only be administered when the potential benefits outweigh risks. Terbinafine is excreted in breast milk; nursing mothers are generally advised to avoid its use to prevent infant exposure.
Children: Age-Specific Dosing, Safety, and Efficacy Evidence
Pediatric use is primarily reserved for severe fungal infections such as tinea capitis. Dosing is weight-based, typically ranging from 62.5 mg to 250 mg daily. Safety and efficacy have been established in older children, though caution remains essential in younger age groups.
Side Effects of Terbinafine
General Overview of Adverse Event Profile
Terbinafine is generally well tolerated, yet it may produce adverse effects in a subset of patients. These range from mild gastrointestinal complaints to rare but severe systemic reactions.
Common Side Effects
- Headache and dizziness
- Gastrointestinal upset such as nausea, diarrhea, or abdominal pain
- Rashes and pruritus
- Altered or diminished sense of taste
Serious Side Effects
- Hepatotoxicity with potential for liver failure
- Severe cutaneous reactions such as Stevens-Johnson syndrome
- Hematologic abnormalities including neutropenia
Monitoring Liver Function and Patient Education
Baseline and periodic liver function tests are advised. Patients should be educated to recognize warning signs such as persistent nausea, jaundice, dark urine, or unexplained fatigue, and seek immediate medical evaluation if they occur.
Drug Interactions
Cytochrome P450 (CYP2D6) Interactions
Terbinafine is a potent inhibitor of CYP2D6, an enzyme responsible for metabolizing many drugs. This interaction can increase plasma levels of co-administered medications, necessitating careful monitoring.
Interactions with Antidepressants, Beta-Blockers, and Antiarrhythmics
Agents such as tricyclic antidepressants, SSRIs, certain beta-blockers, and class I antiarrhythmics may be affected by terbinafine co-administration. Dose modifications and enhanced surveillance may be required.
Risks with Alcohol and Hepatotoxic Drugs
Concurrent alcohol consumption or use of other hepatotoxic agents increases the risk of liver injury. Patients are strongly advised to limit or avoid alcohol during therapy.
Guidance on Managing Polypharmacy
Patients taking multiple medications should inform their healthcare providers. Comprehensive medication reviews help prevent adverse drug interactions and ensure safe prescribing practices.
Contraindications
Known Hypersensitivity to Terbinafine
Individuals with a history of allergic reactions to terbinafine should not use the drug, as exposure can trigger severe hypersensitivity responses.
Severe Liver Disease and Chronic Hepatic Conditions
Pre-existing hepatic impairment is a contraindication due to the drug’s hepatotoxic potential. Safer alternatives should be considered in these patients.
Severe Renal Impairment
Terbinafine clearance is reduced in severe renal insufficiency, increasing systemic accumulation and toxicity risks.
Cautions with History of Lupus Erythematosus
Exacerbation of lupus-like symptoms has been reported in rare cases, requiring cautious use in patients with autoimmune conditions.
Warnings and Important Precautions
Risk of Liver Toxicity and Mandatory Monitoring
Hepatotoxicity remains a significant concern. Regular biochemical monitoring is essential to identify early signs of liver injury.
Potential for Serious Dermatological Reactions
Rare but life-threatening dermatologic conditions, including Stevens-Johnson syndrome and toxic epidermal necrolysis, necessitate prompt discontinuation if skin lesions or mucosal involvement develop.
Allergic Reactions and Anaphylaxis Risk
Patients must be aware of symptoms such as difficulty breathing, facial swelling, or generalized urticaria, which require urgent medical intervention.
Taste and Smell Disturbances
Some patients experience dysgeusia or anosmia, which may affect appetite and nutrition. These effects can persist even after discontinuation.
Monitoring for Psychiatric Side Effects
Mood changes, depression, or anxiety have been occasionally linked to terbinafine use. Close observation is advised, especially in patients with pre-existing psychiatric conditions.
Careful Administration Considerations
Adjustments for Patients with Impaired Hepatic Function
Reduced dosing or alternative therapies should be considered. Close monitoring of hepatic enzymes is mandatory throughout treatment.
Care in Those with Renal Insufficiency
Patients with reduced renal clearance may require modified dosing schedules. Nephrologist consultation may be appropriate for complex cases.
Monitoring in Long-Term Therapy
Extended use requires routine laboratory assessments, including liver and kidney function panels, to minimize cumulative toxicity.
