Tyza Cream, Terbinafine
- Introduction to Tyza Cream (Terbinafine)
- Active Ingredient and Composition of Tyza Cream
- Mechanism of Action: How Tyza Cream Works
- Approved Medical Uses of Tyza Cream (Terbinafine)
- Off-Label Uses of Tyza Cream (Terbinafine)
- Dosage and Administration Guidelines for Tyza Cream
- Terbinafine Dosage for Adults
- Dosage of Terbinafine for Dogs
- Recommended Frequency and Duration of Application by Condition
- Instructions for Skin Preparation Before Use
- Application Technique and Amount to Be Applied
- What to Avoid During Treatment (e.g., Occlusive Dressings)
- Terbinafine Results Before and After
- Dosage Adjustments and Administration in Special Populations
- Common and Serious Side Effects of Tyza Cream
- Contraindications for the Use of Tyza Cream
- Warnings and Precautions for Tyza Cream Usage
- Careful Administration Considerations
- Drug and Product Interactions
- Overdose and Misuse of Tyza Cream
- Handling and Storage Instructions for Tyza Cream
- Important Patient Education and Usage Precautions
Introduction to Tyza Cream (Terbinafine)
Tyza Cream is a topical antifungal treatment primarily used for skin infections such as ringworm, athlete's foot, and jock itch. Its active ingredient, terbinafine hydrochloride, belongs to the allylamine class of medications.
The cream is designed for direct application to the affected skin, allowing it to effectively target the infection with minimal absorption into the bloodstream. It also has a soothing, emollient base.
The availability of Tyza Cream varies by region. In the U.S., it's typically available over the counter. However, in some parts of Europe and Asia, a prescription might be required.
Globally, drugstores in developed areas commonly stock it as a versatile antifungal option. Its broad availability underscores its significance in both general healthcare and specialized dermatological settings.
Active Ingredient and Composition of Tyza Cream
Tyza Cream contains 1% terbinafine hydrochloride by weight, in a cream base designed to improve absorption and ease of use. Other ingredients typically include:
- Sorbitan stearate, which acts as an emulsifier.
- Isopropyl myristate known for improving skin penetration.
- Purified water serves as a solvent.
- Terbinafine is an antifungal medication that works by selectively inhibiting fungal squalene epoxidase. This mechanism differs from azole antifungals (like itraconazole or clotrimazole), which target ergosterol synthesis at a later stage.
When comparing terbinafine to other antifungals:
- Terbinafine vs. Itraconazole: Terbinafine is fungicidal against dermatophytes, meaning it kills the fungi. Itraconazole, on the other hand, is fungistatic (it inhibits fungal growth) and is generally preferred for systemic infections and yeast overgrowth.
- Terbinafine vs. Tolnaftate: Tolnaftate is primarily effective against Candida species. Terbinafine, however, offers broader fungicidal properties, often leading to faster resolution of symptoms.
- Terbinafine vs. Clotrimazole (for Ringworm): Clotrimazole, an azole antifungal, typically requires a longer treatment duration. Terbinafine can achieve a quicker mycological cure for simple cases of ringworm, sometimes in as little as 7 days.
Mechanism of Action: How Tyza Cream Works
Tyza Cream functions as an antifungal by disrupting a crucial pathway in fungal cell development. Its primary mechanism involves inhibiting the squalene epoxidase enzyme, which is essential for producing ergosterol. Ergosterol is vital for maintaining the integrity of fungal cell membranes, much like cholesterol in human cells. By blocking its production, Tyza Cream causes squalene to build up inside fungal cells while simultaneously reducing ergosterol levels.
This action has a pronounced fungicidal (killing) effect on common skin fungi such as Trichophyton and Microsporum species. Against yeast species like Candida albicans, it typically has a fungistatic (growth-inhibiting) effect.
A key advantage of terbinafine, the active ingredient in Tyza Cream, is its prolonged activity within the skin layer; it can remain effective for over a week after treatment cessation. This sustained presence in affected tissues supports flexible dosing schedules and makes Tyza Cream a preferred choice for healthcare providers treating skin conditions due to its rapid and targeted efficacy.
Approved Medical Uses of Tyza Cream (Terbinafine)
Tyza Cream, with hydrochloride as its active antifungal ingredient is officially approved for treating surface fungal infections. The effectiveness of this cream has been confirmed in treating various types of infections, making it an essential component, in current topical antifungal treatments.
Treatment of Tinea Pedis (Athletes Foot)
Tyza Cream works well in treating athlete's foot, which is usually caused by Trichophyton rubrum and Trichophyton mentagrophytes fungi infections, on the skin with symptoms like interdigital fissures, pruritus, itching, flaking, and maceration; it responds positively to terbinafine's properties. In cases, applying once a day for a week is usually enough. Persistent or moccasin style infections might require a longer period of treatment.

Use in Cutaneous Candidiasis
While terbinafine is primarily known for its effectiveness against dermatophyte skin infections, Tyza Cream also demonstrates some efficacy in treating cutaneous candidiasis. Candida strains, particularly C. albicans, often flourish in moist areas like skin folds under the breasts and in the groin.
In such cases, terbinafine acts as a fungistatic agent, meaning it inhibits the growth of the fungi rather than outright killing them. Therefore, alongside applying Tyza Cream, maintaining good hygiene practices is crucial for successful treatment outcomes.
Application in Pityriasis (Tinea) Versicolor
Pityriasis (Tinea) versicolor, also known as tinea versicolor, is a skin condition caused by the yeast Malassezia furfur, leading to discolored patches, typically on the chest and shoulders.
While azole antifungals are usually the go-to treatment, terbinafine (the active ingredient in Tyza Cream) has also proven effective against Malassezia species when applied topically to the affected areas.
This makes Tyza Cream a viable alternative for individuals who cannot tolerate azoles or have recurrent infections.
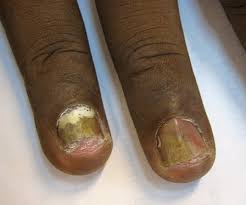
Terbinafine for Nail Fungus
While Tyza Cream isn't a standalone treatment for onychomycosis (nail fungus) due to its limited ability to penetrate the nail, it can be a useful addition to a broader treatment plan. It can help prevent the spread of the infection around the nails and address the visible signs of white toenail fungus. However, oral terbinafine remains the preferred choice for directly treating nail infections.
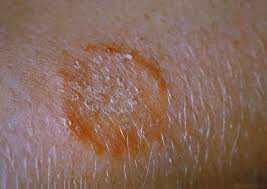
Terbinafine for Ringworm
Tyza Cream is commonly used to treat tinea corporis (body ringworm), which manifests as patches with a center and defined edges. Terbinfine's antifungal properties make it more effective than azoles in achieving a recovery rate from this infection. Early into treatment patients usually notice improvement within the week.
