Fungeeheal, Itraconazole
- Introduction to Fungeeheal (Itraconazole)
- Overview of Fungeeheal and its Clinical Relevance
- Classification: Triazole Antifungal Medication
- Forms Available (Capsules, Oral Solution, Injection)
- Composition and Formulation of Fungeeheal
- Active Ingredient: Itraconazole
- Inactive Ingredients and Excipients
- Differences in Formulation Between Capsule and Oral Solution
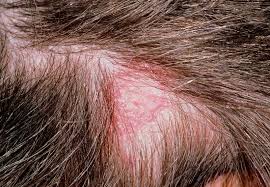
- Terbinafine and Itraconazole
- Itraconazole vs Fluconazole
- Voriconazole vs Itraconazole
- Itraconazole vs Ketoconazole
- Itraconazole vs Nystatin
- Itraconazole vs Diflucan
- Voriconazole vs Itraconazole
- Itraconazole Mechanism of Action
- Itraconazole Half-Life
- Inhibition of Fungal Cytochrome P450 Enzyme
- Disruption of Ergosterol Synthesis in Fungal Cell Membranes
- Antifungal Spectrum: Dermatophytes, Yeasts, and Molds
- Approved Medical Uses of Fungeeheal (Itraconazole)
- Itraconazole for Yeast Infection
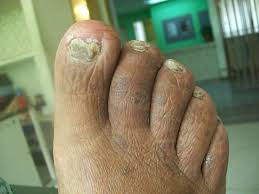
- Itraconazole for Onychomycosis
- Blastomycosis
- Itraconazole for Histoplasmosis
- Aspergillosis (Non-Invasive)
- Candidiasis (Oral, Esophageal, Vaginal)
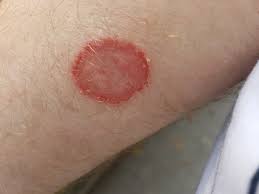
- Dermatophytosis (Tinea Corporis, Tinea Pedis, Tinea Cruris)
- Itraconazole for Toenail Fungus
- Itraconazole for Mold Toxicity
- Itraconazole for Ringworm
- Off-label and Investigational Uses of Itraconazole
- Prophylaxis in Immunocompromised Patients (e.g., Neutropenia, Transplant)
- Treatment of Chromoblastomycosis and Sporotrichosis
- Management of Allergic Bronchopulmonary Aspergillosis (ABPA)
- Use in Certain Cases of Leishmaniasis
- Adjunctive Use in Basal Cell Carcinoma and Other Cancers (Angiogenesis Inhibition)
- Itraconazole for Cats
- Itraconazole for Dogs
- Dosage and Administration Guidelines for Fungeeheal Itraconazole
- Itraconazole Dose for Adults
- Standard Dosage Recommendations for Each Indication
- Itraconazole Dose for Fungal Infection
- Itraconazole Dose for Skin Infection
- Pulse vs. Continuous Therapy for Onychomycosis
- Dosage Adjustments in Hepatic and Renal Impairment
- Administration Tips: With Food vs. Empty Stomach Depending on Formulation
- Itraconazole Dog Dosage
- Itraconazole Dosage Cats
- Itraconazole Dosage for Dogs with Blastomycosis
- Overdose and Emergency Measures for Itraconazole
- Side Effects of Itraconazole
- Itraconazole Interactions
- Warnings and Important Precautions Before Using Fungeeheal
- Itraconazole Contraindications
- Careful Administration in Special Populations
- Storage Instructions for Fungeeheal
- Safe Handling and Disposal of Fungeeheal
- Patient Education and Counseling Points
Introduction to Fungeeheal (Itraconazole)
Fungeeheal is a known type of itraconazole that is widely recognized for its antifungal properties, against various types of fungal infections, both on the surface and within the body tissues. It has significantly impacted treatment by focusing on inhibiting ergosterol production. An element in fungal cell structures. Fungeeheal is commonly recommended for treating ailments such as;
- Fungal nail infections, also known as onychomycosis.
- Fungal infection known as sporotrichosis.
- Histoplasmosis is an infection that affects the lungs.
- Aspergillosis comes in invasive and non-invasive forms.
This antifungal medication is crucial, in treating infections for patients both in outpatient and inpatient settings when other treatments have not been effective or when there is concern about resistance developing.
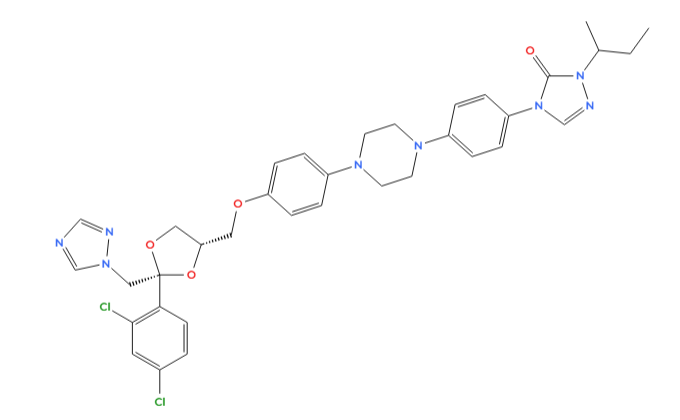
Overview of Fungeeheal and its Clinical Relevance
Itraconazole, found in Fungeeheal can slow down the growth of fungal cells and kill them, depending on the type of fungus and the concentration, in the tissue it targets. It is considered a second-generation triazole with a safety record and broader antifungal coverage in medical practice. It has an attraction to tissues in keratin, like nails and skin, which makes it highly effective against dermatophytosis and candidiasis. Moreover, the way it enters the bloodstream allows for treating infections such as blastomycosis and paracoccidioidomycosis.
Classification: Triazole Antifungal Medication
Fungeeheal is classified as a type of medication known as a triazole that works by blocking the enzyme 14 alpha demethylase in the P450 pathway. The impact of this blockage is the interruption of ergosterol production in fungal cells, leading to destabilization of their membranes. Stopping their growth. In comparison to imidazoles, Fungeeheal and other triazoles, such as itraconazole, provide advantages such as the enhanced ability to penetrate tissues.
Forms Available (Capsules, Oral Solution, Injection)
Fungeeheal comes in some forms to cater to different medical situations.
- Capsules are recommended for term or ongoing treatment purposes. Works well for conditions, like onychomycosis and tinea infections.
- For treating oropharyngeal and esophageal candidiasis, an oral solution is better, due to its absorption rate in the body.
- For infections or when oral absorption is not effective, intravenous (IV) administration is used as a treatment option.
The properties of each formulation result, in a pattern that greatly influences the effectiveness of treatments.
Composition and Formulation of Fungeeheal
Fungeeheal consists of itraconazole as a component, along with a blend of excipients designed to improve its solubility and absorption capabilities. The intricate nature of itraconazole calls for delivery mechanisms to be developed for its oral and injectable variations.
Active Ingredient: Itraconazole
The key ingredient of itraconazole is a molecule that loves fats and has an attraction to ergosterol in particular. It shows effectiveness against a range of pathogens such, as;
- Dermatophytes, like Trichophyton and Microsporum are commonly involved in skin infections.

- Candida and Other non-albic species
- The fungus known as Aspergillus fumigatus is commonly found in environments.
- Histoplasma capsulatum is a type of fungus.
Inactive Ingredients and Excipients
There are differences in the makeup of capsules and oral solutions.
- The capsules consist of sugar spheres along with hypromellose and polyethylene glycol coated with titanium dioxide.
- Oral Solution, with hydroxypropyl beta cyclodextrin, is used to improve the solubility of itraconazole and its penetration, into the mucosa.
The inactive ingredients may not have any properties, but they play a vital role in improving how the body absorbs and stores the medication.
Differences in Formulation Between Capsule and Oral Solution
The liquid form of the medication has absorption rates around 55% compared to capsules, which range from 30 to 40% due to its state in the body's system, and should be taken on an empty stomach for best results, instead of being influenced by food intake like capsules are known to be. These differences in how the medications are absorbed play a role in medical decision-making processes for conditions such as mucosal candidiasis or systemic fungal diseases, where maintaining consistent levels of the drug in the bloodstream is crucial.
