Uvox, Fluvoxamine
- Introduction to Uvox (Fluvoxamine)
- Overview of Uvox: Classification and Brand Information
- History and Approval Status in Various Countries
- Difference Between Uvox and Other SSRIs
- Fluvoxamine Brand Name
- Composition and Pharmaceutical Formulations
- Fluvoxamine Mechanism of Action
- Approved Medical Uses of Uvox (Fluvoxamine)
- Off-Label Uses of Uvox (Fluvoxamine)
- Fluvoxamine Dosage and Administration Guidelines
- Administration Instructions by Patient Group
- Fluvoxamine Side Effects and Serious Side Effects
- Important Warnings and Precautions
- Contraindications to Uvox (Fluvoxamine) Use
- Interactions with Other Medications and Substances
- Careful Administration and Monitoring Considerations
- Storage and Handling Instructions
- Overdose and Emergency Management
- Handling Precautions for Healthcare Providers and Caregivers
- Conclusion and Additional Resources
Introduction to Uvox (Fluvoxamine)
Uvox, a fluvoxamine-based medication, is an SSRI (selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor) primarily prescribed for Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder (OCD) and depression. It works by significantly influencing serotonin levels in the brain. Beyond its main uses, Uvox is increasingly being utilized for anxiety disorders, and ongoing research is exploring its potential in managing inflammation. Its role in medical practice continues to expand.
Overview of Uvox: Classification and Brand Information
Uvox is a Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitor (SSRI) antidepressant and anti-anxiety medication. Marketed as Uvox, it specifically targets serotonin levels in the brain. While it belongs to the SSRI class, it has distinct characteristics in how it binds to receptors.
History and Approval Status in Various Countries
Fluvoxamine, first launched in Switzerland in the 1980s, has received approval from major regulatory bodies including the European Medicines Agency (EMA), Japan's PMDA, and the U.S. FDA (specifically for OCD). Although its FDA approval is more limited than fluoxetine or sertraline, doctors globally frequently prescribe fluvoxamine for other conditions like Generalized Anxiety Disorder (GAD), panic disorder, and Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD).
Difference Between Uvox and Other SSRIs
Fluvoxamine uniquely targets the serotonin transporter (SERT) while also interacting with sigma receptors, setting it apart from other SSRIs. This distinct action may provide benefits in treating conditions such as depression and somatic symptom disorder, as well as certain inflammatory issues.
Here's how it compares to some other common SSRIs:
- Fluoxetine: Known for its long-lasting effects and can have an energizing impact.
- Sertraline (Zoloft): Used for a wide range of conditions and is generally well-tolerated.
- Paroxetine: Characterized by its strong effects and sedative properties.

Fluvoxamine Brand Name
Among the available brands of fluvoxamine, Uvox is one option, alongside others like Luvox (in the United States), Faverin, and Floxyfral. Despite these different brand names, they all contain the same active ingredient: fluvoxamine maleate.
Composition and Pharmaceutical Formulations
Active Ingredient: Fluvoxamine Maleate
Uvox tablets contain fluvoxamine maleate, which is a salt form of fluvoxamine. This makes the compound more soluble and stable. It appears as a white to off-white crystalline powder that dissolves in water and acts as a serotonin reuptake inhibitor.

Available Strengths and Dosage Forms
Uvox is available in 50 mg and 100 mg tablet strengths. While extended-release (ER) versions aren't available everywhere, immediate-release (IR) tablets are typically taken twice daily. Some countries do offer convenient once-daily ER tablets.
Inactive Ingredients and Excipients
Common additives like cellulose microcrystalline, magnesium stearate, and lactose monohydrate are often found in tablet formulations. These ingredients are important because they help maintain the tablet's structure and influence how it dissolves and is absorbed by the body.
Generic and Branded Equivalents
You can find generic versions of fluvoxamine maleate globally, offering similar benefits at a lower cost than branded options like Luvox CR in the USA or Floxyfral in Europe. These branded versions might offer unique release profiles or improved formulations.
Zoloft vs Fluvoxamine
While both Zoloft (sertraline) and Fluvoxamine are SSRIs, they have different primary uses and side effect profiles. Zoloft has a broader range of FDA-approved uses, including social anxiety disorder and PTSD. Fluvoxamine, however, is often preferred for treating OCD due to its specific effectiveness in that area.
In terms of side effects, Zoloft is more commonly associated with gastrointestinal discomfort, whereas Fluvoxamine is more likely to cause drowsiness.