Considerations in Immunocompromised Patients
Patients with suppressed immunity may need prolonged treatment courses and vigilant monitoring to ensure eradication of fungal pathogens.
Overdose and Emergency Management
Symptoms of Terbinafine Overdose
Excessive ingestion may lead to headache, nausea, vomiting, dizziness, and rash. Severe cases may result in hepatic or renal complications.
Supportive Measures and Symptomatic Treatment
There is no specific antidote. Treatment involves supportive care, including hydration, electrolyte monitoring, and symptomatic relief.
Role of Gastric Lavage and Activated Charcoal
In acute overdose scenarios, gastric lavage and activated charcoal may be employed to reduce absorption of the drug. These measures are most effective when administered promptly.
Long-Term Monitoring After Overdose
Patients should undergo extended surveillance of liver and kidney function following significant overdose events to detect delayed complications.
Storage and Handling Precautions
Recommended Storage Conditions for Oral and Topical Forms
Oral tablets should be stored at controlled room temperature, away from excessive moisture and light. Topical forms should be kept in their original containers, tightly closed after use.
Stability and Shelf Life
Most formulations remain stable for up to 2 to 3 years when stored appropriately. Expired products should not be used, as potency and safety cannot be guaranteed.
Safe Handling Instructions for Patients and Caregivers
Caregivers applying topical terbinafine should wash their hands thoroughly after application. Contact with eyes and mucous membranes should be avoided.
Disposal Guidelines for Unused or Expired Medication
Unused terbinafine should be disposed of according to local pharmaceutical disposal guidelines. Flushing into water systems should be avoided to minimize environmental contamination.
Terbinafine, Terbinafine FAQ
- What fungus is terbinafine used for?
- What should I avoid while taking terbinafine?
- Is terbinafine a high risk medication?
- How long does treatment take with terbinafine?
- What are the worst side effects of terbinafine?
- How to tell if terbinafine is working?
- What organ can terbinafine affect?
- Does terbinafine affect sleep?
- Can terbinafine cause weight gain?
- Can terbinafine damage kidneys?
- Can terbinafine cause hair loss?
- Can terbinafine affect your heart?
- Who cannot use terbinafine?
- Can terbinafine cause tiredness?
- How do I know if terbinafine is affecting my liver?
- Can terbinafine cause anxiety?
- How many days does terbinafine stay in your system?
- Is terbinafine the strongest antifungal?
- Does terbinafine make you pee a lot?
- Is it better to take terbinafine in the morning or at night?
- Can I take vitamin C with terbinafine?
- Does terbinafine stop itching?
- Can I buy terbinafine tablets over the counter?
- What are the bad side effects of terbinafine?
- Can terbinafine cause high cholesterol?
- Does terbinafine affect gut bacteria?
- Can your liver recover from terbinafine?
What fungus is terbinafine used for?
Tinea corpus
What should I avoid while taking terbinafine?
Too much caffeine
Is terbinafine a high risk medication?
It's been tied to some serious cases of liver damage, and in a few instances, this has even proved fatal.
How long does treatment take with terbinafine?
2-6 weeks
What are the worst side effects of terbinafine?
- Liver problems
- Blood disorders
- Skin infections
How to tell if terbinafine is working?
As the itching, scaling and flaking subside
What organ can terbinafine affect?
Liver
Does terbinafine affect sleep?
Yes
Can terbinafine cause weight gain?
Yes
Can terbinafine damage kidneys?
Yes
Can terbinafine cause hair loss?
Yes
Can terbinafine affect your heart?
Yes
Who cannot use terbinafine?
- Liver/kidney problems
- Pregnant or trying to become pregnant
Can terbinafine cause tiredness?
Yes
How do I know if terbinafine is affecting my liver?
- Abdominal pain
- Malaise
- Severe jaundice
Can terbinafine cause anxiety?
Yes
How many days does terbinafine stay in your system?
30 weeks
Is terbinafine the strongest antifungal?
itraconazole
Does terbinafine make you pee a lot?
Yes
Is it better to take terbinafine in the morning or at night?
Regardless, as long as you take it at the same time
Can I take vitamin C with terbinafine?
Yes
Does terbinafine stop itching?
Yes
Can I buy terbinafine tablets over the counter?
Yes
What are the bad side effects of terbinafine?
- Nausea
- Vomiting
- Headache
Can terbinafine cause high cholesterol?
Yes
Does terbinafine affect gut bacteria?
No
Can your liver recover from terbinafine?
Yes