Terbinafine and Itraconazole
Both agents work on treating dermatophyte infections but in different ways; Terbinfine blocks squalene epoxidase while itraconazole affects ergosterol synthesis at a stage in the process.
- Terbinafine is more lethal to fungi, while itraconazole may only inhibit their growth depending on the dosage and type of organism involved. Terbinafine is the choice for treating scalp ringworm and toenail infections.
- Itraconazole is useful against a range of infections, like yeasts and dimorphic fungi.
Itraconazole vs Fluconazole
Although fluconazole and itraconazole are both classified as triazoles, in their drug category of properties, there are significant distinctions between the two when it comes to their solubility in water and their ability to reach high levels in cerebrospinal fluid. Characteristics that render fluconazole more suitable for treating cryptococcal meningitis. Despite these similarities in chemical structure, itraconazole is known for its efficacy against Aspergillosis and endemic fungi, setting it apart from fluconazole. Key variations include;
- Fluconazole is known for its ability to penetrate the fluid effectively. Has fewer interactions with other drugs.
- Itraconazole has a range of effectiveness against fungi, but its ability to penetrate the nervous system is restricted.
Voriconazole vs Itraconazole
Voriconazole is a type of triazole that works well against aspergillosis and is commonly chosen for patients with weakened immune systems. However, its unpredictable way of moving through the body and vision issues make it less suitable for use. Itraconazole is still the go to option for treating standing infections that require consistent tolerability over time.
Itraconazole vs Ketoconazole
The use of Ketoconazole has decreased because of its liver damage and limited effectiveness in the body. Itraconazole presents a more efficient method, for treatment as it has improved targeting of tissues and fewer hormonal side effects. Some advantages of Itraconazole include; Greater strength, decreased likelihood of adrenal function suppression. More flexibility in some settings.
Itraconazole vs Nystatin
The use of nystatin is limited to treating candidiasis because it is minimally absorbed into the bloodstream. On the other hand itraconazole is able to reach parts of the body and is effective in treating invasive fungal infections. Only use Nystatin for treating candidiasis on the skin or, in the mouth. Itraconazole is used to treat both systemic infections.
Itraconazole vs Diflucan
Diflucan is the brand name of fluconazole, which is easier to use and better received compared to itraconazole. It lacks the coverage of itraconazole, against molds, like Aspergillus. Choose itraconazole in the following scenarios;
- Non-candida fungal species are suspected
- Fluconazole resistance has been detected.
- Infections that exhibit dimorphism are at play.
Voriconazole vs Itraconazole
The range of effectiveness of voriconazole largely matches that of itraconazole. Also includes Scedosporium and Fusarium species. It is considered appropriate for use in patients at risk, those with hematologic malignancies, or those undergoing transplants.
Despite its benefits, voriconazole needs monitoring due to its metabolism being unpredictable. The risk of causing phototoxicity and hallucinations. Itraconazole continues to be an option for treating terbinafine-resistant fungal infections where safety and cost are top priorities.
Itraconazole Mechanism of Action
Itraconazole is a type of medication from the triazole class that works by blocking the cytochrome P450 enzyme system in fungi and particularly targeting fungal CYP51 (14α demethylase). This enzyme plays a role in converting lanosterol into ergosterol. A sterol that is important for the integrity and functionality of fungal cell membranes.
Disrupting this enzyme activity disrupting the production of ergosterol. Causes the buildup of 14α. Methylated sterols affect the permeability of cell membranes and the functioning of enzymes. This specific disturbance causes fungal cells to become inactive or die out completely when exposed to itraconazole at varying concentrations, and based on the susceptibility of the pathogen involved.
Its strong ability to bond with tissues due to its lipophilicity is particularly effective in areas such as nails and skin, which helps in maintaining its antifungal effectiveness over time.
Itraconazole Half-Life
The rate at which itraconazole is removed from the body follows a two-phase pattern in terms of its elimination half-life characteristics. The initial plasma half-life lasts around 20 to 24 hours following an administration. Prolongs up to 42 hours with recurring doses because of tissue buildup and the saturation of liver enzymes. Essential pharmacokinetic attributes include;
- Extensive liver processing, through the enzyme CYP450, A significant proportion of the protein binds to (>99%).
- The primary mode of waste elimination is through bowel movements.
- Typically, it takes 14 days of administration to reach stable levels in the body for the effects of this medication to kick in fully.
Thanks to its lasting nature in the system, it can be given intermittently, such as for treating fungal infections, like nail fungus.
Inhibition of Fungal Cytochrome P450 Enzyme
The main way itraconazole fights fungi is by stopping the fungal enzyme cytochrome P450 14α demethylase, which is crucial for making ergosterol in their bodies. Without this enzyme working well, the fungus can't grow properly at a cell level.
Something unique about the version of cytochrome P450 compared to ours is that it binds to itraconazole easily, which makes it more targeted for treatment purposes.
By blocking this enzyme's work it causes the fungal cells to have membranes and become weaker until they die off in the end.
Nevertheless, this system also presents a danger, in terms of interactions, between drugs, those processed by the human enzyme CYP 34 A, requiring careful clinical observation.
Disruption of Ergosterol Synthesis in Fungal Cell Membranes
Ergosterol acts as the equivalent of cholesterol found in cells and plays a crucial role in maintaining the fluidity and integrity of plasma membranes while regulating intracellular signaling processes.
Specifically targeting ergosterol synthesis by itraconazole triggers a series of membrane destabilizations, leading to disruptions in functions arising from altered ergosterol biosynthesis.
Malfunctioning enzymes that are bound to the membrane, Issues with transporting nutrients.
The disruption of balance, Itraconazole is especially effective, in treating infections like histoplasmosis or blastomycosis because it increases dysfunction through the build up of abnormal sterol intermediates over time.
Antifungal Spectrum: Dermatophytes, Yeasts, and Molds
Itraconazole is known for its ranging capabilities that target various types of harmful fungi from three main groups.
- Dermatophyte fungi like Trichophyton species and Microsporum species are known to cause conditions such, as athlete's foot (tinea pedis), ringworm (tinea corporis), and fungal nail infections (onychomycosis).
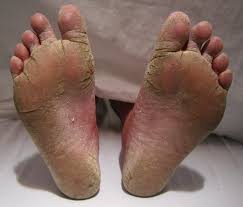
- Common yeasts such as Candida albicans and C. tropicalis are frequently found in both systemic candidiasis infections, alongside C.parapsilosis. Cryptococcus neoformans.
- Organisms, like Aspergillus fumigatus and Histoplasma capsulatum, are known to cause endemic infections, while Blastomyces dermatitidis and Sporothrix schenckii are also associated with these diseases.
Itraconazole plays a role in treatment due, to its ability to combat various types of fungal infections on the surface and deep within the body effectively It is valued for its wide range of effectiveness and distribution in the body which makes it a significant option, for treating patients with weakened immune systems and challenging fungal conditions.
Approved Medical Uses of Fungeeheal (Itraconazole)
Fungeeheal is a medication that includes the drug itraconazole and is authorized for treating various types of skin and internal fungal infections. Having a range of properties and being well distributed in tissues make it a preferred primary or supplementary treatment option, for skin conditions, respiratory issues, and systemic infectious diseases.
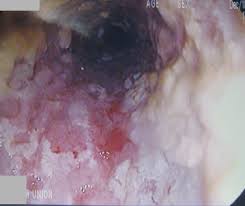
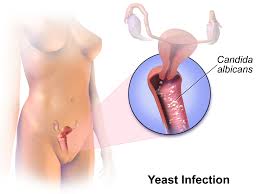
Itraconazole for Yeast Infection
Candida albicans is a cause of yeast infections that can appear in both cutaneous areas of the body. There have been results shown with the use of itraconazole in treating conditions like oropharyngeal candidiasis (in the throat), candidiasis in the esophagus, and vulvovaginal candidiasis. The therapeutic benefits of using itraconazole include: Swift relief from symptoms, in cases where traditional treatments have been ineffective. In cases where fluconazole exhibits decreased effectiveness
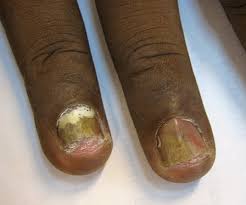
Itraconazole for Onychomycosis
Chronic fungal infections of the nail bed, known as onychomycosis, are often caused by Trichophyton rubrum or Trichophyton mentagrophytes. Fungeeheal is approved for treating onychomycosis in both fingernails and toenails due to its affinity for keratin and ability to stay in nail tissues for a time. Pulse therapy involving a dosage of 200 mg daily for one week each month is commonly used to increase effectiveness while reducing exposure to the medication. This treatment method is especially beneficial for patients with health conditions. Who are taking multiple medications.
