Caspofungin Acetate Injection
- Introduction to Caspofungin Acetate Injection
- Composition and Pharmaceutical Formulation
- Mechanism of Action: How Caspofungin Acetate Works
- Approved Medical Uses of Caspofungin Acetate Injection
- Off-Label Uses of Caspofungin Acetate
- Dosage and Administration Guidelines
- Storage and Stability Requirements
- Common and Serious Side Effects of Caspofungin Acetate
- Important Warnings and Precautions
- Contraindications to the Use of Caspofungin Acetate
- Drug Interactions
- Careful Administration and Monitoring Requirements
- Administration in Special Populations
- Overdosage and Management Strategies
- Handling Precautions for Healthcare Providers
Introduction to Caspofungin Acetate Injection
Overview of Caspofungin Acetate
Caspofungin Acetate Injection is a medication that treats severe fungal infections that don't respond well to standard treatments. It's a synthetic lipopeptide that falls under a new group of antifungal drugs called echinocandins.
History and Development
First discovered in the late 1990s, Caspofungin marked a breakthrough in antifungal therapy by offering an alternative to azoles and amphotericin B. Its development was driven by the rising incidence of invasive fungal infections, especially in immunocompromised populations.
Classification: Echinocandin Antifungal Agent
Echinandins, like Caspofungin, are known for their way of working by focusing on the synthesis of cell walls instead of the typical approach used by other antifungal medications. They are effective at killing Candida species and slowing down the growth of Aspergillus species.
Regulatory Approvals and Global Availability
Approved by the U.S. FDA in 2001, Caspofungin has since gained regulatory clearance across Europe, Asia, and other regions, becoming a vital option in hospitals for treating life-threatening fungal infections.
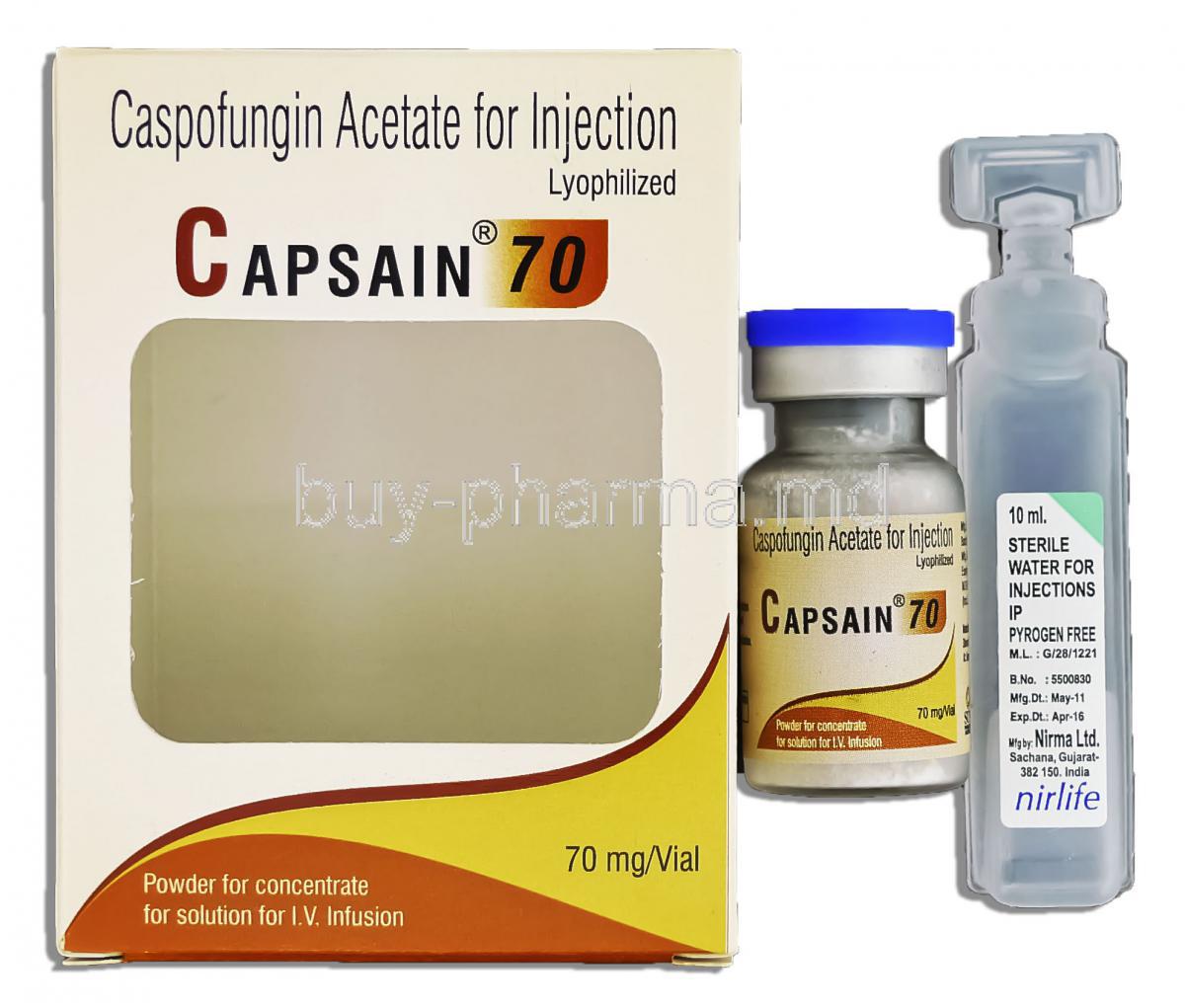
Composition and Pharmaceutical Formulation
Active Ingredient: Caspofungin Acetate
Each small bottle holds sterile Caspofungin Acetate in freeze-dried form, designed for injection into the veins.
Inactive Ingredients and Excipients
- Sucrose
- Mannitol
- Acetic Acid
- Sodium Hydroxide (for pH adjustment)
Available Strengths and Packaging Formats