Fluoxetine and Fluvoxamine
Fluoxetine's longer-lasting effects allow for more flexible dosing, unlike fluvoxamine, which requires stricter adherence due to its shorter duration of action. They also differ in how they're processed by the body: fluoxetine inhibits the CYP3A4 enzyme, while fluvoxamine significantly inhibits CYP1A2 and CYP2C19 enzymes.
Fluvoxamine vs Fluvoxamine Maleate
In pharmacology, both fluvoxamine and fluvoxamine maleate have the same effects once they're in your body; they're chemically very similar in their impact after you take them. The maleate version is specifically designed for manufacturing to improve how the drug is absorbed and to create better tablet formulations.
Fluvoxamine Mechanism of Action
Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibition Explained
Fluvoxamine works by strongly binding to the serotonin transporter (SERT). This prevents serotonin from being reabsorbed into nerve cells, which in turn boosts serotonin levels in that part of the brain. These increased serotonin levels at the synapses then influence neurotransmitter pathways that are involved in managing mood and anxiety.
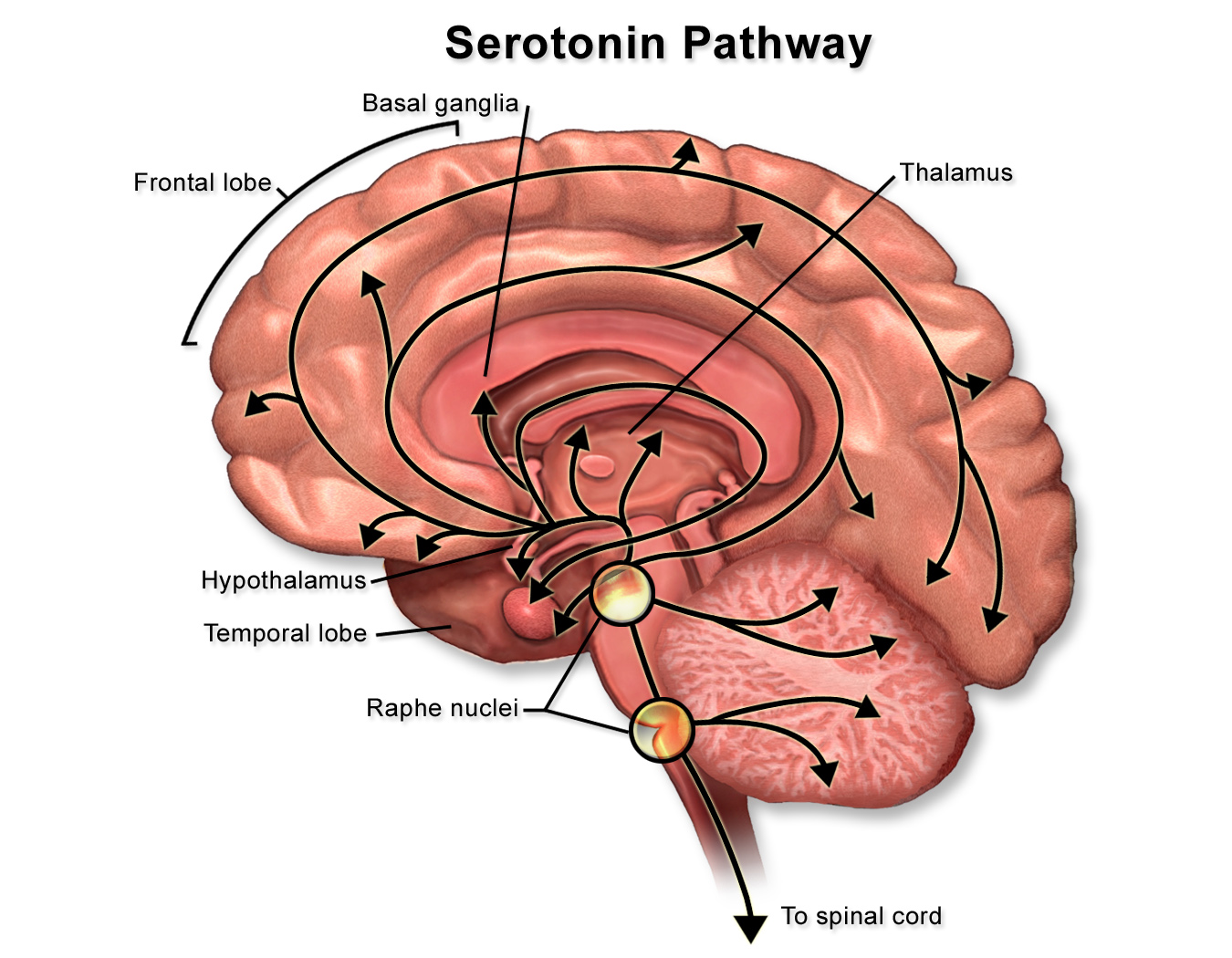
Neurological Impact on Mood and Behavior
Increased serotonin levels influence several key brain regions:
- The amygdala, which is involved in how we perceive threats.
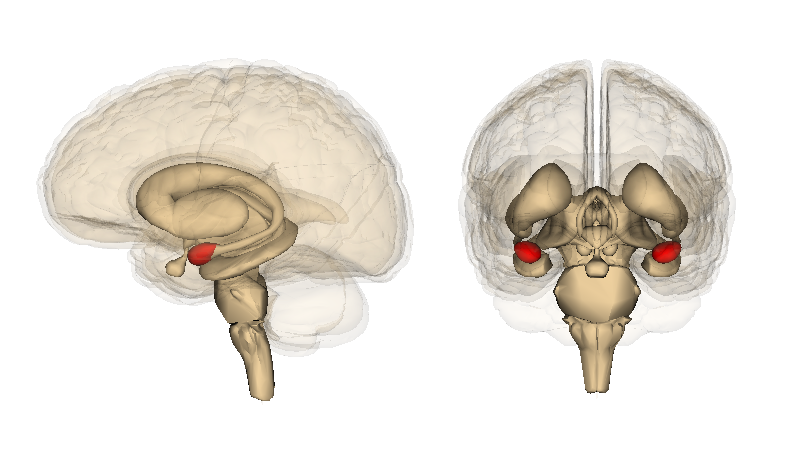
- The prefrontal cortex, associated with decision-making and planning.
- The dorsal raphe nucleus which helps regulate sleep and alertness.
Patients often report feeling more emotionally stable, experiencing fewer intrusive thoughts, and having less severe panic symptoms as a result.
Pharmacokinetics and Metabolism
Fluvoxamine has several key characteristics:
- Absorption: When taken by mouth, about 50% of the substance is absorbed by the body.
- Peak Blood Levels: It usually reaches its highest concentration in the bloodstream within 3 to 6 hours after you take it.
- Metabolism: The liver extensively processes fluvoxamine using CYP enzymes, particularly CYP1A2 and CYP2C19.
It also binds strongly to proteins and undergoes initial processing in the body before being converted into desmethylfluvoxamine, a metabolite that isn't active.
Half Life of Fluvoxamine
The approximate half-life for the elimination of immediate-release fluvoxamine in adults is typically 15 to 22 hours. It's important to adjust the dosage gradually when stopping the medication to prevent withdrawal symptoms such as dizziness, sleep disturbances, or agitation.
Fluvoxamine Extended Release
Extended-release (ER) formulations are designed to deliver a steady level of medication in your bloodstream, minimizing the ups and downs in concentration. This offers several benefits:
- Once-daily dosing: You only need to take the medication once a day, which is more convenient.
- Improved compliance: It's easier to stick to your treatment plan.
- Fewer side effects: It can reduce adverse effects like nausea that are often linked to peak medication levels.
However, ER versions might not be available everywhere, as their approval and accessibility vary by region.
Approved Medical Uses of Uvox (Fluvoxamine)
Social Anxiety Disorder (SAD)
Uvox (fluvoxamine) is an effective treatment for Social Anxiety Disorder (SAD), a mental health condition characterized by an intense fear of being judged or scrutinized in social situations. By regulating serotonin transmission in the brain, fluvoxamine helps to reduce heightened emotional arousal and the anxiety experienced before social interactions, which are common features of SAD.

Healthcare professionals typically start patients on a low dose and gradually increase it to minimize potential side effects. Patients usually begin to see improvements after a few weeks of treatment, including:
- Decreased physical symptoms like blushing, sweating, and trembling.
- Improved social confidence and the ability to speak effectively in social settings.
- Reduced avoidance behaviors.
Fluvoxamine's unique ability to modulate the sigma-1 receptor may offer benefits beyond the typical actions of other SSRIs, potentially making it stand out from medications like paroxetine or escitalopram.
Panic Disorder
Panic disorder, characterized by recurrent panic attacks, is an FDA-approved indication for fluvoxamine in certain regions. This medication effectively reduces the frequency and severity of panic episodes by stabilizing serotonin pathways involved in threat perception and system regulation.
Key benefits of fluvoxamine for panic disorder include:
- Preventing nighttime anxiety attacks.
- Improving the ability to confront situations that trigger agoraphobia.
- Helping to regulate breathing patterns in individuals prone to panic.
Patients should be reassured that it may take 2 to 3 weeks for the therapeutic effects of fluvoxamine to become noticeable after starting treatment.

Fluvoxamine for Anxiety
Although fluvoxamine is not officially approved for the treatment of Generalized Anxiety Disorder (GAD), it is commonly prescribed off-label for a range of anxiety-related conditions. Its therapeutic effects are largely attributed to its selective action on serotonin transporters and its unique ability to activate the sigma-1 receptor, which helps alleviate heightened mental alertness and physical symptoms of anxiety.
Fluvoxamine has been found to be effective in managing:
Individuals who struggle with persistent anxious thoughts and sleep disturbances often experience significant improvement when adhering to a consistent fluvoxamine treatment plan.

Fluvoxamine for OCD
Fluvoxamine is a globally recognized and effective SSRI for treating Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder (OCD), primarily due to its potent inhibition of the serotonin transporter (SERT). This action significantly helps to lessen the intrusive thoughts and repetitive behaviors characteristic of OCD.
Key benefits of using fluvoxamine for OCD include:
- Reduction in intrusive thoughts, such as fears of contamination, worries about harm, or the need for symmetry.
- Decreased repetitive behaviors, like excessive checking and cleaning.
- Improved mental and emotional control.
Treatment for OCD often requires longer durations and typically higher doses than those used for depression. Fluvoxamine's high tolerability at these higher doses makes it a suitable option for individuals with difficult-to-treat (resistant) cases of OCD.