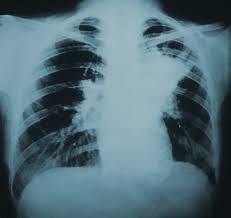
Blastomycosis
Blastomycosis is an infection caused by Blastomyces dermatitidis that mainly impacts the lungs and can spread to the skin well as bones and the genitourinary tract. Itraconazole is considered the treatment for mild to moderate cases of pulmonary and extrapulmonary blastomycosis. Some benefits of this treatment option are;
- Great absorption in fatty tissues.
- A verbal prescription is appropriate for handling outside the hospital.
- Comparatively less harmful than amphotericin B.
Itraconazole for Histoplasmosis
Histoplasmosis, caused by Histoplasma capsulatum is prevalent in certain areas. Often impacts individuals with weakened immune systems. Fungichem proves successful in treating acute pulmonary disseminated and chronic cavitary histoplasmosis. Itraconazole plays a part in the following scenarios;
- Initial treatment for persistent situations that are not severe
- Post-amphotericin induction maintenance treatment.
- For individuals with systems, it is essential to adhere to a consistent regimen of oral medication over an extended period.
Aspergillosis (Non-Invasive)
Itraconazole is used to treat allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis (ABPA), which is a non-invasive form of Pulmonary Aspergillosis caused by Aspergillus fumigatus fungal colonization in the lungs. Its abilities to reduce inflammation and fight infections are beneficial in managing these conditions.
- Minimize the amount of fungus in the lungs.
- Manage flare-ups in Allergic Bronchopulmonary Aspergillosis (ABPA).
- Offer advantages that reduce the need for steroids.

Candidiasis (Oral, Esophageal, Vaginal)
Fungeeheal has been shown to be effective in treating types of candidiasis. From cases to more widespread infections, such as oral thrush and esophagitis. As well as vulvar and vaginal yeast infections that may not respond well to initial azole treatments. Itraconazole is considered superior in these cases due to its qualities and benefits.
- Elevated levels of mucus in the lining.
- Engaging in actions to combat albicant Candida strains.
- An option, for strains that're resistant, to fluconazole
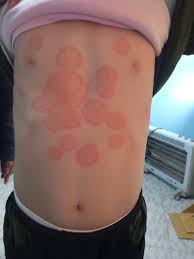
Dermatophytosis (Tinea Corporis, Tinea Pedis, Tinea Cruris)
Dermatophytosis is still a reason to use itraconazole as it works well for skin infections, like body and feet fungi infections offered by Fungeeheal.
- The cream penetrates deeply into the layers of the skin.
- Quick elimination of infections, with reduced chances of them coming back.
- Convenient schedules, for short medication courses
Itraconazole for Toenail Fungus
Treatment of toenail fungus is often challenging because medications have trouble reaching the area effectively. Itraconazole is able to build up in the nail matrix. Continues to fight infections even after treatment stops. These characteristics make it a favorable choice due to its properties;
- Nails that have become thicker or dystrophic
- Mixed occurrences of dermatophytes and yeasts in infections.
- Cases that are stubborn and do not respond well to treatments.
Itraconazole for Mold Toxicity
While it's not a practice to do so, itraconazole has been used unofficially to treat mold-related illnesses in individuals who have been exposed to mold and are showing systemic symptoms. Possible reasons for its effectiveness might include;
- Anti-inflammatory effects through immumodulation
- Reduction of growth in the sinuses and lungs.
- Playing a part in cleansing procedures.
However, the confirmation of the effectiveness in this situation is still being researched.

Itraconazole for Ringworm
Ringworm (known as tinea corporis, in terms) is a skin condition caused by a fungal infection that affects the outer layer of the skin. When the affected areas are widespread or show signs of inflammation or recurrence of symptoms itraconazole proves to be an option compared to using topical antifungal medications. Key points to remember regarding treatment include;
- Systematic removal of infections, from the skin. An effective strategy involves taking a dose of 100 mg for a duration of 2 weeks.
- Consistent performance, in areas of the skin, with a concentration of sebum-producing glands.
- Fungeeheal remains a component, in treating persistent fungal infections due to its wide range of applications and excellent safety record.
Off-label and Investigational Uses of Itraconazole
Itraconazole has been officially approved to treat fungal infections; however, ongoing research, in the medical field has uncovered numerous additional uses that go beyond its initial approval status for off-label and investigational purposes. This expanded utilization highlights the pharmacological profile of itraconazole. Showcasing its effectiveness not as an antifungal agent but also for its anti-inflammatory and potential antitumor properties.
Prophylaxis in Immunocompromised Patients (e.g., Neutropenia, Transplant)
Itraconazole is being increasingly used as a prophylactic treatment in at high-risk groups, like those who have undergone stem cell transplants and individuals experiencing prolonged periods of low neutrophil levels. Lowers the occurrence of aspergillosis.
Offers a range of protection through oral forms. It is frequently paired with monitoring of medication levels. Many transplant centers include itraconazole as a component of their antifungal prevention plans, even though its universal approval for prophylaxis is not guaranteed; this is particularly true in cases where there are worries about mold resistance.
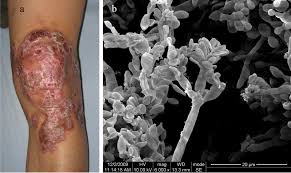
Treatment of Chromoblastomycosis and Sporotrichosis
Skin and tissue fungal infections, like chromoblastomycosis and lymphocutaneous sporotrichosis, usually need long-term treatment, with medications that work throughout the body. Itraconazole has shown effectiveness in treating these infections.
Based on what doctors have seen in practice it is commonly used for these conditions because;
- Delving deeply into the layers.
- Consistent levels of tissue presence.
- Acceptable tolerance, during periods of treatment
In some cases, like chromoblastomycosis and lymphocutaneous sporotrichosis, where potassium iodide therapy is not an option or recommended due to reasons like contraindications or ineffectiveness for some patient's a common approach involves prescribing itraconazole for a period ranging from 6 to 12 months in the former and several months in the latter.
Management of Allergic Bronchopulmonary Aspergillosis (ABPA)
ABPA is a response triggered by the presence of Aspergillus fumigatus, in the body and commonly impacts people with asthma or cystic fibrosis. Itraconazole doesn't provide a cure. It is important in lessening levels and controlling immune system reactions. Its advantages are as follows;
- Decrease in reliance on corticosteroids
- Enhancement of lung function measurements
- Reduction of Ig type E. Decrease of eosinophils.
Patients who experience repeated flare-ups or those unable to use steroids, term find itraconazole to be highly efficient.
Use in Certain Cases of Leishmaniasis
While not commonly used as a treatment option for leishmaniasis cases initially presented with medications; itraconazole has demonstrated effectiveness against certain types of the disease, like cutaneous leishmaniasis resulting from Leishmania mexicana and similar strains of the parasite. The efficacy of this drug in inhibiting the production of ergosterol sterols in protozoa serves as the basis for its use in treating these specific conditions. According to findings from studies;
- Moderate effectiveness, in skin lesions that are confined to an area
- In situations where standard treatments have failed or when a condition resurfaces utility can be explored as a salvage option.
- The possible combination, with compounds containing antimony
More studies are required to confirm its application in managing leishmaniasis.