Caspofungin Acetate Injection is commonly available in vials containing 50 mg or 70 mg of powder for reconstitution, supplied in single-use glass vials.
Mechanism of Action: How Caspofungin Acetate Works
Inhibition of β-(1,3)-D-Glucan Synthesis
Caspofungin specifically inhibits the enzyme β-(1,3)-D-glucan synthase, a key component involved in the synthesis of the fungal cell wall. This inhibition leads to osmotic instability and ultimately fungal cell death.

Impact on Fungal Cell Wall Integrity
By targeting the glucan component of the cell wall, Caspofungin weakens the structural integrity of fungal cells, causing them to lyse under osmotic stress, which is critical for eradicating invasive infections.
Spectrum of Antifungal Activity
Caspofungin demonstrates broad-spectrum antifungal activity against multiple Candida species and Aspergillus species, making it highly effective in both empirical and targeted therapies.
Fungal Species Susceptible to Caspofungin
Approved Medical Uses of Caspofungin Acetate Injection
Treatment of Invasive Candidiasis
Empirical Therapy for Presumed Fungal Infections in Febrile Neutropenic Patients
Neutropenic patients with fever, despite receiving broad-spectrum antibiotics, may opt for therapy to manage the possibility of fungal infections that may be lurking beneath the surface.
Treatment of Invasive Aspergillosis in Patients Refractory or Intolerant to Other Therapies
Patients with aspergillosis who are unsuccessful with or unable to tolerate initial treatments like amphotericin B or itraconazole may turn to caspofungin as a secondary option.
Off-Label Uses of Caspofungin Acetate
Use in Fungal Endocarditis
Though not formally approved, Caspofungin has been used successfully in cases of fungal endocarditis, often in combination with surgical intervention.
Therapy for Esophageal Candidiasis
Sometimes doctors use it to treat candidiasis when other medications, like azoles, don't work or for patients with weakened immune systems.
Adjunctive Therapy in Cryptococcal Meningitis
Use in Immunocompromised and Solid Organ Transplant Patients
More and more caspofungin is being prescribed, off label for organ transplant patients and those with immune system deficiencies to treat or prevent invasive fungal infections.