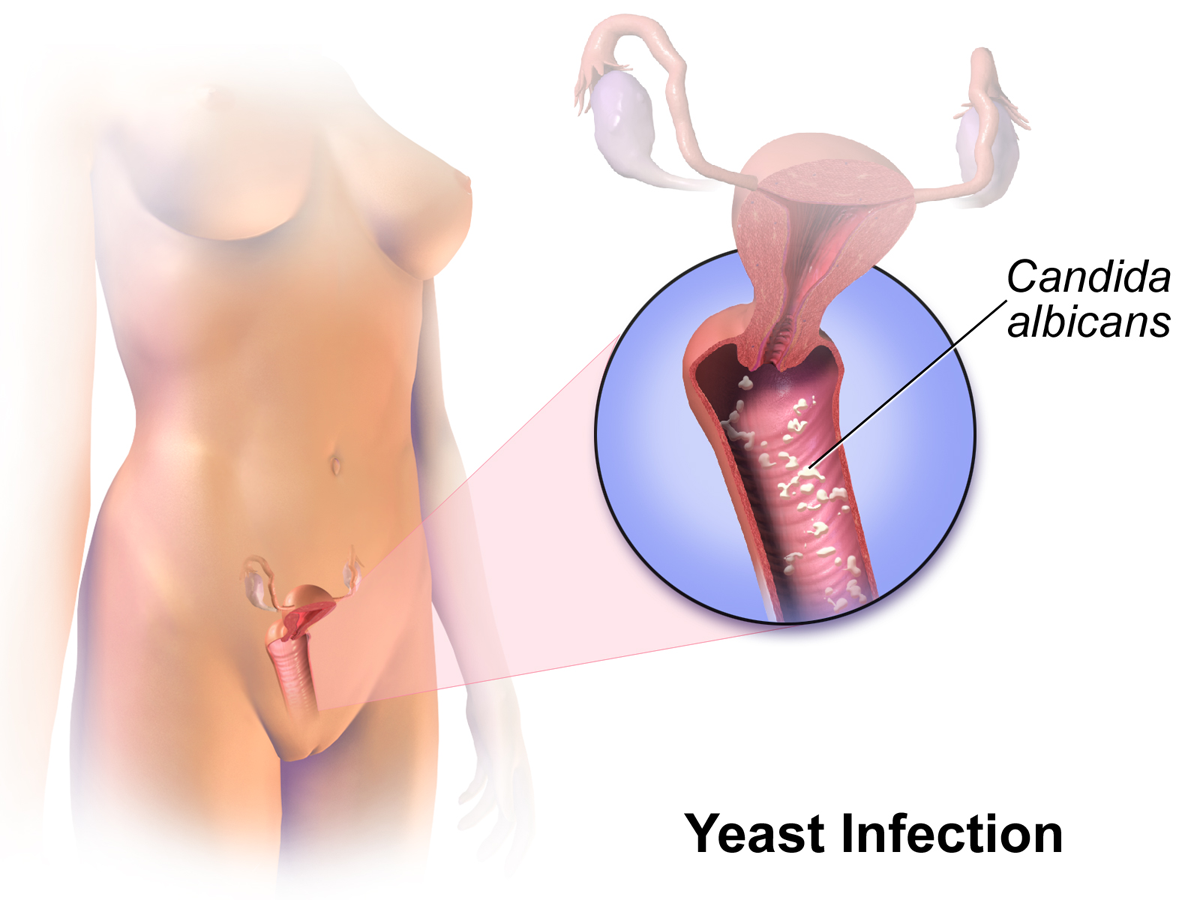
Terbinafine for Yeast Infection
While terbinafine isn't typically the first choice for yeast infections, it can provide relief for cutaneous (skin) yeast infections caused by Candida. It helps ease common symptoms like redness, itching, and the formation of satellite pustules. However, azoles remain the standard of care for treating candidiasis.
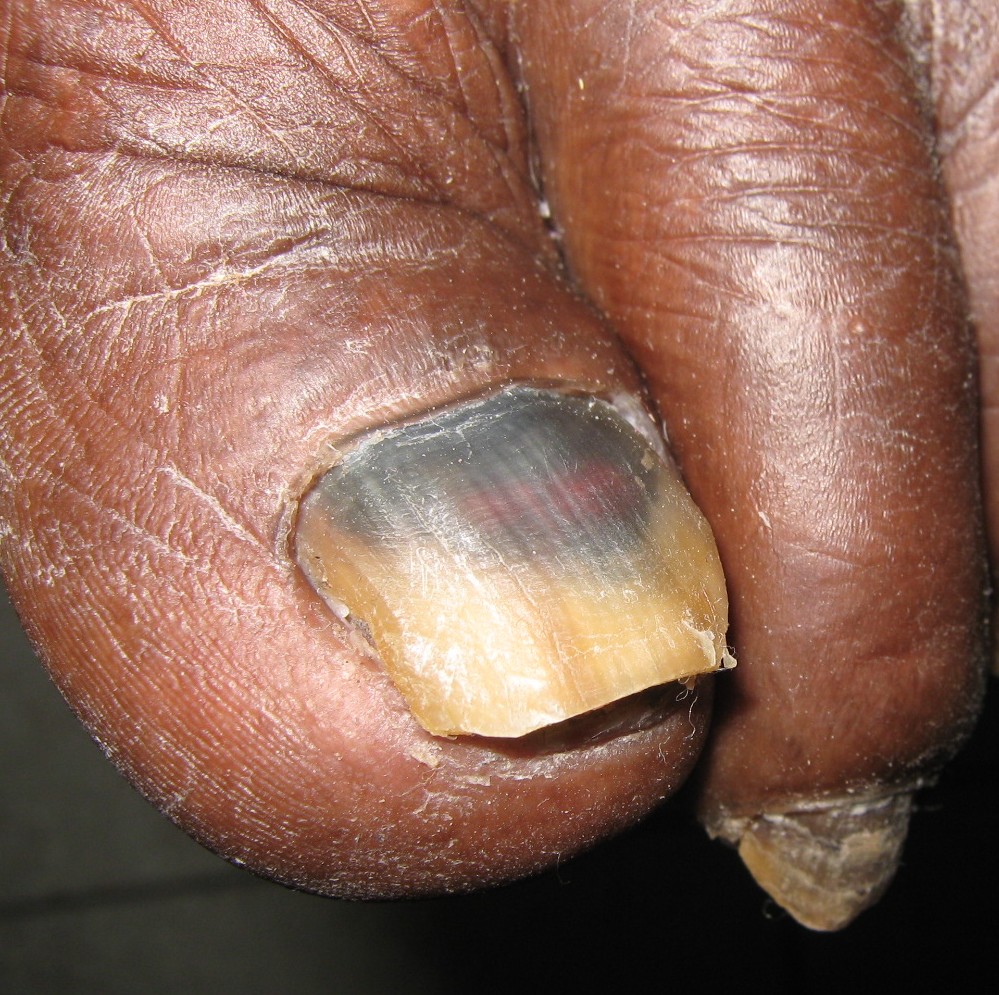
Terbinafine for Onychomycosis
Topical terbinafine has some limitations in treating onychomycosis. When used alongside oral medications or nail debridement procedures, Tyza Cream can help improve local fungal control and decrease the chances of recurrence. It is also an option for children or individuals who cannot take drugs.