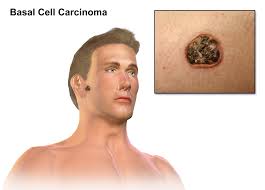
Adjunctive Use in Basal Cell Carcinoma and Other Cancers (Angiogenesis Inhibition)
Studies have shown that Itraconazole exhibits properties that can restrict blood vessel growth and cell proliferation in cancer research studies. Its ability to block the Hedgehog signaling pathway and slow down the growth of cells, in blood vessels has prompted research into its effectiveness against cancers like basal cell carcinoma (BCC) non non-small cell lung cancer, and prostate cancer. Exciting possibilities for using it in cancer treatment are being explored.
Decrease in the size of basal cell carcinoma lesions and the frequency of their recurrence. Slowed down the growth of tumors in late-stage prostate cancer. Enhanced cooperation with chemotherapy medications. Itraconazoles affordability and proven safety record make it a promising option, for repurposing in cancer treatment; however extensive trials are still awaiting confirmation.
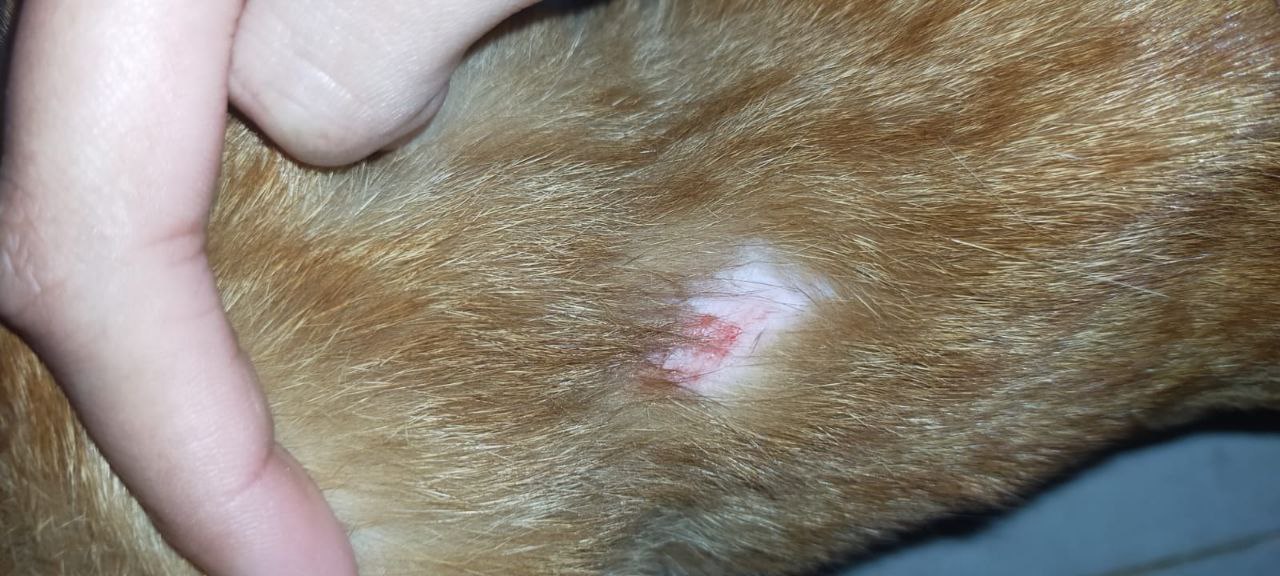
Itraconazole for Cats
In veterinary practice itraconazole is often used off-label to treat skin infections in cats and is particularly useful in managing the following conditions;
- Skin infection caused by a type of fungus, sporotrichosis
- Microsporum canis.
- Cryptococcosis is an infection that can affect both humans and animals.
It is preferred over ketoconazole because it is better tolerated with risk to the liver. The dosage schedules should be adjusted based on the metabolism of each species, and regular monitoring of liver enzymes is advised for use.
Itraconazole for Dogs
Itraconazole is commonly given to dogs to help with infections such as those listed below;
- Blastomycosis, an infection caused by Blastomyces dermatitidis.
- Histoplasmosis is an infection caused by inhaling spores of the Histoplasma capsulatum fungus.
- Aspergillosis is a condition.
Its strong ability to bind to tissues and its good absorption when taken by mouth make it a great option for treatment regimens in veterinary care settings. It is practice to use animal medications or custom-made doses to ensure the right amount and taste appeal for pets. While not officially approved for this purpose in animals, yet widely accepted in the field of mycology, it is gaining popularity for its anti-inflammatory properties that can help alleviate long-term skin conditions in dogs.
Dosage and Administration Guidelines for Fungeeheal Itraconazole
Correct dosing and proper administration of Fungeeheal (itraconazole) play a role in enhancing the effectiveness of treatment while reducing potential side effects to a minimum level. The dosage required may differ depending upon the nature of the infection being treated and individual patient characteristics well as the specific form of the medication utilized. Following established guidelines supported by evidence is key to achieving the possible treatment results.
Itraconazole Dose for Adults
For grown-up patients, the treatment needs to match the seriousness of the infection and the specific organism causing it. In some cases, daily oral doses can vary from 100 mg to 400 mg. Extended treatment periods might be needed for issues or widespread infections.
- For systemic infections, the recommended daily dosage is between 100 and 200 milligrams.
- Instructions for invasive infections are to take 200 mg twice a day.
Regular monitoring of plasma levels is recommended for individuals on long-term treatment plans, those with immune systems.
Standard Dosage Recommendations for Each Indication
Therapy approaches differ depending on the type of infection.
- Treatment for onychomycosis involves taking 200 milligrams a day for either 12 weeks for toenails or 6 weeks for fingernails. Alternatively pulse dosing can be done by taking 200 milligrams for one week per month and repeating this cycle for 2 to 3 months.
- Blastomycosis or Histoplasmosis treatment typically involves taking 200 mg of medication for a duration of 6 to 12 months.
- Aspergillosis treatment typically involves a dosage ranging from 200 to 400 mg based on the seriousness of the disease.
- Treatment, for vaginal yeast infection includes taking 200 mg twice a day for one day or 200 mg for three days.
Itraconazole Dose for Fungal Infection
When treating infections, with itraconazole medication usually starts at 200 mg daily dose initially but may be increased to 400 mg daily in severe or widespread cases and taken in separate doses throughout the day for better effectiveness. For long term treatment of infections like mycoses the therapy should be continued with regular monitoring of liver function, for safety.
Itraconazole Dose for Skin Infection
Superficial skin infections, like ringworm, on the body or groin area and athlete's foot typically improve with treatment.
- Take 100 milligrams each day for a period of 15 days, suitable for treating mild to moderate infections.
- 200 milligrams per day, for a week (short-term treatment).
Antifungal creams can be applied in addition to treat skin lesions more effectively.

Pulse vs. Continuous Therapy for Onychomycosis
There are two courses of treatment using itraconazole for nail infections.
- Dosage recommendation, for pulse therapy is 200 mg taken daily for one week per month with a total of two pulses for fingernail treatment or three to four pulses, for toenail treatment.
- Continuous treatment involves taking 200 milligrams a day for either 6 weeks (for fingernail treatment ) or 12 weeks for toenail treatment).
Treatment, in pulses enhances adherence. Lowering liver damage risks while administering medication continuously might result in increased overall recovery rates for severe conditions.
Dosage Adjustments in Hepatic and Renal Impairment
Patients with liver or kidney issues should be careful because their bodies may process and remove drugs differently.
- Please use this medication carefully if you have liver issues, and make sure to check your liver function through tests.
- Renal dysfunction is better managed with the use of solution than capsules, as it allows for improved absorption.
- It is advisable to avoid the IV formulation due to the risk of cyclodextrin buildup.
It might be necessary to monitor the drugs to make sure they work well and don't cause harm in these groups of people.
Administration Tips: With Food vs. Empty Stomach Depending on Formulation
Itraconazole shows absorption properties that depend on the formulation used.
- Remember to consume the capsules with a meal to improve absorption through stomach acid.
- Recommended usage of the solution on the stomach to enhance thorough mucosal absorption.
Taking drinks such as cola alongside the medication might enhance absorption for patients with stomach acid levels.