Sertraline vs Fluvoxamine for OCD
Both sertraline and fluvoxamine are FDA-approved for treating Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder (OCD), but their mechanisms of action differ. Sertraline has some effect on dopamine reuptake and interacts with serotonin receptors. Fluvoxamine, on the other hand, primarily targets the serotonin transporter (SERT) and also affects sigma receptors.

Key distinctions between the two include:
- Sertraline may have a more energizing effect, making it potentially beneficial for patients experiencing lethargy.
- Fluvoxamine is often preferred for individuals who also struggle with significant anxiety or sleep disturbances.
- Regarding side effects, fluvoxamine may cause increased drowsiness, while sertraline is more commonly associated with gastrointestinal issues.
Ultimately, the choice between these two medications often depends more on an individual's specific symptom profile and their tolerance to potential side effects, rather than solely on their general effectiveness.
Fluvoxamine for Depression
While fluvoxamine isn't as commonly prescribed for Major Depressive Disorder (MDD) as fluoxetine or sertraline, it proves effective, especially for individuals experiencing atypical depression or melancholic features. It offers particular benefits when anxiety and obsessive thoughts are prominent.
Specific advantages observed include:
- Improved sleep quality, notably a delay in the onset of REM sleep.
- Reduced physical symptoms, such as headaches or stomach issues.

- Increased drive for patients experiencing fatigue.
However, due to its interactions with various enzymes in the body, fluvoxamine requires careful dosing and monitoring when used alongside other medications.
Off-Label Uses of Uvox (Fluvoxamine)
Generalized Anxiety Disorder (GAD)
Uvox (fluvoxamine) is frequently used "off-label" to treat Generalized Anxiety Disorder (GAD), even though it may not have official regulatory approval for this condition in many regions. Its widespread clinical use for GAD is attributed to its rapid anxiety-reducing effects, achieved by:
- Restoring balance in serotonin pathways that regulate emotions.
- Alleviating physical symptoms like stomach discomfort and muscle tension.
- Improving sleep quality and reducing nighttime overthinking.

For individuals who don't respond well to benzodiazepines or are at risk of dependency, fluvoxamine can be a valuable non-addictive, long-term treatment option.
Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD)
Fluvoxamine may offer relief for individuals with Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD). While not usually a first-line treatment in professional guidelines, clinicians often use Uvox in difficult PTSD cases marked by recurring traumatic memories and intense emotions. Its impact on serotonin and sigma receptors helps with brain adaptation and emotional coping.
Potential benefits of this treatment include:
- Minimizing flashbacks and disturbing dreams.
- Reducing reactivity to trauma-related triggers.
- Improvements in managing feelings of detachment and avoidance behaviors.
Fluvoxamine could also help alleviate co-occurring issues such as depression, sleep problems, and substance abuse, which are often present in chronic PTSD cases.
Premenstrual Dysphoric Disorder (PMDD)
While not FDA-approved for Premenstrual Dysphoric Disorder (PMDD), research suggests fluvoxamine may offer relief for patients experiencing this severe form of PMS, characterized by mood swings and irritability during the luteal phase due to hormonal shifts. Studies indicate it could be as effective as fluoxetine, whether taken continuously or just during the luteal phase.
Observed positive effects include:
- Improved mood swings and reduced irritability.
- Decreased fatigue and physical discomfort (like stomach upset and breast tenderness).
- Better social interactions on symptomatic days.
Given its rapid action, fluvoxamine could be a valuable treatment option for women with cyclical mood swings where hormonal interventions are not suitable, such as due to birth control contraindications.
Eating Disorders Including Bulimia Nervosa
Clinical observations suggest that Fluvoxamine is commonly used as a treatment for eating disorders, particularly bulimia nervosa. It aims to help manage appetite control and reduce impulsive overeating, while also addressing underlying mood issues that contribute to unhealthy eating patterns.

Key benefits of this treatment include:
- Reduced frequency of binge-purge episodes.
- Improved ability to manage impulses and self-regulate.
- A decrease in excessive concern about body image and anxiety.
While fluoxetine is the only medication specifically approved by the FDA for treating bulimia nervosa, evidence indicates that fluvoxamine, with its similar pharmacological characteristics, may also be beneficial in a comprehensive, multi-faceted approach to treating various eating disorders.
Fibromyalgia and Chronic Pain Management
Chronic pain conditions such as fibromyalgia often involve nerve-related issues, as well as muscle and emotional symptoms. Fluvoxamine's ability to increase serotonin levels and activate sigma-1 receptors may influence the brain's pain pathways, making it a potential treatment option for these disorders.
Some possible mechanisms by which it works include:
- Reduced amplification of pain signals in the spinal cord and brainstem.
- Improved sleep patterns, which are often disrupted in individuals with fibromyalgia.
- Increased capacity to cope with stress-exacerbated pain.
While still under investigation, anecdotal reports and case studies suggest that fluvoxamine warrants further research in multidisciplinary pain clinics.
COVID-19 (As an Anti-Inflammatory Investigational Agent)
During the pandemic, fluvoxamine gained attention for its potential to reduce inflammation by activating sigma-1 receptors and suppressing the release of immune system cytokines. Studies observed that fluvoxamine might help prevent mild COVID-19 cases from progressing to severe illness requiring hospitalization.
Potential advantages of using fluvoxamine in COVID-19 treatment include:
- Inhibition of inflammatory cytokines, such as IL-6 and TNF-alpha, which are crucial for managing the body's inflammatory responses.
- Stabilization of endothelial function and a decreased risk of blood clotting.
- Prevention of a hyperinflammatory response and cytokine storm.
While not universally endorsed by all experts, the effectiveness of fluvoxamine in treating early-stage COVID-19 patients continues to be actively investigated in international research projects.
Fluvoxamine and Long COVID
For individuals experiencing Long COVID symptoms like brain fog, fatigue, and dysautonomia, there's growing speculation that fluvoxamine could offer benefits. Its impact on the sigma-1 receptor and its ability to influence inflammation are thought to provide positive effects on brain function.
Early observations suggest:
- Improved mental clarity and concentration.
- Reduced dysregulation of bodily functions, such as heart rate fluctuations and lightheadedness.
- Better management of mood swings and improved sleep patterns.
Despite the current limited data, fluvoxamine is increasingly being recognized as a potential medication in the multi-disciplinary approach to treating Long COVID.