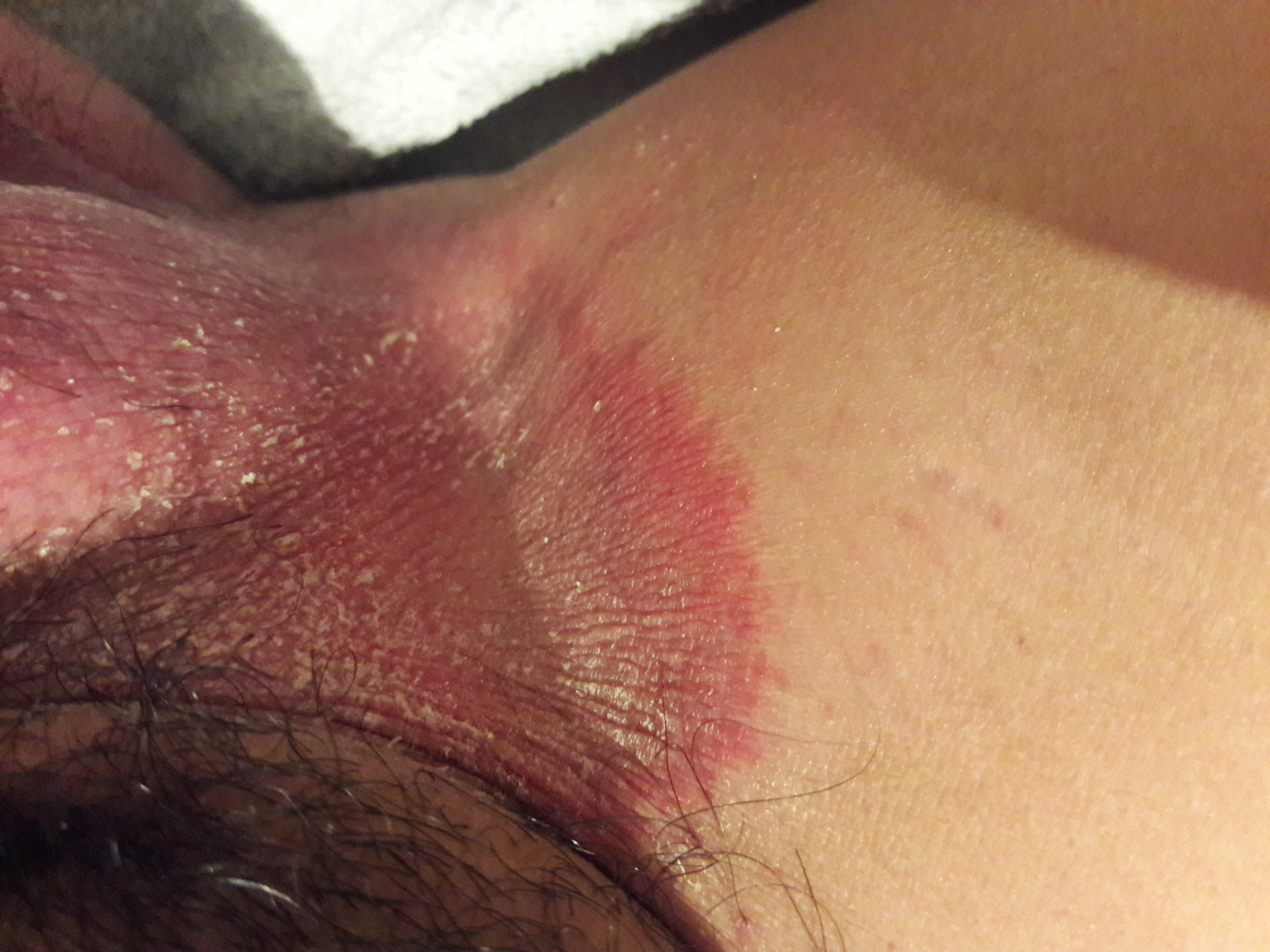
Terbinafine for Jock Itch
Tyza Cream is a commonly recommended treatment for jock itch, medically known as tinea cruris. This fungal infection usually affects the inner thighs and groin creases, causing significant itching, redness, and flaky skin.
The oily properties of terbinafine, Tyza Cream's active ingredient, allow it to deeply penetrate affected skin layers. Its consistent antifungal action often leads to recovery in under fourteen days.
For individuals prone to recurrent jock itch, especially athletes or those in humid climates, applying preventative measures alongside treatment is also advisable.
Off-Label Uses of Tyza Cream (Terbinafine)
Experimental Use in Seborrheic Dermatitis
While not yet officially approved for the treatment of seborrheic dermatitis, Tyza Cream has garnered interest from healthcare professionals due to its perceived effectiveness against this challenging and recurring skin condition. Seborrheic dermatitis primarily affects sebum-rich areas like the scalp, nasolabial folds, and upper chest, and is often linked to an overgrowth of Malassezia yeast species.
Although ketoconazole and ciclopirox are standard treatments, terbinafine's partial efficacy against these yeasts suggests it could be a suitable alternative in specific situations, such as:
- When patients show intolerance or a lack of response to azole treatments.
- When dermatophyte colonization is suspected.
Anecdotal evidence from both professionals and patients suggests that intermittent topical application of Tyza Cream may reduce redness, itching, and skin flaking, particularly in mild to moderate cases.
However, these observations lack confirmation from controlled research studies. Therefore, more robust evidence is needed before Tyza Cream becomes a routine treatment for seborrheic dermatitis.