Itraconazole Dog Dosage
In practice, it is common to prescribe itraconazole for skin fungal infections, in dogs even though it is not officially approved for this use. The usual dose for canines is as follows;
- Take 1 dose of 9 milligrams, per kilogram by mouth each day.
- The length of treatment may vary from a weeks to months based on how the patient responds to the treatment and the seriousness of the illness.
It is recommended to keep an eye out for any liver-related side effects during the treatment process.
Itraconazole Dosage Cats
Itraconazole is commonly prescribed for skin infections, in cats like ringworm and other serious fungal infections such as sporotrichosis and cryptococcosis, with dosage instructions to follow. Administer an oral dose of 10 milligrams per kilogram. For individuals with varying drug metabolism rates it may be essential to consider treatment periods. Regularly checking liver enzyme levels and observing symptoms is crucial during the entire treatment process.

Itraconazole Dosage for Dogs with Blastomycosis
Treating blastomycosis in dogs involves the use of treatment with itraconazole being given over a prolonged period, at specified intervals;
- Administer 500 micrograms per kilogram two times a day, during the week.
- Then the dosage is lowered to 5-10 mg/kg per day for a period of 60-90 days.
To avoid a relapse, treatment should be maintained for a minimum of one month after the patient shows improvement and the radiographic results normalize.
Overdose and Emergency Measures for Itraconazole
While itraconazole is usually well received by the body, taking much of it – whether accidentally – can lead to various harmful effects throughout the system. It is important to recognize and address this situation.
Signs and Symptoms of Itraconazole Overdose
Excessive use could show up with worrying symptoms.
- Feeling sick, to your stomach with an urge to throw up, and abdominal pain.
- Hepatic dysfunction ( levels of enzymes called transaminases and yellow discoloration of the skin and eyes).
- Symptoms, like feeling lightheaded or disoriented might be experienced in the system.
- Swelling in the arms and legs, along with imbalances in electrolytes
- In some instances patients with existing liver or heart issues might experience arrhythmias or liver damage.
Immediate Interventions and Supportive Care
There isn't an antidote for itraconazole toxicity. The main approach is supportive management.
- Please stop taking itraconazole.
- If the ingestion occurred recently consider giving charcoal.
- Keep an eye on the functions of the liver, kidneys, and heart.
- Please start with managing symptoms of nausea or arrhythmias.
During cases of poisoning or toxicity levels, in the body being high enough to cause harm to organs may require hospitalization and intravenous fluids to ensure organ function and help the body eliminate the toxins more effectively.
When to Seek Emergency Medical Attention
In situations, urgent action is necessary;
- Symptoms of liver failure include yellowing of the skin and eyes (jaundice)
- Blood clotting issues and cognitive impairment ( encephalopathy).
- Symptoms related to the heart include feelings of irregular heartbeat (palpitations), heart rate (bradycardia), and prolongation of the QT interval.
- Experiencing stomach issues along with an imbalance in electrolytes.
Recognizing the issue early and taking an approach are key to avoiding complications in instances of itraconazole.
Side Effects of Itraconazole
Itraconazole is considered beneficial. Comes with a range of side effects that differ in how often they occur and how serious they are known to be. Knowing about its safety record is important, for taking care and minimizing risks when undergoing antifungal treatment.
Frequently Reported Side Effects
Many patients generally handle itraconazole well; However, some may encounter side effects at the beginning of their treatment. These side effects commonly include:
- Feeling sick to your stomach is sometimes linked to the amount of medication you take. It can be reduced by eating a meal when taking it in capsule form.
- Headache is usually an issue that can be controlled with pain relievers.
- Digestive discomfort may be linked to irritation of the stomach lining or stress on the liver.
- Mild and temporary diarrhea may be linked to an imbalance in the gut flora.
The typical outcomes of these conditions are usually harmless. Lessen as the body gets used to the medicines effects.

Less Common but Serious Side Effects
While rare occurrences may happen with itraconazole use. May lead to side effects that require prompt medical care due to their potential seriousness.
- The effects on the liver can range from showing no symptoms with liver enzyme levels to experiencing sudden liver failure.
- If the levels of liver enzymes like ALT or AST are high. There's an increase in bilirubin levels detected in the blood tests. It's essential to stop whatever is causing it.
- Congestive heart failure (CHF); Itraconazole might have an impact, on heart muscle contraction strength. Should not be used in patients with ventricular dysfunction.
- Symptoms of peripheral neuropathy include sensations of tingling and numbness well as potential motor issues. This condition is usually reversible upon cessation of the underlying cause.
The responses highlight the significance of personalized treatment approaches for individuals with preexisting liver issues or heart and brain conditions.

Monitoring Requirements During Therapy
Patients taking itraconazole should undergo monitoring, especially if the treatment lasts longer than two weeks or is, for infections.
- It's recommended to conduct liver function tests (known as LFTs) regularly for monitoring purposes.
- In cases where individuals have heart-related conditions or are taking medications that may prolong the QT interval, it is advisable to assess their electrocardiogram.
- Monitoring drug levels is beneficial for patients with immunocompromised systems or difficult-to-treat infections.
- The recommended target levels are at least 0.5mcg/mL for prophylaxis and at least 1.0mcg/mL for treatment purposes.
Early detection of irregularities helps in taking action and avoiding damage from irreversible toxicity.
Itraconazole Side Effects in Dogs
The use of itraconazole in medicine is typically considered safe for dogs; however it can still lead to some effects that are commonly seen in practice;
- Anorexia and losing weight may be caused by irritation in the gastrointestinal system.
- Liver damage can become more noticeable with usage of a substance it is crucial to keep an eye on ALT and ALP levels.
- Feeling tired and having stomach troubles can lead to vomiting or diarrhea in some cases when taking doses.
Pets receiving care for fungal infections require regular monitoring through consistent blood tests and thorough physical examinations to guarantee both safety and effectiveness.

Itraconazole Interactions
Itraconazole strongly blocks the cytochrome CYP3A4 enzyme, leading to pharmacokinetic interactions with drugs in terms of how the body processes them. Its narrow range of effective doses means that using it with medications requires careful attention to prevent harmful effects or treatment not working as intended.
CYP3A4 Inhibition and Interaction Profile
When itraconazole hinders CYP34 activity in the body's metabolism process of substances gets affected, leading to severe outcomes or even fatal results, depending on the other medication being taken concurrently. Some of the substances impacted by this interaction are;
- Medications that block calcium channels
- Immunosuppressive medications
- Cholesterol lowering medications called statins
- Antiarrhythmic medications
Changes in the dosage or switching to medications that do not interact may be necessary to reduce risks.
Contraindicated Drugs (e.g., Cisapride, Quinidine, Simvastatin)
Certain medications should not be taken with itraconazole because they could lead to life-threatening situations.
- Warning about cisapride's potential to cause heart rhythm irregularities as a result of prolonging the QT interval.
- Quinidine increases the chances of developing torsades de pointes, a type of heart rhythm disorder.
- Simvastatin and Lovastatin can lead to chances of rhabdomyolysis and liver damage.
It is highly recommended to use medications that do not depend heavily on CYP34 metabolism when itraconazole treatment is required.
Interaction with Antacids, PPIs, and H2 Blockers Affecting Absorption
Itraconazole absorption depends on the level. It is especially important for the capsule form as it works best in an acidic environment to be most effective in the body's system. When taken along with gastric acid suppressants can lead to levels in the blood which may affect how well it works.
- Antacids should be given with a gap of 2 hours before or after taking itraconazole.
- Proton Pump Inhibitors (PPIs) may decrease absorption.
- You could think about switching to a solution or acidic drinks.
The timing of administration or opting for the oral solution form that is less influenced by changes in pH could enhance results.
Interactions with Immunosuppressants and Anticoagulants
Itraconazole notably increases the levels of immunosuppressants and blood thinners in the bloodstream. This necessitates monitoring.
- Cyclosporine, sirolimus, and tacrolimus have narrow therapeutic windows, so it is important to keep an eye on their trough levels.
- Warfarin enhances the effect, requiring monitoring of INRs.
- The risk of increased bleeding is higher with Rivaroxaban and Apixaban because they inhibit CYP34 and P glycoprotein.