Fluvoxamine Dosage and Administration Guidelines
Fluvoxamine Starting Dose and Maintenance Doses for Each Indication
Uvox (fluvoxamine) dosing varies based on the condition being treated and must be tailored to each patient's tolerance, age, and overall health. Generally, treatment begins with a low dose, which is then gradually increased to a stable therapeutic level.
Here's a typical breakdown of dosing:
- For Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder (OCD), initial treatment usually starts at 50 mg per day, with maintenance doses typically ranging from 100 to 300 mg per day, divided into multiple doses.
- For depression, treatment usually begins with 50 to 100 mg per day, potentially increasing to a maintenance dose of 100 to 200 mg per day.
- For anxiety disorders (including GAD, panic disorder, and social anxiety disorder), the starting dose is typically 25-50 mg per day, with maintenance doses usually between 100-200 mg per day, adjusted based on the patient's response.
All dose adjustments should be made individually, with careful monitoring for side effects and changes in treatment effectiveness.
Fluvoxamine Dose for Anxiety
For anxiety issues like Generalized Anxiety Disorder (GAD) and social anxiety, fluvoxamine typically starts at 25 to 50 mg per day. It's often recommended to take this initial dose at night to help avoid daytime drowsiness.
To maintain consistent levels in the body, maintenance doses usually range from 100 to 200 mg daily, often split into two doses. Patients who experience significant anxiety or strong physical reactions might benefit from a slower increase in dosage, with close monitoring of their progress during the early stages of treatment.
Fluvoxamine Dosage for OCD
Treating OCD typically requires higher medication doses than other mental health conditions. The usual starting dose is 50 mg per day, with maintenance therapy typically ranging from 150 to 300 mg per day, often taken twice daily. For severe or treatment-resistant cases, the maximum benefits are usually seen at the higher end of this dosage range, sometimes even requiring doses as high as 300 mg per day. To reduce side effects like drowsiness or stomach upset, it's best to take the medication in the evening or use extended-release versions if available.

Fluvoxamine Dosage for Depression
When using fluvoxamine to treat depression, the usual starting dose is 50 to 100 mg per day. This dose is slowly adjusted based on how well you tolerate it. Most people respond well to 100 to 200 mg daily.
Some individuals might benefit from splitting their daily dose, as this can improve how they handle the medication and its effectiveness. However, for others, taking the entire dose once a day in the evening might be enough. If you're dealing with melancholic or anxious depression, it's particularly important to increase the dosage gradually to avoid worsening symptoms like agitation or insomnia, especially when you first start treatment.
Titration and Dose Adjustments
When taking fluvoxamine, your dosage should be increased gradually. You'll typically raise the dose by 50 milligrams every 4 to 6 days, depending on how you tolerate it. It's important to monitor for any side effects, especially during the first two weeks.
Your doctor will also adjust your dosage to account for any drug interactions that might affect how the medication is processed in your body, particularly those involving CYP1A2 and CYP2C19 enzymes.
If you have liver or kidney issues, or if you're taking other medications, your dosage will be adjusted more slowly, and you'll be closely monitored for any harmful drug interactions or buildup of the medication in your system.
Fluvoxamine Maximum Dosage
For severe OCD, the maximum recommended dose of fluvoxamine is typically 300 mg. It's vital not to go over this limit due to the risk of serious side effects like serotonin syndrome, elevated liver enzymes, and increased drowsiness. If your daily dose exceeds 100 mg, you should split it into two administrations; this helps keep the medication levels stable and is easier on your stomach.
Missed Dose Instructions and Tapering Off
If you miss a dose, take it as soon as you remember, unless your next dose is almost due. Never double your dose.
If you've been on the medication for a while and need to stop, it's best to gradually reduce your dose over several weeks to prevent withdrawal symptoms like dizziness, irritability, strange sensations, and sleep problems.
Here's a suggested plan for tapering:
- Decrease your dosage by 25 to 50 milligrams every one to two weeks.
- If you've been on high doses for a long time, you might need an even slower tapering schedule.
- It's important to monitor yourself closely during this process for any signs of your original symptoms returning.
Administration Instructions by Patient Group
Administration to Elderly Patients: Dose Considerations and Monitoring
Older adults may have reduced liver function and can be more sensitive to the physical and mental effects of SSRIs. For their safety, it's best to start with a low dose of 25-50 mg per day and increase it gradually. During this time, carefully monitor for signs of low sodium (hyponatremia), dizziness when standing (orthostatic hypotension), or memory problems.
Here are some additional precautions:
- Assess the risk of falls due to sedation.
- Regularly check sodium levels in those on long-term treatment.
- Adjust the dosage for patients with kidney problems or potential drug interactions.
Use During Pregnancy and Breastfeeding: Safety Profile and Recommendations
Fluvoxamine falls under Pregnancy Category C, meaning some caution is advised during pregnancy, although the exact risk of birth defects in humans isn't definitively known. When prescribing it, especially for severe OCD or depression, a risk-benefit analysis is crucial, as leaving the illness untreated could pose a greater risk.

Breastfeeding considerations are also important:
- Fluvoxamine is present in breast milk, potentially at significant levels.
- Newborns should be monitored for issues like feeding difficulties, sleep disturbances, and increased fussiness.
- If appropriate, alternative medications with more established lactation safety data might be a better choice.
Fluvoxamine and Pregnancy
When considering fluvoxamine during pregnancy, healthcare providers should only use it if the mother's health is prioritized over potential risks to the fetus. Collaboration with psychiatric professionals is crucial. While SSRI exposure in the third trimester might be linked to neonatal adaptation syndrome and persistent pulmonary hypertension of the newborn (PPHN), there's limited specific information about fluvoxamine in this regard.
Pediatric Administration: Approved Age Ranges and Dosing Safety
In countries where approved, fluvoxamine is used to treat OCD in children aged 8 and older. The starting dose is usually 25 mg per day, gradually adjusted based on how the child tolerates it and responds to the medication. Typically, the maximum doses given to children are lower than for adults.
During treatment, it's important to monitor several key aspects:
- Developmental factors and body mass.
- Behavioral changes, including restlessness or thoughts of self-harm.
- Progress in social performance over time.
Adjustments for Hepatic or Renal Impairment
If you have liver problems, the metabolism of fluvoxamine might slow down because the activity of your cytochrome P450 enzymes could be compromised. In such cases, it's recommended to start with a lower dose and closely monitor for signs of drug buildup or liver issues, such as fatigue, yellowish skin, and elevated liver enzyme levels.
For kidney problems, no specific dosage adjustments are typically required. However, it's still advisable to be cautious, as there's limited information on how the drug is processed in patients with kidney impairment. Regularly checking kidney function and monitoring the patient's response to treatment is prudent, especially if other health conditions are present.
Fluvoxamine Side Effects and Serious Side Effects
Most Frequently Reported Side Effects (Nausea, Headache, Insomnia)
Like other SSRIs, fluvoxamine has a range of side effects that are typically temporary and depend on the dosage.
- Nausea is common when first starting the medication but usually gets better with continued use or a dosage adjustment.

- Mild to moderate headaches can often be eased by staying hydrated and using over-the-counter remedies.
- Initial sleep problems might require adjusting your evening dose or using sleep aids.
Other common side effects can include lightheadedness, dry mouth, drowsiness, or stomach discomfort. These usually diminish as your body adjusts to the medication over time.
Fluvoxamine Sexual Side Effects
Sexual dysfunction is a recognized side effect of fluvoxamine and other SSRIs, presenting in various ways:
- Decreased libido: A reduced interest in sexual activities.
- Difficulty or delay in achieving orgasm: Affecting both men and women.
These symptoms can occur throughout treatment or develop gradually. Sometimes, reducing the dosage or taking medication breaks are considered. However, for persistent symptoms, doctors might add bupropion to the treatment plan or switch to a different type of antidepressant.
Rare but Serious Adverse Effects (Serotonin Syndrome, Hyponatremia)
Though uncommon, fluvoxamine use can lead to severe side effects that require immediate medical attention.
Serious Side Effects of Fluvoxamine
- Serotonin Syndrome is a rare but life-threatening condition caused by excessive serotonin activity in the body. Symptoms include increased reflexes (hyperreflexia), muscle contractions (clonus), restlessness (agitation), and fluctuations in blood pressure and heart rate (autonomic instability). In severe cases, it can even lead to seizures or a coma.
- Hyponatremia (low sodium levels in the blood) is more common in elderly individuals. It can cause confusion, lethargy, and in severe cases, seizures due to electrolyte imbalances.
Recognizing and acting quickly in these situations is critical, as taking other serotonergic medications or diuretics can significantly increase these risks.
Fluvoxamine Side Effects Long-Term
While most people tolerate fluvoxamine well over time, some might experience lasting or delayed side effects. These can include changes in body weight, feeling mentally slow or emotionally numb, and in some cases, sexual problems that persist even after stopping the medication. To help prevent these long-term issues, it's advisable to regularly reassess the need for treatment and adjust the dosage as necessary.
Fluvoxamine Side Effects in Females
Due to hormonal and metabolic interactions, some side effects may be more prominent in women:
- Nausea might be more noticeable during certain points in the menstrual cycle.
- Menstrual irregularities can occasionally occur.
- An increase in mood changes may be experienced before menopause.