Dosage and Administration Guidelines
Initial and Maintenance Dosing for Various Indications
- Loading Dose: 70 mg on Day 1
- Maintenance Dose: 50 mg once daily thereafter
Dosage Adjustments in Hepatic Impairment
Patients with moderate hepatic impairment require dosage adjustment, typically reducing the maintenance dose to 35 mg daily to mitigate drug accumulation risks.
Infusion Rate and Preparation Instructions
The diluted reconstituted solution should be given over an hour to reduce the risk of reactions, during infusion, and it is important to maintain proper cleanliness when preparing it.
Duration of Therapy Based on Infection Type
The length of therapy is determined by how the patient responds to treatment and whether the infection-causing microorganisms are eliminated, while also considering the improvement in system function; it usually lasts between 2 and 4 weeks.
Storage and Stability Requirements
Recommended Storage Conditions Before Reconstitution
Please store the vials between 2 °C and 8°C (36°F and 46°F). Keep them away from light to ensure their effectiveness and stability.
Stability After Reconstitution and Dilution
The reconstituted solution is stable for 24 hours when refrigerated and should be further diluted and used promptly thereafter to prevent microbial contamination.
Handling Precautions During Storage
- Use sterile techniques to avoid contamination.
- Do not freeze the reconstituted solution.
- Inspect visually for particulate matter and discoloration before administration.
Common and Serious Side Effects of Caspofungin Acetate
Overview of Frequently Reported Side Effects
In cases, Caspofungin is well received by patients without causing any issues, but there is a possibility of side effects arising during treatment, which requires careful monitoring to recognize any negative reactions promptly.
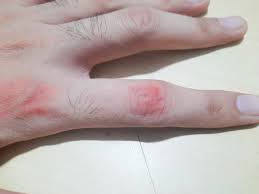
Common Side Effects: Fever, Rash, Phlebitis, Elevated Liver Enzymes
- Fever and chills, particularly early in therapy
- Rash and pruritus indicating potential hypersensitivity
- Phlebitis at the infusion site
- Transient elevations in alanine aminotransferase (ALT) and aspartate aminotransferase (AST)
Serious Adverse Effects: Anaphylaxis, Hepatic Dysfunction, Hemolytic Anemia
- Anaphylactic reactions require immediate discontinuation and emergency intervention
- Severe hepatic dysfunction, including hepatocellular injury and cholestasis
- Rare cases of hemolytic anemia necessitate close monitoring of hematologic parameters
Important Warnings and Precautions
Risk of Hepatic Enzyme Elevation
Caspofungin Acetate has been associated with elevations in hepatic transaminases, including alanine aminotransferase (ALT) and aspartate aminotransferase (AST). These changes may indicate hepatocellular injury and require vigilant monitoring, particularly during prolonged therapy.
Hypersensitivity and Infusion-Related Reactions
Severe allergic reactions have been documented in some cases, including anaphylaxis and symptoms such as skin rash, facial swelling, itchiness, feeling warm, or difficulty breathing (bronchospasm). If any of these reactions happen it is crucial to stop the medication and seek medical attention.
Use in Patients with Pre-existing Liver Disease
Patients who already have liver problems are more likely to experience worsened liver function when undergoing Caspofungin treatment. It is crucial to adjust the dosage and use caution during therapy while monitoring liver function markers regularly throughout the treatment period.
Monitoring Recommendations During Treatment
- Periodic liver function tests (LFTs)
- Monitoring for signs of anaphylactic reactions during infusion
- Close observation for clinical deterioration in immunocompromised patients
Contraindications to the Use of Caspofungin Acetate
Known Hypersensitivity to Caspofungin or Other Echinocandins
Caspofungin is contraindicated in individuals with a known hypersensitivity to Caspofungin Acetate or other members of the echinocandin class, due to the risk of life-threatening allergic reactions.