Treatment protocols may include lowering the dose of medication or increasing monitoring to avoid any side effects that may arise from either treatment option.
Itraconazole Drug Interactions
Considering the way it interacts with the body's systems and other medications taken at the time – itraconazole should be carefully prescribed after thoroughly reviewing all current medications being used by the patient.
- Taking benzodiazepines like midazolam and triazolam can lead to levels of drowsiness.
- Decreased breathing function.
- Oral diabetes medications can lead to a risk of blood sugar due to changes in metabolism.
Macrolide antibiotics can lead to inhibition of CYP34 enzymes. Healthcare providers need to review the medication history of every patient to prevent side effects and maintain the effectiveness of itraconazole treatment.

Warnings and Important Precautions Before Using Fungeeheal
Fungeeheal is a type of itraconazole that requires evaluation of risks before starting treatment because of its effects in the body and various interactions with other medications. It is crucial to take precautions when prescribing Fungeeheal to individuals with underlying health conditions or those who need long-term therapy. Customizing the treatment based on each persons needs can help prevent complications and improve the effectiveness of the therapy.
Liver Function Monitoring During Prolonged Use
Itraconazole goes through metabolism in the liver. Requires monitoring of liver function due to this process. There should be testing of liver enzymes, like ALT, AST, alkaline phosphatase, and bilirubin, when using it for a period of time exceeding 30 days. Having your liver function tests (known as LFTs for short) done is a requirement. Please stop the treatment immediately if the levels of transaminases go over three times the limit of what is considered normal, especially if you experience any symptoms. Patients who have long-term liver conditions need to be monitored. May need changes in their medication dosages. In cases of elevations, without symptoms, it may be advisable to continue with caution under the guidance of a specialist.
Risk of Heart Failure and Cardiac Events
Itraconazole causes weakening of the heart's pumping ability. Its use is associated with the development or worsening of congestive heart failure (CHF). It should not be used in people with heart muscle weakness or a previous CH diagnosis. Clinical signs that require stopping the medication are;
- Experiencing shortness of breath.
- Swelling in the extremities or feeling tired.
- Experiencing an increase in weight due to retaining fluids.
- Experiencing sudden or worsening atrial fibrillation.
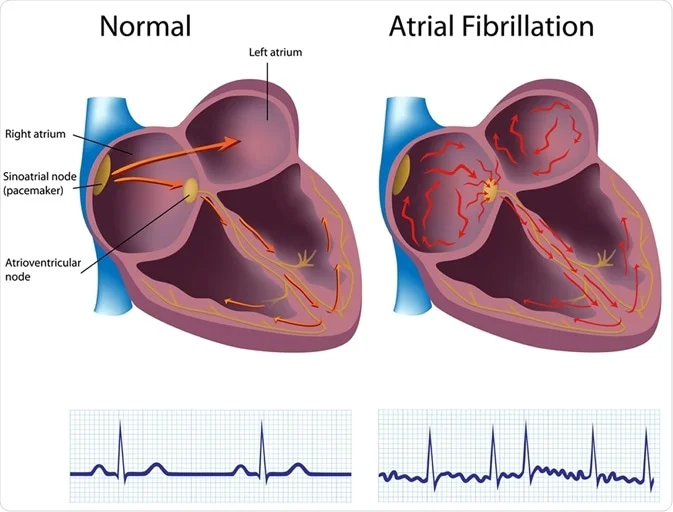
Patients at risk should undergo heart monitoring to monitor their cardiac health closely, particularly those with pre-existing structural heart issues or taking medications that may affect the heart's function.
Potential for Hearing Loss with Prolonged Therapy
It has been noted that sensorineural hearing loss can occur in individuals using itraconazole for a period of time, although this is uncommon. This side effect could potentially be permanent in some instances. It is usually linked to the dosage level. Initial signs may include:
- The ringing sound in your ears, known as tinnitus.
- Feeling dizzy and unsteady.
- Reduction in hearing ability, from a perspective.
It is recommended to conduct hearing tests and consider stopping treatment as any signs of hearing problems appear.
Avoid Alcohol During Treatment
It is recommended to avoid drinking alcohol while undergoing itraconazole treatment because it can harm your liver by adding stress on it and potentially worsening any liver damage present. Alcohol disrupts the breakdown and removal of drugs from the body. Raises the chance of liver function test (LFT) elevation and liver failure. It may worsen system side effects, like feelings of dizziness or confusion. It is recommended to avoid alcohol during the treatment period to protect the liver's health and ensure the effectiveness of the therapy.

Itraconazole Contraindications
Certain groups of patients and specific medical situations may present relative reasons to avoid using itraconazole medication. It is essential to identify these conditions to prevent negative effects.
Known Hypersensitivity to Itraconazole
People who have a confirmed allergy to itraconazole or any antifungal medications should avoid using Fungeeheal as they could experience allergic reactions ranging from minor skin rashes to severe anaphylaxis. There is a chance of cross-reactivity with azoles. It is advised against undergoing emergency desensitization. Different types of medications, with chemical structures, should be taken into account.
Patients with Ventricular Dysfunction or History of Heart Failure
Itraconazole should not be used in patients who have ventricular dysfunction. This includes individuals with the conditions;
- Severe heart failure (NYHA Class III or IV)
- Episodes of heart damage caused by drug use in the past
- Diminished pumping power of the ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF).
Even if patients, with no symptoms have had issues with their hearts' pumping ability it is important for them to undergo a cardiac assessment before any treatment is administered.
Co-administration with Contraindicated Drugs
There are medicines that should not be taken with itraconazole because of interactions that affect how they work in the body, mainly through inhibiting the enzyme CYP34.
- Avoid using drugs like Cisapride, Pimozide or Quinidine as they can cause heart irregularities.
- Potential side effects of Simvastatin and Lovastatin include muscle breakdown known as rhabdomyolysis, and severe liver damage.
- Prolonged use of Triazolam or Midazolam, by mouth can lead to sedation and breathing difficulties.
It is important to conduct a review of medications before prescribing itraconazole to prevent interactions.
Pregnancy Unless Life-Threatening Infection
Itraconazole has been found to cause birth defects in animals. Should not be used during pregnancy in the first trimester unless it is necessary to treat severe fungal infections with no other safe options available. It's important to use birth control during treatment and for two months. It is advisable to conduct a pregnancy test before starting treatment in women of age. It is advised for breastfeeding moms to steer clear of taking itraconazole since there's a risk of it being passed on through breast milk.
Itraconazole and Alcohol
Using alcohol at the same time as taking itraconazole treatment greatly raises the risk of liver damage. The liver faces a workload in breaking down both ethanol and itraconazole, which can result in liver failure in individuals who consume alcohol chronically. Recommendations advise against; It is recommended to refrain from consuming any beverages throughout the duration. Screening for alcohol abuse issues before beginning treatment. People who have had liver disease caused by alcohol should usually steer clear of taking itraconazole unless they are closely monitored.
Itraconazole Foods to Avoid
Some types of food and drinks could affect how itraconazole is absorbed or strengthen side effects. It's advised to consider the following recommendations;
- Vitamin C-rich grapefruits and their juice can boost the levels of itraconazole in the bloodstream by acting as inhibitors of CYP34 enzymes.
- Consuming beverages with caffeine may amplify systemic effects, leading to symptoms, like headaches or restlessness.
- High-fat meals are helpful when consumed in capsule form, but can be harmful when taken as a solution.
The guidance for use should be tailored according to the medication prescribed.

Itraconazole Natural Alternatives
Some patients who can't or don't want to use itraconazole may find that certain natural substances have effects; however none of them are as strong or broad in scope as pharmaceutical azoles are.
- Tea tree oil is known to be useful when applied topically to treat dermatophytosis and candidiasis.
- Garlic extract, known as allicin has shown properties, in laboratory settings.
- Caprylic acid can be discovered in coconut oil. Has the potential to slow down the growth of Candida in the GI tract.
These alternatives could be employed as measures or, in severe instances with the oversight of a healthcare professional; however they should not be viewed as replacements for comprehensive antifungal treatment, in cases of invasive infection.