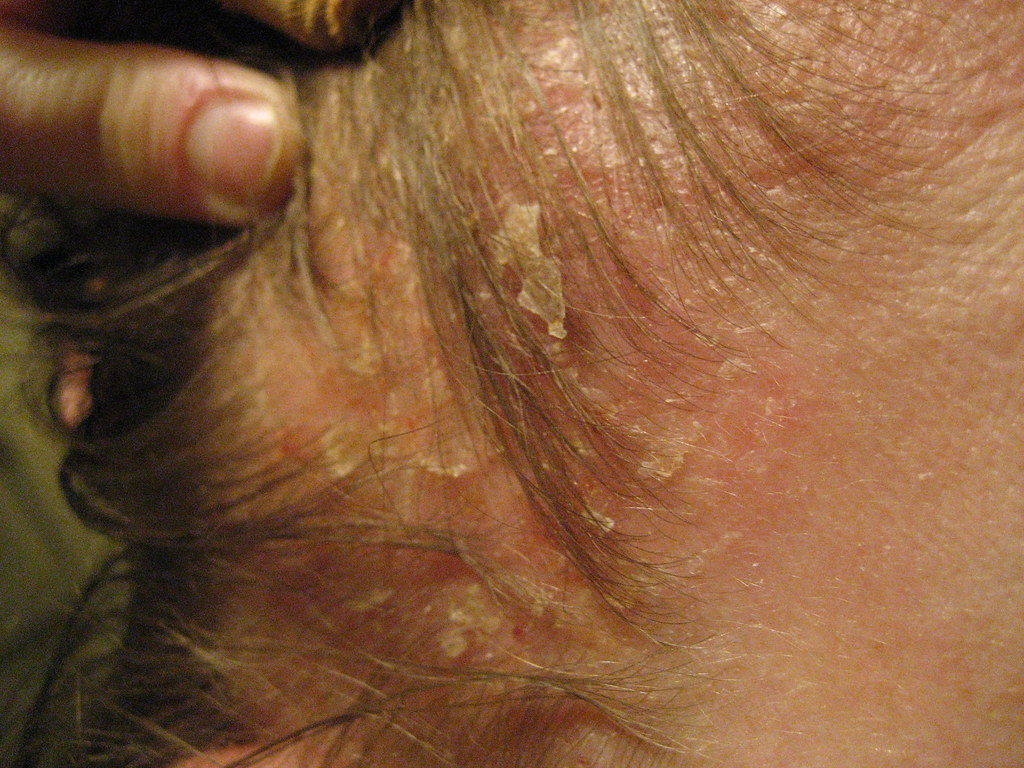
Application for Interdigital Fungal Infections in Immunocompromised Patients
Individuals with compromised immune systems, such as those undergoing chemotherapy or organ transplants, are more susceptible to unusual and challenging fungal infections between their fingers and toes. These infections often present with deep cracks and secondary bacterial infections. Tyza Cream offers several benefits in managing these complex cases:
- It's effective against a variety of skin fungi, including dermatophytes, yeasts, and certain molds.
- Its minimal absorption into the bloodstream reduces the risk of drug interactions, which is crucial for patients already on multiple medications.
Terbinafine, the active ingredient in Tyza Cream, is sometimes used in immunocompromised patients, either alongside other treatments or as a standalone option for specific skin lesions where systemic medications might pose too high a risk. While this use isn't officially approved, it's becoming more common in hospital dermatology practices under careful medical supervision.
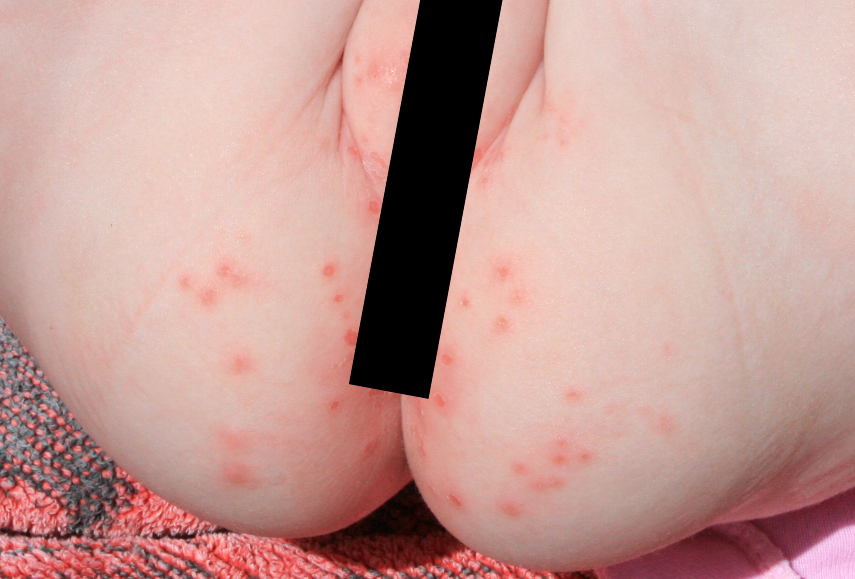
Investigational Treatment in Diaper Rash with Fungal Overgrowth
Diaper rash complicated by infections like Candida albicans can be challenging to treat. While standard care typically involves barrier creams and antifungals such as nystatin or clotrimazole, some researchers have explored Tyza Cream as an alternative for recurring cases.
Tyza Cream may offer benefits by:
- Reducing the characteristic redness and small pimples often seen with yeast infections in skin folds.
- Improving symptom management, especially when the effectiveness of conventional medications is limited by drug interactions or resistance.
However, extreme caution is necessary when considering Tyza Cream for infants due to their higher skin absorption rate and underdeveloped liver metabolism.
It's crucial to consult a pediatrician before applying the cream to covered areas or extensive skin patches.
Nevertheless, positive results have been observed when the cream is used sparingly under the guidance of a dermatologist.
Dosage and Administration Guidelines for Tyza Cream
Terbinafine Dosage for Adults
Adults should apply a thin layer of Tyza Cream to the affected area once or twice daily, depending on the severity and location of the fungal infection. The duration of treatment varies:
- For tinea pedis (athlete's foot), it typically takes 1 to 2 weeks.
- Tinea cruris (jock itch) and tinea corporis (ringworm) usually resolve within a week.
- Cutaneous candidiasis generally requires about two weeks of treatment.
For persistent or chronic cases, the treatment period may need to be extended. It's generally recommended to continue using the cream even after symptoms clear up to prevent the infection from returning.
Dosage of Terbinafine for Dogs
In dermatology, terbinafine is sometimes used to treat skin infections in dogs, even though it's not officially approved for veterinary use. While oral administration is more common, applying terbinafine cream topically can be a useful adjunctive treatment for infections like ringworm. It's crucial to follow a veterinarian's instructions carefully and take precautions to prevent dogs from licking off the cream.