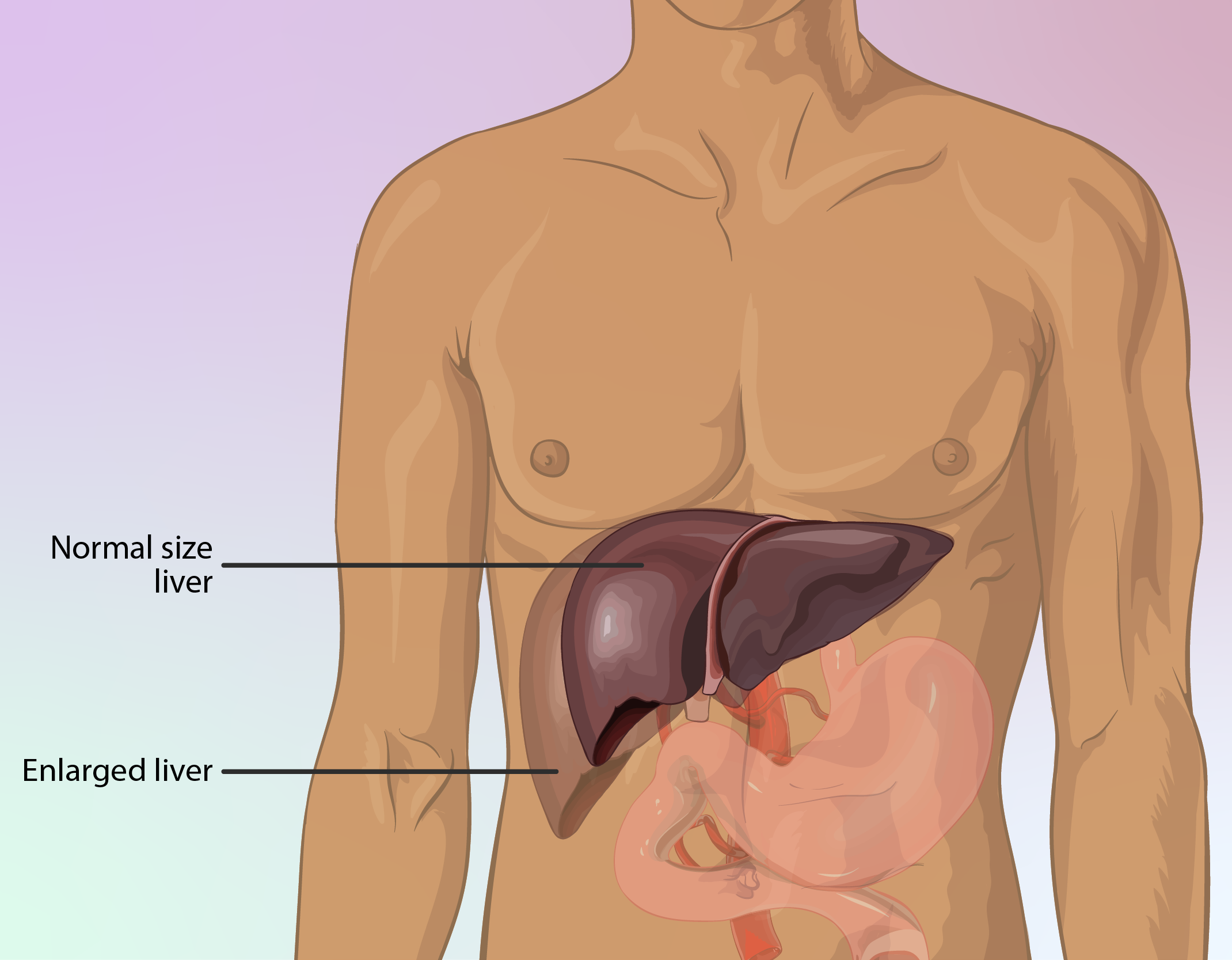
Caution in Severe Hepatic Impairment
Individuals with liver damage (classified as Child Pugh Class C) should use Caspofungin carefully and undergo risk-benefit evaluations before starting treatment; typically, lower maintenance doses are advised in such cases.