Careful Administration in Special Populations
Fungeeheal (itraconazole) administration needs attention when dealing with patients, due to factors like age-related changes and underlying health conditions that can impact how the medication works in the body and requires adjustments in dosage and close monitoring, for optimal treatment outcomes to ensure safety and effectiveness of the therapy.
Use in Elderly Patients
Elderly individuals frequently face difficulties caused by aging processes in their bodies, and the presence of health conditions along with complicated medication schedules can further complicate matters. The way the body processes itraconazole may undergo changes among this group of people.
- As people age, their liver might experience reduced blood flow and enzyme activity, which could result in drugs staying longer in the system and building up.
- Renal function decline may impact the tolerability and metabolite exposure of itraconazole despite its excretion.
Age-related changes in filtration could play a role in this scenario. Analyzing the risks and benefits is crucial when it comes to individuals who are taking medications at once. It is important to be aware that having medications can lead to interactions between drugs by inhibiting the CYP3A4 enzyme activity. This can raise the chance of experiencing effects, like heart or liver issues. It is recommended to check liver enzymes and perform ECG tests especially if the treatment is term or involves high doses.
Use in Pregnant Women and Nursing Mothers
Extreme care should be taken when considering the use of itraconazole during pregnancy and breastfeeding because of its potential to cause birth defects and harm to the developing embryo or fetus, based on findings from animal studies showing abnormalities, in the internal organs that vary with dosage levels. Risks of Birth Defects;
- Abnormalities in structure were noted in studies on rodents and rabbits at doses similar to those in humans.
- Avoid use during pregnancy unless it is necessary to treat a life-threatening infection for which there are no safer alternatives available especially in the first trimester.
Before starting any treatment, women who could become pregnant should make sure they are not pregnant first. To ensure safety during treatment and for two months after stopping to how long itraconazole stays in the body and tissues, effective birth control should be used.
If a woman is breastfeeding, itraconazole passes into breast milk, although levels in the blood are low; the impact it may have on the baby is not known. Breastfeeding advice suggests refraining from nursing while undergoing treatment or exploring formula feeding when systemic itraconazole use is necessary. Risk communication needs to be straightforward.
It's worth exploring antifungal choices that are safer for pregnant and nursing individuals when needed.

Use in Pediatric Patients
Using itraconazole in children needs evaluation because there is no data on its safety and effectiveness in younger age groups. The drug may not be approved for all infants or children under an age, depending on the regulations in place. Safety information for children under the age of 12 is not fully established.
It is recommended to use off-label treatments for infections that do not respond to standard therapy. Dosage should be adjusted cautiously according to body weight and age. It usually falls within the range of 3 to 5 mg/kg/day. It is divided into one or two doses.
When giving itraconazole to patients or children and during pregnancy or breastfeeding periods, attention should be paid to liver enzyme levels and drug amounts in the blood to prevent negative effects and ensure the best treatment results, especially when dealing with serious fungal infections or weakened immune systems, in kids.
Storage Instructions for Fungeeheal
To maintain Fungeeheal (itraconazole)'s effectiveness, store it precisely as recommended; improper handling could weaken it and lead to poor treatment outcomes.
Optimal Storage Conditions for Capsules and Oral Solution
Both types of Fungeeheal formulations require settings to maintain their chemical composition.
- Remember to store the capsules in a place between 15 and 30 degrees Celsius (59-86 degrees Fahrenheit).
- Make sure to keep them in their original blister pack or a sealed container to avoid any deterioration.
- Ensure the oral solution is kept at room temperature between 20 to 25 degrees Celsius (68 to 77 degrees Fahrenheit).
- Avoid storing it in the refrigerator or freezing it.
Changes in temperature, beyond the recommended range could impact the solubility of drugs. Decrease their effectiveness when exposed to tropical environments.
Protection from Moisture, Light, and Heat
Itraconazole is affected by changes in the environment, so taking precautions can help prolong its shelf life and minimize the chances of deterioration. Remember to keep this in an environment and opt for containers with desiccants when storing capsule formulations.
- Remember to shield it from the sun's rays and store it in containers that are either opaque or dark, if you can.
- Avoid placing the product near radiators or ovens or inside vehicles, as high temperatures could lead to changes in the capsule shells' shape or the breakdown of the solution.
Assess the conditions where belongings are kept carefully and give attention to areas with climate regulation.
Shelf Life and Expiry Considerations
You can generally expect Fungeeheal to be good for 2 to 3 years from when it's made, but some versions might have a slightly different lifespan due to their ingredients. Don't use FungeeHeal after its expiration date—it might not work as intended and could even be unsafe. Once you open the seal, be sure to use the solution within the time recommended in the package insert. Always check your FungeeHeal before using it: if you notice any changes in its color or smell, or if it just looks unusual, don't risk it; throw it away right away.
Safe Handling and Disposal of Fungeeheal
Properly managing and getting rid of products containing itraconazole is crucial to protect the safety of patients and the environment, as those taking care of them are alike. Improper disposal could potentially endanger wildlife and water sources, especially when dealing with forms.
Proper Handling of Capsules and Liquids
Remember to wash your hands both before and after you handle anything.
- Please do not crush the capsules.
- Opening or chewing them is also not recommended.
- Make sure to use calibrated dosing syringes, spoons are also good, for accurately giving oral solutions.
- Please ensure that all products are stored securely away from the access of children and pets.
- In case of swallowing or spillage it's important to seek advice right away and follow the appropriate cleanup procedures promptly.
Disposal of Unused or Expired Medication
Expired Fungeeheal should not be thrown away in household garbage or flushed down the drain into sewage systems; it's important to follow disposal guidelines such as;
- Visit a pharmacy that offers a program for returning medications.
- If you cannot access it at the moment, try blending it with materials, like coffee grounds or cat litter, then seal it in a bag and dispose of it in the household trash following local guidelines.
- Make sure to never heat up or destroy Itraconazole items.
Healthcare institutions must adhere to procedures for handling pharmaceutical waste to guarantee its safe decontamination and disposal.

Instructions for Caregivers or Healthcare Providers
Those in charge of managing itraconazole should receive training on dosage instructions and proper handling procedures well as emergency response protocols.
- Remember to wear gloves while dealing with the solution in places where the immune system is weakened.
- Keep a record of when medications are taken and how patients react to them.
- This is particularly important for children and older adults. Be vigilant for any reactions or indications of toxicity.
It's an idea to have labels and keep track of medication usage in places where multiple caregivers are involved to prevent mistakes or giving duplicate doses.
Patient Education and Counseling Points
Established patient comprehension and dedication are factors in treating fungal infections using Fungeeheal medications. Counsel should be detailed directed to the individual. Consistently reinforced during the treatment process.
Importance of Completing Full Course
Patients should know that it's important to finish the course of treatment as directed by their healthcare provider, even if they start feeling better before the end of the treatment period because stopping early could lead to a chance of the infection returning and resistance to antifungal medications developing.
- Maintaining therapeutic levels of medication is crucial for treating stubborn infections that are deeply rooted.
- Symptomatic relief might be achieved with treatment. The underlying pathogen may not be fully eradicated.
Ensuring that patients understand how long their treatment will last and when they can expect to see results is important for keeping them on track with their medication plan.
Recognizing Early Signs of Adverse Effects
It's crucial to catch side effects so that we can act quickly and reduce any harm to patients, who should be informed about keeping an eye on symptoms and speaking up about them. Signs of liver toxicity include jaundice (yellowing of the skin and eyes), dark urine coloration and ongoing tiredness. Unexplained difficulty breathing (related to heart issues). Feeling a tingling sensation or numbness in the extremities. Educational resources, along with symptom lists and regular check-ins, play a role in enhancing awareness of safety measures.
Adherence Strategies and Follow-Up Requirements
Skipping doses or not using itraconazole regularly can greatly lower its effectiveness, for treatment purposes, and ways to enhance compliance involve the strategies;
- Don't forget to set reminders for taking your medication or use alarms.
- Planning your medication doses with a pill organizer.
- Connecting the timing of taking medication with tasks, such as eating meals.