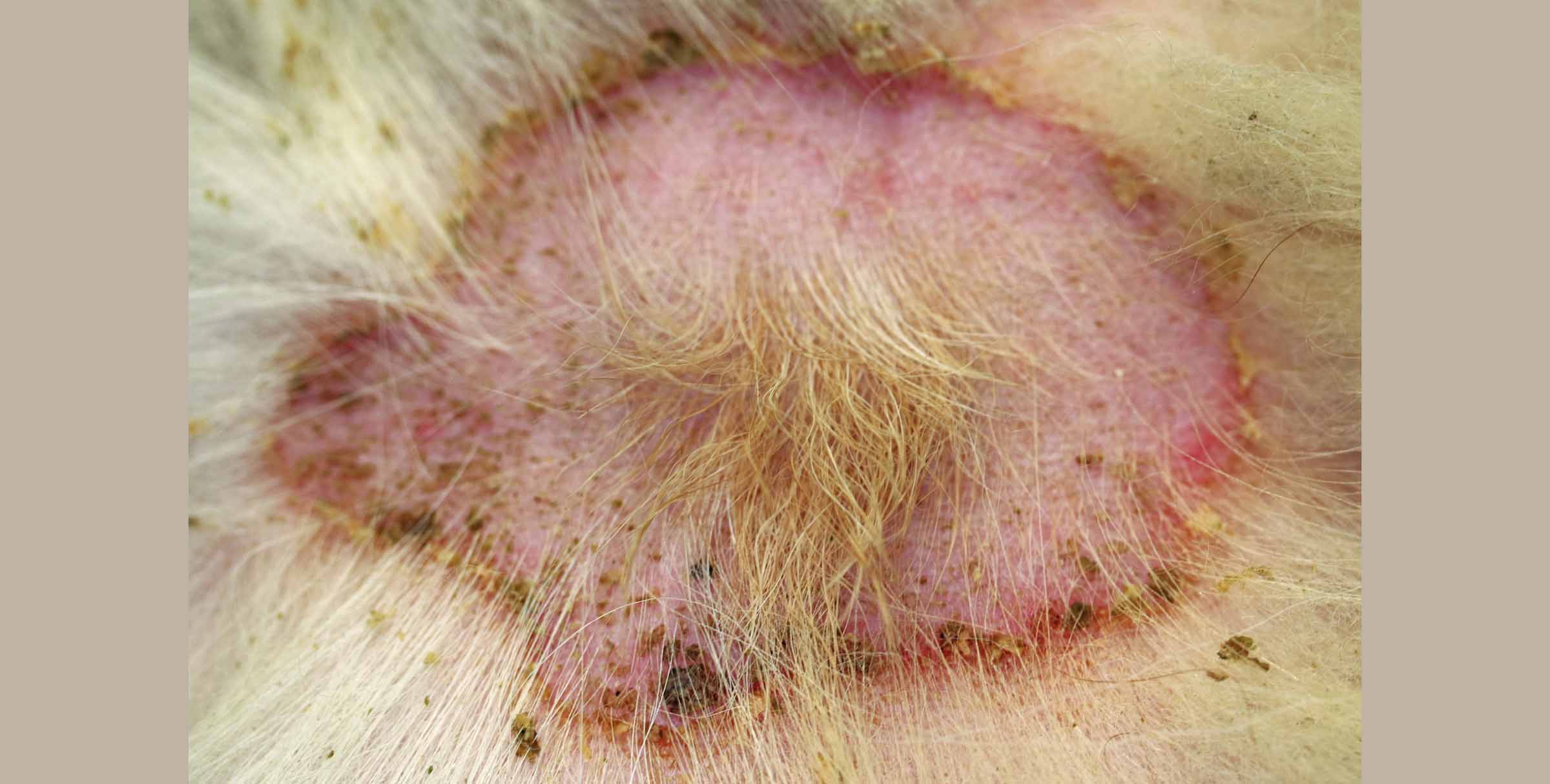
Recommended Frequency and Duration of Application by Condition
How often you apply the cream depends on the condition you're treating:
- For ringworm on the body and jock itch, apply once a day.
- For athlete's foot and yeast infections in skin folds, apply twice a day.
Treatment typically lasts between one and four weeks. However, chronic conditions or those in individuals with weakened immune systems might require longer treatment periods under close medical supervision.
Instructions for Skin Preparation Before Use
Proper skin preparation is key to ensuring better absorption and effectiveness of topical treatments.
To prepare the skin:
- Wash the affected area thoroughly with soap and warm water.
- Gently pat it dry with a clean cloth, avoiding vigorous rubbing.
- Ensure the skin is free of any moisturizers or heavy creams before applying the treatment.

Application Technique and Amount to Be Applied
Apply Tyza Cream sparingly. A fingertip amount (0.5g) is sufficient for an area the size of your palm. Gently rub the cream into your skin until it's fully absorbed, making sure to extend the application 1 to 1.25 inches beyond the visible lesion to treat any hidden spread of the infection.
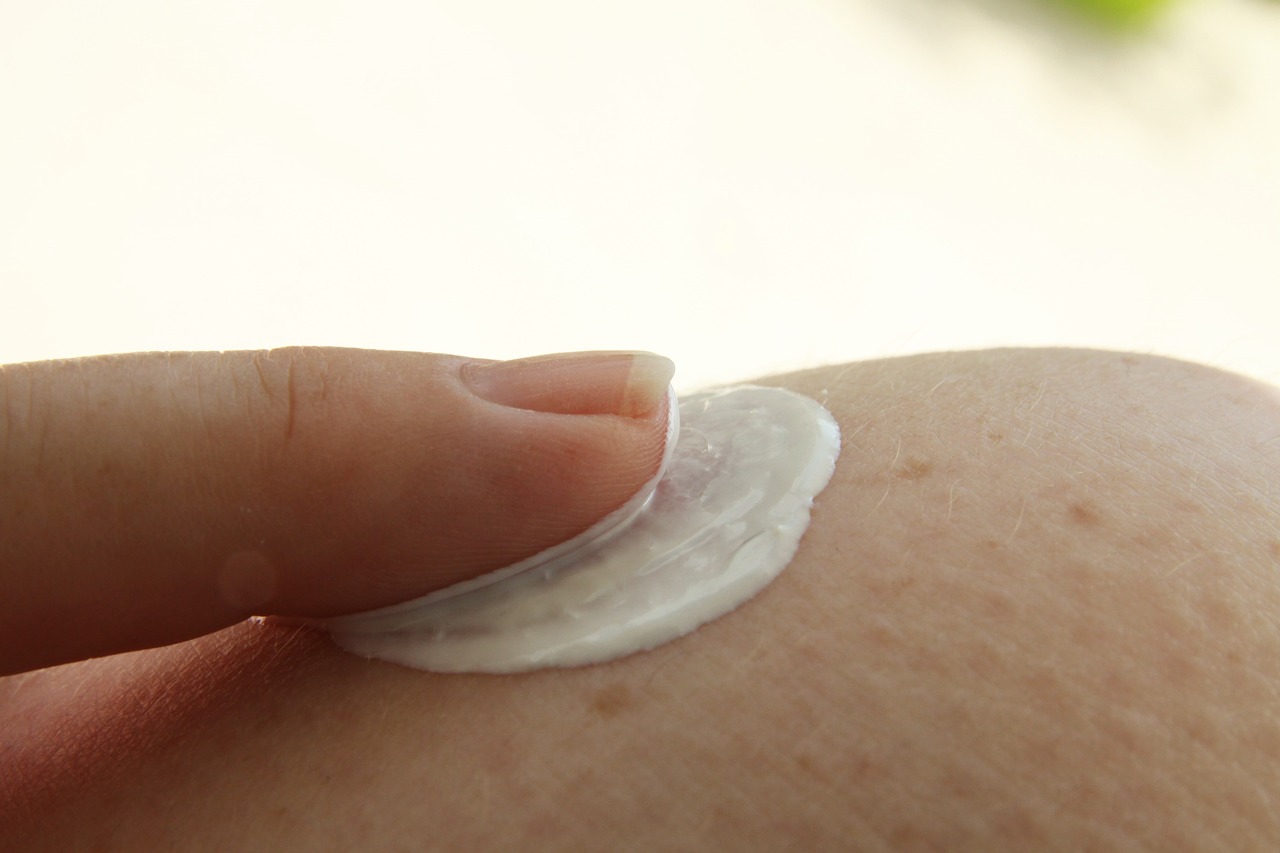
What to Avoid During Treatment (e.g., Occlusive Dressings)
To avoid irritation and ensure the cream's effectiveness, keep these points in mind:
- Only use airtight bandages if specifically instructed by a doctor.