During clinical monitoring, it's important to discuss women's reproductive health and sexual well-being, as patients often don't bring up these topics on their own.
Fluvoxamine Weight Gain
While weight gain isn't a common side effect of fluvoxamine, it can occur, though it's generally considered weight-neutral compared to medications like tricyclics or mirtazapine, which are known for their impact on weight. However, some patients may still experience weight changes due to:
- Increased hunger or carb cravings.
- A slowed metabolism with long-term, higher doses of the medication.
- Weight fluctuations influenced by mood changes and activity levels.
Regularly monitoring your weight and getting dietary advice can help proactively manage this potential risk.
Fluvoxamine Hair Loss
Hair loss, specifically telogen effluvium, is a reversible side effect that can occur with fluvoxamine use. It typically appears as uniform thinning or in patches, usually becoming noticeable within the first few months of starting treatment.
Several factors can contribute to this:
- Drug-induced changes in the hair growth cycle.
- Stress-induced hair loss.
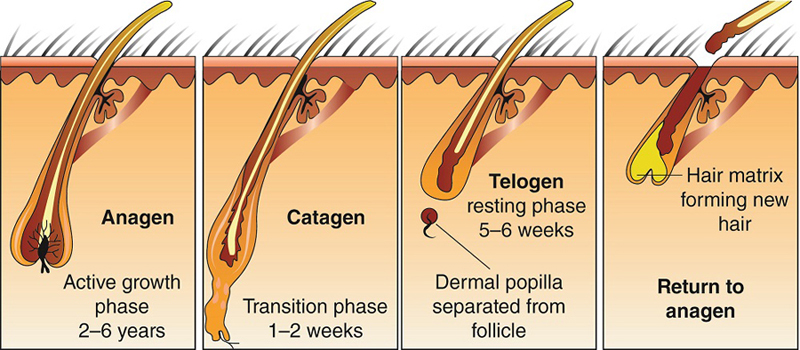
- Recovery usually begins after reducing the dosage or stopping the medication entirely. If hair loss persists, consulting a dermatologist may be necessary.
Important Warnings and Precautions
Risk of Suicidal Ideation and Behavior in Adolescents and Young Adults
Fluvoxamine and other antidepressants come with a caution about the likelihood of experiencing suicidal thoughts and behaviors among those under 25 years old especially when starting treatment and adjusting doses. Recommended measures to address this concern are as follows;
- Keep a watch for signs of thoughts of self-harm or suicide as well as any unusual shifts in behavior or restlessness.
- Involving caregivers in recognizing warning signals.
- Regular visits to the clinic are important in the 3 months of treatment.
Monitoring Requirements During Therapy
During fluvoxamine treatment, regular check-ins are crucial to ensure both safety and effectiveness. These check-ups should monitor for:
- Changes in mental state and mood fluctuations.
- Body mass (weight).
- Liver function tests for long-term users or those with existing liver conditions.
- Serum sodium levels, particularly in at-risk individuals.
Additionally, extra vigilance is needed to watch for any signs of serotonin syndrome in patients who are also taking other medications with serotonergic components.
Cautions with Abrupt Discontinuation
When discontinuing fluvoxamine, individuals may experience SSRI discontinuation syndrome, a form of withdrawal. This can manifest as:
- Dizziness and "electric zaps" (a sensation resembling an electric shock).
- Irritability and mood swings.
- Gastrointestinal issues and sleep disturbances.
To minimize these symptoms, it's recommended to gradually reduce the dosage, typically by 25 to 50 milligrams every one to two weeks, adjusting the tapering schedule based on the patient's individual response.
Risk of Mania/Hypomania in Bipolar Patients
Individuals diagnosed with bipolar disorder should be careful when taking fluvoxamine, as it might trigger a shift from depression into hypomanic or manic states if not accompanied by other mood stabilizers. Close clinical attention is especially important for patients who have:
- A family history of bipolar disorder.

- Frequent or easily irritable mood changes.
- Experienced depressive episodes with manic or hypomanic features at a young age.
When appropriate or recommended, using mood stabilizers like lithium or valproate alongside fluvoxamine can help manage and reduce this risk. If treatment isn't effective or if mood shifts occur, it may be wise to re-evaluate the diagnosis for further assessment and necessary adjustments.
Contraindications to Uvox (Fluvoxamine) Use
Known Hypersensitivity to Fluvoxamine or Excipients
Individuals with an allergy to fluvoxamine maleate or any of its components should not take Uvox (fluvoxamine). Allergic reactions can appear as skin rashes (like hives or swelling), difficulty breathing or chest tightness, and in severe cases, anaphylactic shock.
If an allergic reaction is suspected, the medication must be stopped immediately, and symptoms should be treated. While it's rare for there to be cross-reactivity with other SSRIs, this possibility should be considered for patients with a history of allergies.
Concomitant Use with MAO Inhibitors and Certain Other Drugs
Taking fluvoxamine alongside monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOIs), including intravenous methylene blue, is strongly advised against because it significantly increases the risk of serotonin syndrome, a potentially fatal condition.
Here are the guidelines for concurrent use:
- Ensure a 14-day washout period after stopping an MAOI before starting fluvoxamine.
- Wait at least 14 days after discontinuing fluvoxamine before starting an MAOI.
- Additionally, avoid combining fluvoxamine with tizanidine or ramelteon, as fluvoxamine's CYP enzyme inhibition can lead to increased effects of these medications.
Severe Liver Dysfunction
Fluvoxamine is primarily processed by the liver's CYP1A2 and CYP2C19 pathways. If someone has liver problems, their body might not clear the drug effectively, leading to higher blood levels and an increased risk of side effects.
In such cases:
- Fluvoxamine should only be used when absolutely necessary.
- It's crucial to assess liver function tests before starting and throughout treatment.
- For patients with liver issues, considering medications that are less taxing on the liver might be a better option.
Interactions with Other Medications and Substances
Drug-Drug Interactions (CYP1A2 and CYP2C19 Substrates)
Fluvoxamine is a strong inhibitor of several cytochrome P450 (CYP) enzymes, particularly CYP1A2 and CYP2C19. When fluvoxamine is taken with other medications that are processed by these same enzymes, it can lead to higher levels of those drugs in the bloodstream, increasing their effects and potential side effects.
Some important drugs affected include:
- Theophylline: Taking it with fluvoxamine can significantly increase the risk of toxicity due to elevated blood levels.
- Clozapine: Combining it with fluvoxamine raises the chance of seizures and excessive drowsiness.