Drug Interactions
Interaction with Cyclosporine
Concurrent administration with cyclosporine has been shown to increase the plasma concentrations of Caspofungin, potentially enhancing toxicity. Combined use should be reserved for situations where benefits clearly outweigh risks, with intensified monitoring.
Effects When Combined with Tacrolimus
Caspofungin may modestly decrease tacrolimus plasma concentrations. Clinical monitoring of tacrolimus levels is advised when these agents are co-administered, with dose adjustments as necessary.
Potential Interference with Inducers of Drug Metabolism (e.g., Rifampin, Efavirenz)
Drugs that induce hepatic enzymes, such as rifampin, efavirenz, nevirapine, phenytoin, and dexamethasone, can reduce Caspofungin levels, potentially diminishing its antifungal efficacy. Dose escalation of Caspofungin may be considered in such cases.
Implications for Concurrent Antifungal Therapy
When used with other antifungal agents, careful evaluation is necessary to avoid antagonistic effects or cumulative toxicity. Coordination with infectious disease specialists is often beneficial.
Careful Administration and Monitoring Requirements
Importance of Laboratory Monitoring (Liver Function Tests)
Baseline and periodic monitoring of liver enzymes are essential to detect hepatotoxicity early and guide therapeutic adjustments accordingly.
Observation for Signs of Anaphylaxis
Healthcare professionals must be prepared to manage anaphylaxis during Caspofungin administration, including access to emergency interventions such as epinephrine and airway support.
Special Considerations for Infusion Reactions
To mitigate infusion-related reactions, Caspofungin should be administered over approximately one hour. Slowing the infusion rate or premedication with antihistamines may be considered in susceptible individuals.
Administration in Special Populations
Administration to Elderly Patients
Pharmacokinetic Considerations in Older Adults
While the pharmacokinetic profile of Caspofungin is generally similar between elderly and younger adults, age-related organ function decline warrants careful monitoring during therapy.
Dosage Recommendations and Monitoring
No specific dose adjustments are required solely based on age; however, close clinical monitoring is prudent to detect adverse reactions early in geriatric patients.
Administration During Pregnancy and Lactation
Animal Reproduction Studies and Risk Assessment
Animal studies have demonstrated embryofetal toxicity at doses causing maternal toxicity. The safety of Caspofungin in pregnant women has not been established.
FDA Pregnancy Category
Caspofungin is classified as Pregnancy Category C, indicating that risk cannot be ruled out. Use during pregnancy should be considered only if the potential benefit justifies the potential risk to the fetus.
Recommendations for Breastfeeding Mothers
It is unknown whether Caspofungin is excreted into human milk. Caution is advised when administering to nursing mothers, and a decision should be made to discontinue nursing or discontinue the drug, considering the importance of the therapy to the mother.

Administration to Pediatric Patients
Safety and Efficacy in Neonates and Children
Caspofungin is approved for pediatric use in patients 3 months of age and older. Clinical trials demonstrate efficacy and a safety profile consistent with that observed in adults.
Dosage Adjustments for Pediatric Patients
- Patients 3 months to 17 years: loading dose of 70 mg/m² on Day 1, followed by 50 mg/m² once daily
- Maximum maintenance dose typically not exceeding adult dosage recommendations
Monitoring Pediatric Responses and Adverse Events
Enhanced vigilance is necessary to monitor for infusion reactions, liver function abnormalities, and electrolyte disturbances in pediatric patients receiving Caspofungin.
Overdosage and Management Strategies
Reported Cases of Overdose
Clinical experience with Caspofungin overdose is limited. Overdoses reported involved administration of up to 400 mg on a single day without significant toxicities observed.
Symptoms and Clinical Manifestations
Potential overdose symptoms may include elevated liver enzymes, rash, facial swelling, pruritus, or respiratory distress.
Recommended Medical Interventions
- Symptomatic and supportive care
- Continuous monitoring of vital signs and organ functions
- No specific antidote; hemodialysis is unlikely to be beneficial due to high protein binding
Handling Precautions for Healthcare Providers
Guidelines for Safe Preparation and Administration
Strict aseptic technique must be maintained during reconstitution and dilution. Use sterile water for injection and a compatible infusion solution as specified in the prescribing information.