- Avoid applying the product to mucous membranes (like in the mouth or nose), broken skin, or near the eyes.
- Do not use corticosteroids on the same area unless your doctor advises it.
Remember, allowing the skin to breathe is essential when treating fungal infections.
Terbinafine Results Before and After
You'll typically see signs of improvement within days of starting treatment. Within the first week, redness (erythema), flaking (scaling), and itching (pruritus) usually lessen significantly.
It's common for skin lesions to disappear completely after 2 to 4 weeks of applying the treatment. "Before and after" pictures often clearly show these changes in patient records, highlighting:
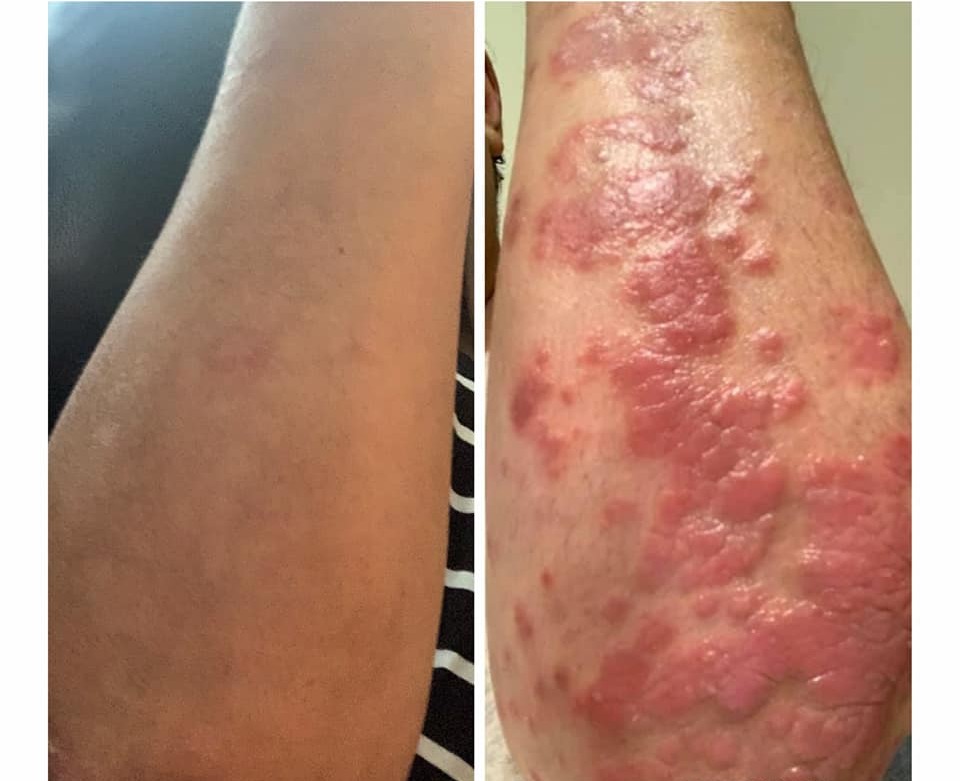
- A decrease in inflammation.
- The return of natural skin color and smoothness.
- No more scaling or active borders on the lesions.
Dosage Adjustments and Administration in Special Populations
Administration in Elderly Patients
Pharmacokinetic Considerations
Research shows that topical terbinafine isn't significantly absorbed into the bloodstream. However, age-related changes in skin absorption and metabolism might slightly influence how the body processes the drug.
Skin Sensitivity and Thinning in Geriatric Use
As skin ages, it can become more fragile, with oils and moisture, which can lead to being more sensitive, to irritation or dryness when using antifungal creams.

Monitoring for Local Reactions
It's advisable for older adults to have check-ups with a dermatologist— if they have pre-existing skin conditions, like dermatitis or venous insufficiency or if they've been using topical products for an extended period.
Administration in Pregnant Women and Nursing Mothers
Terbinafine Pregnancy
Topical terbinafine is classified by the FDA as Pregnancy Category B. This means animal studies haven't shown a risk to the fetus, but there isn't enough controlled data from human pregnancies.

FDA Pregnancy Category and Safety Profile
Topical terbinifine has systemic absorption, into the bloodstream and is usually deemed safe for use during pregnancy when used correctly; however it should only be used if absolutely necessary and, under the supervision of a professional.
Risk vs Benefit Considerations
Only utilize this approach when the advantages are greater than the risks, in theory. Try not to apply much of the product on areas of your skin or in places where it might get trapped or covered up for long periods.
Guidelines for Breastfeeding Women
It's best to avoid applying this medication to the chest or nipple area if you're breastfeeding, as it could expose the baby. However, using it sparingly on areas like the feet is generally considered acceptable.

Administration in Pediatric Patients
Safety and Efficacy in Children Under 12
There's no safety data available for terbinafine cream use in children under 12. While it's generally used with caution in older children, it's typically avoided for infants and toddlers unless a pediatrician specifically recommends it.
Recommended Precautions for Young Children
Only use it on localized areas. Make sure to keep an eye on things to avoid swallowing or coming into contact with areas like mucous membranes.
Specific Indications and Age-Related Limitations
When treating ringworm on a child's body or scalp, doctors should consider age-appropriate formulations in conjunction with other therapies. It's crucial that caregivers receive proper instructions on how to use these medications. Importantly, if oral antifungal medication is deemed necessary, topical creams should not be used as a substitute for that treatment.
Common and Serious Side Effects of Tyza Cream
Common Side Effects
Tyza Cream is generally well-tolerated. It can cause minor skin reactions, but these are typically confined to the application site and clear up on their own. However, it's important to quickly identify and manage these side effects to ensure patients continue their treatment as prescribed.
Mild Erythema and Peeling
In the first few days of using the cream, you might notice some redness and peeling on your skin, especially if you have athlete's foot or body fungus with thickened skin. These symptoms are usually mild and tend to disappear within 48 to 72 hours. To ease any discomfort, you can try using cool compresses or soothing creams.

Local Irritation and Dryness
You might experience dry skin (xerosis) and irritation, particularly if you have a compromised skin barrier. This is often due to the alcohol-based ingredients in the product.