- Diazepam and other benzodiazepines: Using them alongside fluvoxamine can result in prolonged sedation and breathing difficulties.
Therefore, if patients are taking these medications, it's recommended to monitor their drug levels or adjust their doses when starting or stopping fluvoxamine.
Interactions with NSAIDs, Antiplatelets, and Anticoagulants
Taking fluvoxamine with medications that affect blood clotting, such as nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), antiplatelet medications (like aspirin or clopidogrel), or oral blood thinners (like warfarin or direct oral anticoagulants [DOACs]), can increase the risk of bleeding.
This is because fluvoxamine can interfere with how platelets clot by reducing serotonin absorption in them, potentially leading to bleeding problems in susceptible individuals. It's crucial to monitor for any signs of bleeding, particularly in the stomach or brain.
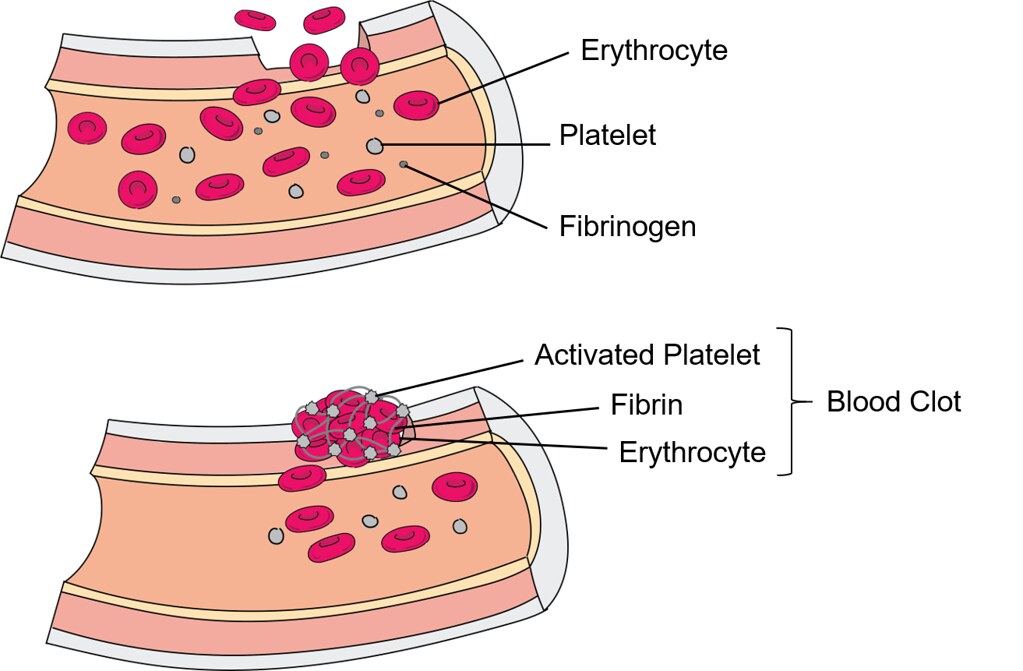
Alcohol and Caffeine Interactions
Fluvoxamine and Alcohol
- While there's no strict ban on alcohol consumption with fluvoxamine, drinking can worsen the cognitive side effects of the medication. Patients should be advised to limit or avoid alcohol to reduce the risk of increased central nervous system depression and behavioral changes.
Fluvoxamine and Caffeine
- Fluvoxamine significantly inhibits CYP1A2, the enzyme responsible for metabolizing caffeine. This means even a small amount of caffeine can lead to increased stimulation, sleep disturbances, tremors, or heart palpitations.
- Consider keeping your caffeine intake under 100 mg per day.
- Watch out for symptoms of caffeine toxicity, such as a fast heartbeat and feeling jittery.
Herbal Supplements and Over-the-Counter Drugs to Avoid
Several over-the-counter (OTC) medications and supplements can interact with fluvoxamine.
- St. John's Wort, when taken with SSRIs like fluvoxamine, should be used cautiously as it can increase the risk of serotonin syndrome.
- Naturally occurring compounds such as 5-HTP and tryptophan can also enhance serotonin effects, potentially leading to similar risks when combined with fluvoxamine.
- Diphenhydramine and other sedating antihistamines can worsen the sedative effects of fluvoxamine.
Before starting fluvoxamine, it's crucial for patients to openly discuss all supplements and OTC medications they are currently taking with their healthcare provider.
Fluvoxamine and Melatonin
Fluvoxamine can significantly increase melatonin levels in your blood because it slows down how your body breaks melatonin down, due to its effect on the CYP1A2 enzyme. If you take them together, this could lead to drowsiness or changes in your sleep patterns. If combining them can't be avoided, you should reduce your melatonin dose and avoid taking other sleeping medications at night.
Careful Administration and Monitoring Considerations
Patients with a History of Seizures
While fluvoxamine is generally considered to have a low risk of causing seizures, caution is advised when prescribing it to individuals with a history of seizure disorders. SSRIs, particularly at higher doses or when combined with medications like tramadol or clozapine, could potentially lower the seizure threshold.
Here are some clinical recommendations and considerations:
- Start with the lowest effective dose.
- Avoid co-treatments known to provoke seizures.
- Monitor closely for any new or breakthrough seizures.
Those with Cardiovascular Disease
For individuals with pre-existing heart conditions such as arrhythmias or ischemic heart disease, fluvoxamine should be used cautiously because it can potentially prolong the QT interval and interact with other medications.
Before starting fluvoxamine in high-risk patients, it's advisable to perform a baseline ECG for safety. Additionally, consider these precautions:
- Monitor electrolyte levels in individuals taking diuretics or experiencing vomiting or diarrhea.
- Avoid combining fluvoxamine with other medications known to prolong the QT interval, such as haloperidol or citalopram.
Monitoring in Patients with Diabetes
Fluvoxamine can affect blood sugar management in individuals with Type 1 or Type 2 diabetes. SSRIs have the potential to either increase insulin sensitivity or worsen glucose regulation, depending on an individual's metabolic response.
Recommended actions include:
- Regularly checking blood sugar levels when starting or adjusting fluvoxamine doses.
- Adjusting diabetes treatment plans as needed.
- Being aware of the risk of hypoglycemia (low blood sugar) for individuals using insulin or sulfonylureas.
Risk of QT Prolongation in Predisposed Individuals
While its uncommon there have been reports of fluvoxamine causing QT interval prolongation especially when taken alongside QT prolongation medications or in individuals, with long QT syndrome. Here are some ways to minimize the risks;
- Preventing imbalances, in levels such, as potassium and magnesium levels
- Evaluation of medications that can impact the hearts repolarization process.
- When the QT interval exceeds 500 milliseconds (ms) it is advisable to stop using fluvoxamine or refrain from using it.
Storage and Handling Instructions
Recommended Storage Conditions (Temperature, Humidity)
Store Fluvoxamine, in a controlled environment to keep its effectiveness intact between 20°C and 25°C (68°F to 77°F) with deviations allowed from 15°C to 30°C (59°F, to 86°F). Excessive moisture exposure can impact the stability of the ingredient. Cause it to break down prematurely.
- Remember to store in an airy place.
- Remember to steer clear of sunlight and areas with moisture like bathrooms.
- If the packaging is torn or damaged make sure to store the items, in airtight containers.
Shelf Life and Packaging Information
The Uvox (fluvoxamine) tablets generally last for 2 to 3 years after they are manufactured as, per the guidelines of the manufacturers specifications.The expiration date is clearly indicated on each blister pack or bottle. Should be followed closely.
- Make sure not to use it after the expiration date printed on the packaging.
- Remember to keep the medicine in its packaging, for the possible protection.
- Be careful not to move pills into bottles in order to minimize mistakes in dosage.
Disposal of Expired or Unused Medication
Once you're finished with fluvoxamine. Have any leftover make sure to dispose of it to avoid harming the environment or accidental consumption by mistake. It's important not to flush it down the toilet or throw it away in household trash bins. Here are some suggestions for disposal;
- Head back to a drugstore that provides take back services.
- If there is no option for returns or exchanges to you after use of the tablets is completed you can mix them with an active material like coffee grounds or cat litter to render them unusable, before sealing them in a plastic bag and disposing of them in the trash can.
- Make sure to hide any details on prescription labels before throwing away the packaging.