Protective Measures to Avoid Exposure
Healthcare personnel should use gloves and, if needed, protective eyewear when handling the medication to prevent inadvertent contact with skin or mucous membranes.
Disposal of Unused or Expired Product
Unused, expired, or contaminated Caspofungin Acetate should be discarded following established institutional procedures for pharmaceutical waste, ensuring compliance with environmental safety regulations.
Caspofungin Acetate Injection FAQ
- What is the use of acetate injection?
- How long is the treatment for caspofungin?
- What are the side effects of caspofungin acetate?
- Is caspofungin IV or oral?
- What is the purpose of caspofungin?
- How many days it will take to cure fungal infection?
- How effective is caspofungin?
- How to give caspofungin injection?
- Does caspofungin affect liver?
- How long can you take caspofungin for?
- How long is the course of caspofungin?
- What is the generic for caspofungin acetate?
- When do you use caspofungin?
- Is caspofungin an antibiotic?
- Is acetate safe to use?
- What is the indication of caspofungin acetate?
- Is caspofungin an antibacterial?
- Is caspofungin safe?
- When was caspofungin approved?
- What is the purpose of caspofungin?
What is the use of acetate injection?
Helps address sodium levels in the body, which are crucial for maintaining hydration and supporting muscle and nervous system health.
How long is the treatment for caspofungin?
Patients who are diagnosed with an infection are usually advised to undergo treatment for a minimum of 14 days following the positive culture result. It is recommended to continue the treatment for 7 days after both neutropenia and clinical symptoms have subsided.
What are the side effects of caspofungin acetate?
Adverse reactions to caspofungin are infrequent overall. Typically involve symptoms such as chills or fever alone, along with issues like phlebitis/thrombophlebitis or tachycardia, as well as gastrointestinal complaints, including nausea or diarrhea.
Is caspofungin IV or oral?
Intravenously
What is the purpose of caspofungin?
The injection of caspofungin is prescribed for treating infections such as candidemia (blood fungal infection), esophageal candidiasis (esophageal fungal infection), various candidiasis infections, and aspergillosis (lung fungal infection).
How many days it will take to cure fungal infection?
1 and 4 weeks
How effective is caspofungin?
Both Caspofungin and L Amphotericin B showed effectiveness, with both drugs achieving a response rate of around 34%.
How to give caspofungin injection?
Administer Caspofungin daily through an intravenous infusion, injecting it into a vein, which takes approximately 1 hour to complete.
Does caspofungin affect liver?
Yes
How long can you take caspofungin for?
In adults aged 18 and older, Caspofungin should be administered through a continuous infusion lasting approximately 1 hour.
How long is the course of caspofungin?
11.9 days, with a range of 1 to 28 days
What is the generic for caspofungin acetate?
Caspofungin acetate
When do you use caspofungin?
In adults and children aged 3 months and above, caspofungin injection is employed to address yeast infections in the bloodstream, abdomen, lungs, and the esophagus (the passage linking the throat to the stomach), for particular fungal infections that were unresponsive to alternative treatments.
Is caspofungin an antibiotic?
Antifungal antibiotic
Is acetate safe to use?
Yes
What is the indication of caspofungin acetate?
Treatment with caspofungin acetate injection is recommended for adults and children ( 3 months and above) who have aspergillosis and have not responded well to or cannot tolerate other treatments.
Is caspofungin an antibacterial?
Under certain conditions, caspofungin shows strong antifungal and antibacterial properties.
Is caspofungin safe?
Yes
When was caspofungin approved?
1/26/2001
What is the purpose of caspofungin?
Casposfungin injection is utilized for the treatment of infections that include candidemia (fungal infection in the bloodstream), esophageal candidiasis (fungal infection of the throat), various other candidal infections, and aspergillosis (fungal infection in the lungs).
Customers also bought
150 mcg/g