Burning or Stinging Sensation at Application Site
You might feel a burning or stinging sensation right after applying the product, especially in areas where skin folds or if there's existing inflammation. This discomfort usually subsides within a few minutes and doesn't necessarily indicate an allergic reaction.
Rash and Skin Terbinafine Side Effects
Some people may experience skin rashes or red patches that're usually not related to the immune system and can go away by adjusting the dosage or taking a break, from the treatment temporarily.
Terbinafine Hair Loss
While alopecia or telogen effluvium is usually linked to use of medication, in cases; some reports have mentioned occurrences, in patients using terbinadine cream for long durations as well The exact cause of this remains uncertain and is likely influenced not just one factor but multiple factors.
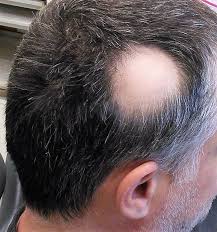
Terbinafine Weight Gain
While medical guidelines don't officially list weight gain as a side effect of terbinafine cream, there have been anecdotal reports since the medication's release that have prompted occasional investigations. However, no solid evidence has been found to link topical terbinafine use with changes in metabolism
Serious and Rare Side Effects
Allergic Contact Dermatitis
Though rare, some people might experience allergic contact dermatitis (ACD) from Tyza Cream. This can show up as itching, localized swelling, and blisters. If reactions are unusual or keep recurring, a patch test might be needed to confirm the allergy.
If you suspect you have ACD, it's crucial to stop using the cream immediately. Your doctor might recommend topical corticosteroids to help relieve the symptoms.
Skin Blistering or Ulceration
Severe skin reactions, such as blistering or ulceration at the application site, are rare. These could signal a strong irritant reaction or reveal an underlying skin condition.
Secondary Bacterial Infections
Damaging your skin barrier, often from scratching or over-applying products, can raise your risk of bacterial infections, typically caused by Staphylococcus aureus. If this happens, you might notice pus drainage, increased pain, and warmth in the affected area.
Depending on how severe the infection is, you might need antibiotics, either applied to the skin or taken orally. Keeping the area consistently clean is also crucial to prevent these issues.
Terbinafine Side Effects Liver
Topical terbinafine, when applied to the skin, is unlikely to cause liver damage because it's only minimally absorbed into the bloodstream.
This is a crucial distinction from oral terbinafine, which has documented cases of causing liver problems. This difference in risk can be confusing for patients.
If someone is taking oral terbinafine concurrently, their liver function should be monitored regularly. However, this monitoring isn't necessary when using the topical form.
Contraindications for the Use of Tyza Cream
Known Hypersensitivity to Terbinafine or Cream Components
You should not use Tyza Cream if you've previously had an allergic reaction to terbinafine hydrochloride or any other ingredient in the product. Using it despite a known allergy could lead to reactions such as:
In severe cases, it could trigger contact dermatitis or even broader systemic immune reactions affecting your whole body.
If you're unsure whether you're sensitive to any of the ingredients, consider undergoing allergy testing or patch testing before using the cream.
If there's a suspected sensitivity, your doctor might suggest alternative antifungal treatments like azoles or polyenes.
Previous Severe Skin Reactions to Topical Antifungals
If you've previously had skin reactions to other topical antifungal creams, it's safest to avoid using Tyza Cream. This is because you might be sensitive to similar antifungal medications with shared chemical structures, potentially leading to adverse reactions such as:
- Stevens-Johnson Syndrome (SJS)
- Toxic Epidermal Necrolysis (TEN)
- Acute Generalized Exanthematous Pustulosis (AGEP)
It's highly recommended to consult a dermatologist before beginning any treatment if you have such a history.
Warnings and Precautions for Tyza Cream Usage
Avoidance of Mucous Membranes and Eyes
Tyza Cream is for external skin use only. It should never come into contact with mucous membranes like your mouth or eyes, as this can cause adverse reactions such as a stinging sensation or irritation, potentially leading to chemical conjunctivitis in the eyes.
If accidental exposure occurs:
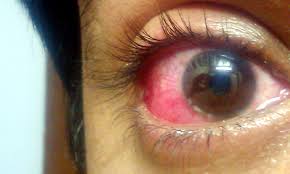
- Rinse the affected area thoroughly with plenty of water.
- If symptoms persist, seek medical advice and assistance.
Discontinue Upon Signs of Hypersensitivity
If you experience any signs of an allergic reaction, such as severe itching or widespread redness, stop using the product immediately. This will help prevent your symptoms from worsening and could avert a more serious allergic response.
Do Not Apply on Broken or Inflamed Skin
Applying Tyza Cream to scraped or inflamed skin can easily cause irritation and adverse reactions. Damaged skin also absorbs the cream more readily, increasing the risk of systemic exposure. It's best to apply the cream only after the skin barrier has properly healed, or if a doctor specifically advises its off-label use on compromised skin.
Monitoring for Worsening Symptoms
If you don't see any improvement or if your condition worsens after two weeks, it could indicate several issues:
- Misdiagnosis: The condition might be something else entirely, like psoriasis or eczema, rather than a fungal infection.
- Secondary Infection: A new infection, such as a bacterial superinfection, may have developed.
- Antifungal Resistance: The fungus might be resistant to the treatment, which is becoming a growing concern.
If the condition continues to deteriorate, it's crucial to reevaluate the diagnosis and consider further tests, such as fungal cultures or susceptibility testing.
Careful Administration Considerations
Patients with Chronic Dermatoses
If the condition shows no improvement or worsens after two weeks, it might indicate:
- Incorrect Diagnosis: The problem might actually be something else, like psoriasis or eczema, rather than a fungal infection.
- Secondary Infection: Another infection, such as a bacterial superinfection, could have developed.
- Antifungal Resistance: The fungus may have developed resistance to the medication, which is an increasing concern.
In such cases, it's important to re-evaluate the situation and consider further diagnostic tests, such as fungal cultures or susceptibility testing, if the condition continues to decline.
Use in Immunocompromised Individuals
Patients with compromised immune systems—due to conditions like chemotherapy, organ transplants, or advanced HIV—may experience unusual symptoms and varied responses to fungal infections compared to healthy individuals. Tyza Cream could be beneficial in such cases, but it's crucial to consult a specialist before use. One key factor to consider is the possibility of an extended treatment period.