Safe Handling Precautions to Prevent Accidental Ingestion
To prevent accidental consumption of medications or other risky substances, follow these safety measures:
- Store medications out of reach of children and pets.
- Avoid leaving tablets on kitchen counters, nightstands, or in accessible bags.
- If you use pill organizers, choose ones with child-resistant features.
Overdose and Emergency Management
Signs and Symptoms of Fluvoxamine Overdose
A fluvoxamine overdose, whether accidental or intentional, can cause a range of dangerous symptoms. Recognizing these signs is crucial for effective treatment.
Symptoms may include:
- Nausea, dizziness, vomiting, and tremors.
- Rapid heart rate or high blood pressure.
- Drowsiness, confusion, and seizures.
- Signs of high serotonin levels, such as overactive reflexes, restlessness, and rigid muscles.
Recommended First Aid and Emergency Response
If you suspect an overdose, immediate action is crucial. Do not induce vomiting unless a medical professional specifically advises it.
Instead:
- Contact your local poison control center and call emergency services right away.
- Ensure the person's airway is clear and they are breathing.
- Do not give any food, beverages, or other medications unless instructed by an expert.
Have the medicine bottle readily available so you can inform emergency personnel about the specific medication and dosage taken.
Hospital-Based Interventions and Monitoring
In an environment or healthcare setting, overseeing and addressing cases of drug overdose could involve;
- Administering charcoal can help lessen absorption if given within 1 to 1.5 hours.
- Administering fluids through an IV to maintain the stability of the system.
- Monitoring an Electrocardiogram (ECG). Looking out for heartbeats or prolonged QT intervals.
- Treatment for seizures. Serotonin syndrome focusing on managing symptoms.
Patients might need to be observed for a period based on how much they took. If they also had alcohol or benzodiazepines.
Long-Term Follow-Up After Recovery
After receiving treatment to stabilize the condition following an incident—especially if it was deliberate—it is crucial to prioritize ongoing care and monitoring for recovery purposes.
- Psychological assessment for thoughts of suicide or mental health conditions.
- Assessment of medications and possible interactions, among them
- Ensuring that medications are stored safely and taken as directed according to the dosages.
It may be recommended to continue monitoring to identify any delayed issues or relapses in health.
Handling Precautions for Healthcare Providers and Caregivers
Tablet Splitting and Dose Customization Guidelines
When it comes to dosing needs, for medication some people might split tablets if necessary.. Remember to do this with tablets that have a score line and use a clean tablet cutter for accuracy.
- Please refrain from dividing tablets that are not scored or have a film coating.
- Make sure to talk to a pharmacist to confirm that the bioavailability is not affected.
- Remember to keep the divided tablets in a labeled container for temporary storage.
Safe Storage in Households with Children or Cognitively Impaired Patients
In households where there are children or individuals with challenges it's important to take care and implement safety measures, like risk prevention strategies.
- Ensure that you store your medications in locked cabinets or safes.
- It is advisable not to keep items in handbags or on bedside tables or in the kitchen.
- Clearly indicating the use and potential risks of medications.
Make sure to teach your family and caregivers about how crucial it is to keep medications secure and follow the protocols consistently.
Procedures for Accidental Exposure or Ingestion
If someone who shouldn't have taken it accidentally ingests the substance call poison control. Seek emergency help right away. Keep an eye on them for signs of feeling sleepy or restless or any physical discomfort. If the substance gets in their eyes or, on membranes rinse, with water. See a doctor if irritation continues.
Conclusion and Additional Resources
Summary of Key Therapeutic Benefits and Precautions
Fluvoxamine continues to be a medication, for treating compulsive disorder and depression along with certain off label uses as well It is considered beneficial when used carefully under clinical supervision Yet due, to its strong enzyme blocking properties side effects and potential interactions it requires careful consideration when prescribing and monitoring treatment
When to Consult a Healthcare Provider
Seek advice in the situations outlined below;
- Sudden appearance of thoughts of self harm or unexpected shifts in behavior.
- Warning indicators of a response or serotonin syndrome.
- Persistent or severe side effects that interfere with activities
- Worries regarding how drugs may interact with each other or the management of underlying health conditions.
Accessing Further Clinical Information and Patient Guides
You can find current advice on fluvoxamine from sources such as the ones listed below;
- Visit the FDA Medication Guide at [www.fda.gov].
- Check out the National Institutes of Health (NIHS) Drug Portal at [www.nlm.nih.gov].
- Professional organizations in the field of psychiatry include the American Psychiatric Association (APA) and the Royal College of Psychiatrists.
- Pharmacy Consultation Services are offered at pharmacies, in your area or hospitals.
These tools offer the information for professionals regarding fluvoxamine treatment safety and efficacy by providing dosage calculators and patient education materials alongside tools for monitoring drug safety and reporting any adverse effects.
Uvox, Fluvoxamine FAQ
- What is Fluvoxamine?
- How long does Fluvoxamine stay in your system?
- Does Fluvoxamine make you sleepy?
- Does Fluvoxamine help with anxiety?
- Can you drink on Fluvoxamine?
- Can you take Fluvoxamine while pregnant?
- How to wean off Fluvoxamine?
- Can Fluvoxamine cause weight gain?
- Is Fluvoxamine an antipsychotic?
- Does Fluvoxamine help with depression?
- Why is Fluvoxamine so expensive?
- Fluvoxamine how long does it take to work?
- What cold medicine can I take with Fluvoxamine?
- Fluvoxamine maleate what medications to avoid?
- Are Fluvoxamine and Fluoxetine the same?
- Are Fluvoxamine and Fluvoxamine the same thing?
- Are Fluvoxamine and Fluvoxamine maleate the same?
- Can Fluvoxamine cause weight gain?
- Can Fluvoxamine make you tired?
- Can Fluvoxamine cause insomnia?
- Can Fluvoxamine cause constipation?
- Can Fluvoxamine be cut in half?
- Can Fluvoxamine be crushed?
- How Fluvoxamine works?
- Fluvoxamine how long to work?
- Fluvoxamine how to take?
- Fluvoxamine how to stop?
- What Fluvoxamine used for?
- Fluvoxamine what does it do?
- Fluvoxamine what type of drug?
- Fluvoxamine what time to take?
- What is Fluvoxamine maleate used for?
- Fluvoxamine when to take?
- Fluvoxamine when pregnant?
- Fluvoxamine when to stop?
- When does Fluvoxamine start working?
- When was Fluvoxamine invented?
- When should Fluvoxamine be taken?
- Where is Fluvoxamine manufactured?
- Fluvoxamine which class?
- Fluvoxamine which group?
- Which is better Fluvoxamine or Sertraline?
- Which is better Fluvoxamine or Fluoxetine?
- Who cannot take Fluvoxamine?
- Who can prescribe Fluvoxamine?
- Why Fluvoxamine is the best SSRI?
- Why is Fluvoxamine taken at night?
- Why is Fluvoxamine rarely prescribed?
What is Fluvoxamine?
How long does Fluvoxamine stay in your system?
The effects of Fluvoxamine can linger in the body for quite some time after stopping it due to its ability to last around 15 to 22 hours.