During follow-up visits or appointments with your healthcare provider or doctor should involve checking how well your liver is functioning and monitoring drug levels if necessary, while assessing how you are responding to treatment with each visit.
Avoiding Self-Adjustment of Dosage or Skipping Doses
Patients should always consult a healthcare professional before making any changes to their itraconazole dosage regimen, as skipping doses or taking twice the prescribed amount can result in either treatment or potential harm, from toxicity.
If you forget to take a dose, make sure to take it as you remember unless it's close to your next scheduled dose. If you notice any signs of an overdose, it's crucial to report them.
Maintaining counseling sessions and having ways to communicate with healthcare professionals can lower the chances of making mistakes on your own and improve the effectiveness of your treatment plan.
Fungeeheal, Itraconazole FAQ
- How long does Itraconazole take to work on fungal infection?
- How long does Itraconazole stay in your system?
- How long does Itraconazole take to work?
- How long for Itraconazole to work in dogs?
- How long does Itraconazole take to work on skin?
- What happens if you drink alcohol with Itraconazole?
- How long does Itraconazole take to work on yeast infection?
- Terbinafine or Itraconazole which is better?
- How long for Itraconazole to work in cats?
- How long after Itraconazole can you drink alcohol?
- Are Itraconazole and Fluconazole the same?
- What are Itraconazole capsules used for?
- Can Itraconazole cause hair loss?
- Can Itraconazole treat yeast infection?
- Can Itraconazole damage kidneys?
- Can Itraconazole treat Candida?
- Can Itraconazole and Griseofulvin be taken together?
- How Itraconazole works?
- How Itraconazole works in fungal infection?
- What Itraconazole is used for?
- When should Itraconazole be taken?
- Where is Itraconazole absorbed?
- Itraconazole which class of drug?
- Why Itraconazole is better than Fluconazole?
- Is Itraconazole a strong antibiotic?
- How many days should I take Itraconazole?
- What should I avoid while taking Itraconazole?
- Does Itraconazole have side effects?
- Why is it important to take Itraconazole with food always?
- What happens when you stop taking Itraconazole?
- Can Itraconazole cause liver damage?
- Is Itraconazole bad for kidneys?
- Does Itraconazole weaken the immune system?
- How long can you be on Itraconazole?
- What is more powerful than Itraconazole?
How long does Itraconazole take to work on fungal infection?
Itraconazole usually starts to exhibit signs of improvement in about 1 to 2 weeks after starting treatment; however, the full recovery may require weeks based on the severity of the fungal infection.
How long does Itraconazole stay in your system?
Itraconazole and its active metabolite may stay in the system for 2 weeks, after the dose because of their long half life and accumulation, in tissues.
How long does Itraconazole take to work?
It typically begins to take effect after a few days; however noticeable progress may vary, between 1 to 4 weeks based on the location of the infection and the type of fungus involved.
How long for Itraconazole to work in dogs?
With dogs' health conditions showing signs of getting better in 2 to 4 weeks time frame, and requiring longer treatment durations spanning over a few months for dealing with systemic or severe fungal infections.
How long does Itraconazole take to work on skin?
Superficial fungal skin infections usually start getting better in 1 to 2 weeks; however complete recovery may require 3 to 6 weeks.
What happens if you drink alcohol with Itraconazole?
Drinking alcohol while taking Itraconazole can raise the chances of liver problems and stomach issues so its usually not recommended.
How long does Itraconazole take to work on yeast infection?
Yeast infections, like vaginal candidiasis may show signs of getting better in 3 to 7 days and typically clear up, within 1 to 2 weeks.
Terbinafine or Itraconazole which is better?
Terbinafine usually works better for skin infections caused by dermatophytes, whereas Itraconazole is an option, for treating a range of fungal infections, like yeast and certain systemic mycoses.
How long for Itraconazole to work in cats?
In cats treated with Itraconazole, improvement typically starts showing after 2 to 4 weeks; however, the treatment may need to continue for a period ranging from 4 to 12 weeks or depending on the severity of the infection.
How long after Itraconazole can you drink alcohol?
It is recommended to wait around 7 to 14 days after finishing your Itraconazole medication before drinking alcohol to lower the chances of liver harm.
Are Itraconazole and Fluconazole the same?
Itraconazole and Fluconazole are not the same; they belong to different classes of drugs and have unique ranges of effectiveness and dosage requirements.
What are Itraconazole capsules used for?
Itraconazole capsules are prescribed for treating infections, like aspergillosis, blastomycosis, histoplasmosis, onychomycosis, and oropharyngeal candidiasis.
Can Itraconazole cause hair loss?
Hair thinning or hair loss has been noted as an occurrence, in patients taking Itraconazole.
Can Itraconazole treat yeast infection?
Itraconazole works well for clearing up yeast infections such, as those in the mouth and throat, as vaginal candidiasis.
Can Itraconazole damage kidneys?
It's not usual for Itraconazole to cause kidney issues; however its recommended to be cautious, with patients who already have kidney problems.
Can Itraconazole treat Candida?
Itraconazole shows its efficacy, against Candida species, in cases where there is a suspicion of Fluconazole resistance.
Can Itraconazole and Griseofulvin be taken together?
It's usually not an idea to use them because they might interact in a bad way and cause similar harmful effects.
How Itraconazole works?
Itraconazole functions, by blocking an enzyme known as cytochrome P450 which is essential, for its survival; this action hinders the production of ergosterol and destabilizes the structure of the fungal cell membrane.
How Itraconazole works in fungal infection?
It specifically aims at enzymes, for creating cell membranes to stop the growth and reproduction of fungi efficiently.
What Itraconazole is used for?
It is commonly utilized for addressing a range of infections affecting both organs and the skin surface such, as histoplasmosis and onychomycosis.
When should Itraconazole be taken?
Remember to have a meal, with itraconazole to improve absorption levels and try to take it around the time every day.
Where is Itraconazole absorbed?
Itraconazole mostly gets absorbed in the stomach and small intestine. Has absorption when taken with food or, in acidic conditions.
Itraconazole which class of drug?
Itraconazole is classified as a medication belonging to the triazole group of drugs.
Why Itraconazole is better than Fluconazole?
Itraconazole provides a range of protection compared to Fluconazole as it is effective against molds such as Aspergillus that Fluconazole cannot target.
Is Itraconazole a strong antibiotic?
Itraconazole isn't an antibiotic. It's an antifungal medication.
How many days should I take Itraconazole?
The length of treatment differs depending on the type of infection; minor infections might need 7 to 14 days of therapy, while severe ones could require weeks to months of treatment.
What should I avoid while taking Itraconazole?
It's best to steer clear of alcohol and medications like antacids and proton pump inhibitors that might interfere with the effectiveness or safety of drugs due to their interactions, with CYP34 enzymes.
Does Itraconazole have side effects?
Common side effects may consist of symptoms, like queasiness and headaches as skin rashes and elevated levels of liver enzymes. Meanwhile more severe effects could manifest as liver damage and heart failure in individuals, with existing conditions.
Why is it important to take Itraconazole with food always?
When you have Itraconazole with a meal it helps the body absorb it better and makes sure you reach the levels, in your blood for treatment to work effectively.
What happens when you stop taking Itraconazole?
Stopping the treatment early could lead to not getting rid of the infection, which might raise the chances of it coming stronger or becoming resistant, to treatment.
Can Itraconazole cause liver damage?
Itraconazole has been linked to liver damage. It is important to keep an eye on liver function while undergoing treatment.
Is Itraconazole bad for kidneys?
Although it's not usually harmful to the kidneys as such, it's recommended to be careful, in cases of kidney issues, because there isn't data available and there might be a risk of build up.
Does Itraconazole weaken the immune system?
Itraconazole doesn't weaken the system. It focuses on attacking cells specifically.
How long can you be on Itraconazole?
The length of treatment can vary from a days, to months based on how severe the infection is and how well the patient responds to the treatment.
What is more powerful than Itraconazole?
When it comes to tackling stubborn infections effectively and thoroughly voriconazole or posaconazole are often seen as the top choices, due to their strong potency and wider range of effectiveness, against various types of molds and yeasts.