Does Fluvoxamine make you sleepy?
Feeling sleepy is an outcome, for individuals when they opt to consume it during the night hours.
Does Fluvoxamine help with anxiety?
Fluvoxamine has been given the light for managing conditions linked to anxiety such as, OCD and social anxiety disorder.
Can you drink on Fluvoxamine?
It's highly recommended to steer clear of alcohol when using Fluvoxamine since it can worsen drowsiness and affect abilities negatively.
Can you take Fluvoxamine while pregnant?
It's important to talk to a healthcare provider before taking Fluvoxamine during pregnancy making sure the benefits outweigh the risks.
How to wean off Fluvoxamine?
Tapering off medication should be a process that is overseen by a healthcare professional to prevent experiencing withdrawal symptoms like dizziness, stomach and shifts in mood.
Can Fluvoxamine cause weight gain?
Gaining weight is not a side effect, for people but it could happen to some individuals based on how long they take the medication and how their body reacts to it.
Is Fluvoxamine an antipsychotic?
Fluvoxamine is classified as an SSRI antidepressant and not as a medication.
Does Fluvoxamine help with depression?
Fluvoxamine is prescribed for managing major depressive disorder and can potentially enhance one's mood as well as aid in improving sleep and appetite.
Why is Fluvoxamine so expensive?
Prices can change based on the brand options you have, the insurance you have, and the pricing in your area. However, generic versions are usually less expensive.
Fluvoxamine how long does it take to work?
It might require, around 2 to 3 weeks for any noticeable changes, in symptoms to become apparent and the complete therapeutic impact usually becomes evident within 7 to 8 weeks.
What cold medicine can I take with Fluvoxamine?
Steer clear of remedies that have dextromethorphan or serotonergic ingredients and seek advice, from a pharmacist, for options that are safe for you to use.
Fluvoxamine maleate what medications to avoid?
Avoid taking MAOI inhibitors and certain medications like thioridazine and tizanidine as they can lead to interactions such as serotonin syndrome when combined with triptans.
Are Fluvoxamine and Fluoxetine the same?
Fluvoxamine and Fluoxetine are not the same; they belong to different classes of SSRIs. Have unique properties and uses.
Are Fluvoxamine and Fluvoxamine the same thing?
While they both fall under the category of SSRIs ( serotonin reuptake inhibitors) they vary in terms of how they're metabolized in the body and their half-life duration as well, as the specific purposes approved by the FDA for each of them.
Are Fluvoxamine and Fluvoxamine maleate the same?
Fluvoxamine maleate and the salt form are essentially interchangeable when it comes to being utilized in medications since they denote the same compound.
Can Fluvoxamine cause weight gain?
It's not common, there are cases where patients might notice changes in their weight over time, like gaining some pounds.
Can Fluvoxamine make you tired?
Many people often experience tiredness and sleepiness as side effects.
Can Fluvoxamine cause insomnia?
During the stages of treatment, with Fluvoxamine in instances there may be disruptions in sleep patterns.
Can Fluvoxamine cause constipation?
Gastrointestinal issues such, as constipation may be experienced at times.
Can Fluvoxamine be cut in half?
You can cut immediate release tablets if they have a scoreline, but avoid splitting extended-release versions and follow the instructions provided by the pharmacy.
Can Fluvoxamine be crushed?
You can crush immediate release tablets if needed; however extended release forms should not be modified.
How Fluvoxamine works?
Fluvoxamine works by boosting serotonin levels in the brain through blocking its reabsorption process, which leads to enhancing mood and decreasing actions.
Fluvoxamine how long to work?
You might start noticing some benefits after two weeks; however it usually takes around 6 to 6 weeks to see the results.
Fluvoxamine how to take?
Take this medication by mouth with or without food as directed by your doctor; a day, at bedtime or split into multiple doses as recommended.
Fluvoxamine how to stop?
Taper off slowly with guidance from a doctor to reduce the chances of experiencing withdrawal symptoms.
What Fluvoxamine used for?
Fluvoxamine what does it do?
It helps control feelings and actions by increasing serotonin levels in the brain.
Fluvoxamine what type of drug?
Fluvoxamine belongs to a class of medications known as serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs).
Fluvoxamine what time to take?
At times suggested for use because of its calming properties but effectiveness can differ depending on how each person reacts to it.
What is Fluvoxamine maleate used for?
It is commonly recommended for individuals dealing with OCD as depression and specific types of anxiety disorders.
Fluvoxamine when to take?
Typically taken once a day in the evening unless advised differently by a professional.
Fluvoxamine when pregnant?
Only use if absolutely necessary and as advised by a healthcare professional considering the risks, to the baby.
Fluvoxamine when to stop?
It's important to discontinue treatment under the guidance of a professional to avoid experiencing discontinuation syndrome.
When does Fluvoxamine start working?
It's possible to experience some relief from symptoms in 1 to 3 weeks. It usually takes about 4 to 6 weeks to see the benefits.
When was Fluvoxamine invented?
In 1970 Fluvoxamine was invented. Subsequently authorized for use in nations during the 1980 and 1990 periods.
When should Fluvoxamine be taken?
Usually taken in the evening because it might cause drowsiness; however the dosage can be customized based on needs.
Where is Fluvoxamine manufactured?
Fluvoxamine is produced by companies worldwide; this includes manufacturers in the United States and regions, across Europe and Asia.
Fluvoxamine which class?
It falls under the category of a serotonin reuptake inhibitor known as an SSRI.
Fluvoxamine which group?
It falls under the category of antidepressants known as SSRIs specifically.
Which is better Fluvoxamine or Sertraline?
Effectiveness can differ from person, to person; while both are SSRIs and used for treatment purposes. Fluvoxamine is often favored for OCD specifically while Sertraline has applications.
Which is better Fluvoxamine or Fluoxetine?
Both Fluvoxamine and Fluoxetine are known to be SSRIs; however Fluvoxamine is commonly preferred for OCD specifically while Fluoxetine has a range of FDA approved uses.
Who cannot take Fluvoxamine?
People who are taking MAOI inhibitors or have liver problems should steer clear of using Fluvoxamine if they are allergic, to it.
Who can prescribe Fluvoxamine?
Healthcare professionals, with licenses such as psychiatrists and primary care physicians are joined by nurse practitioners, in the field of healthcare.
Why Fluvoxamine is the best SSRI?
There is evidence supporting its effectiveness in treating OCD. It possesses distinct pharmacological characteristics; however, the determination of the "best" option hinges on an individual's response and specific condition.
Why is Fluvoxamine taken at night?
Nighttime use of this medication helps decrease tiredness during the day, due, to its effects.
Why is Fluvoxamine rarely prescribed?
Compared to SSRIs, in the market, with indications and fewer drug interactions this particular one has a more limited range of uses, making it less commonly prescribed for routine treatment.