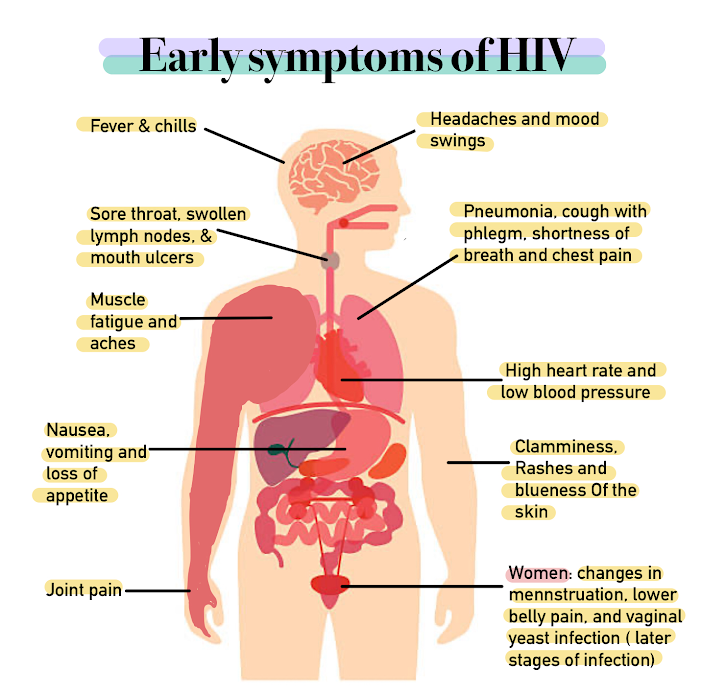
Risk of Resistance with Inappropriate Use
Individuals with weakened immune systems—such as those undergoing chemotherapy, organ transplants, or living with advanced HIV—may exhibit unusual symptoms and responses to fungal infections that differ from healthy people. Tyza Cream might offer benefits in these situations, but always consult a specialist before using it. Be prepared for a longer treatment duration in such cases.
Drug and Product Interactions
Potential Interaction with Other Topical Products
Be cautious when using Tyza Cream with other skincare products, as they might interfere with its effectiveness or the absorption of terbinafine. It's recommended to wait at least 30 minutes between applying different products to ensure they work properly and remain stable on your skin.
Risk of Compounded Irritation with Corticosteroids or Exfoliants
Mixing Tyza Cream with corticosteroids or chemical exfoliants (such as salicylic acid or alpha hydroxy acids) can intensify skin irritation and redness. It can also disrupt your skin's natural barrier, leading to increased water loss and localized adverse effects, especially on delicate or inflamed skin.
Therefore, concurrent use of these products should be limited and ideally overseen by a dermatologist. If combination treatment is necessary, it's best to apply them at different times of the day.
Guidance on Concurrent Antifungal Use
Unless medically necessary, it's generally not recommended to use Tyza Cream with other antifungal treatments, whether they're applied topically or taken orally.
For infections that are hard to treat with standard therapies alone, a combination of treatments might be recommended. This approach should be tailored to the specific fungus identified through laboratory tests like culture and susceptibility testing.
When choosing between antifungal classes like azoles and allylamines, it's important to consider how each works and the location of the infection.
Terbinafine Alternatives
When considering other antifungal medications, several options are available, each with distinct properties:
- Clotrimazole: This is an imidazole antifungal effective against various skin fungi and yeast infections, including Candida.
- Ciclopirox olamine: Known for its broad-spectrum antifungal activity, it also possesses anti-inflammatory properties, which can be beneficial in reducing associated symptoms.
- Efinaconazole: Primarily used for treating onychomycosis (nail fungus), it's designed to penetrate the nail plate effectively.
- Naftifine: Another allylamine antifungal, similar to terbinafine, with a comparable effectiveness profile against certain fungal infections.
The choice of alternative medication depends on several factors: the specific type of pathogen causing the infection, its location on the body, the patient's overall health, and their response to any previous treatments.
Terbinafine Interactions with Alcohol
Topical terbinafine, the active ingredient in products like Tyza Cream, doesn't interact with alcohol. However, oral terbinafine can harm your liver, and drinking alcohol while taking it increases that risk. Many people aren't aware of this distinction, so it's important to inform patients about the safety considerations for the specific formulation they're using.

Terbinafine and Caffeine
There is no known connection, between using terbenafine and consuming caffeine together. When taken orally terbenafine might affect how the body processes caffeine in the liver by slowing down CYP1A2 enzymes. This impact is not significant when applied topically because very little of it gets absorbed into the system.
Terbinafine and Ibuprofen
Topical terbinafine generally doesn't interact with nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) like ibuprofen in typical use. However, if you're taking oral terbinafine, it's wise to be cautious. In rare cases, the oral form can lead to liver or kidney problems for some people.
Overdose and Misuse of Tyza Cream
Symptoms of Accidental Ingestion or Excessive Topical Use
If you accidentally overuse Tyza Cream or swallow it, you might experience mild symptoms. If consumed, this could include nausea or general stomach discomfort. If overused on the skin, you might notice severe irritation or a burning sensation, potentially leading to skin inflammation.
The risk of serious harm to your body's systems is very low because topical terbinafine isn't easily absorbed into the bloodstream.
Emergency Management and First Aid Measures
If you accidentally swallow the product, rinse your mouth thoroughly and monitor for any symptoms. Only induce vomiting if a medical professional tells you to.
For overexposure to the affected skin area, gently clean it with water. Avoid applying anything else until a healthcare provider has assessed the situation.

Poison Control Center Guidance
If someone accidentally swallows a significant amount of the medication, contact a poison control center immediately. Be ready to share details from the product label, such as "terbinafine hydrochloride," to ensure they can provide the proper assistance. For minor exposure, observation might be all that's needed.
Handling and Storage Instructions for Tyza Cream
Recommended Storage Temperature and Conditions
Keep Tyza Cream in a controlled temperature environment, between 15°C to 30°C (59°F to 86°F). Don't expose it to extreme heat or freezing conditions, as this can alter its stability and consistency.
Shelf Life and Stability After Opening
Once unsealed, the cream remains chemically stable for about six months if stored properly. Always check the expiry date before using it, and discard any leftover product after that date to ensure it's both safe and effective.
Safe Handling Practices to Avoid Contamination
Always apply the cream with dry hands or a sterile applicator. Don't share the tube with anyone, as this can spread contamination. After each use, make sure the cap is on tightly and keep the tube in its original packaging to protect it from light and moisture. Following these hygiene practices helps maintain the cream's effectiveness and reduces the risk of microbial contamination over time.

Important Patient Education and Usage Precautions
Emphasizing Adherence to Full Treatment Course
Even if you start feeling better quickly with Tyza Cream, it's crucial to follow the prescribed treatment duration. This helps eliminate any lingering fungal elements and prevents the infection from coming back or developing resistance.
- Complete the full course as prescribed; this typically ranges from 1 to 4 weeks, depending on your specific condition.
- Try to use the medication at the same time every day to maintain consistent levels in the affected area.
- Remember, visible improvement doesn't always mean the infection is fully gone.
Sticking to your treatment protocol is essential for a lasting recovery and can help you avoid needing more extensive treatments later on.
Avoid Sharing Medication with Others
Tyza Cream should never be shared with others, even if they have similar symptoms. Fungal infections are often misidentified, and using the cream without a proper diagnosis can lead to unintended consequences. Sharing it could:
- Lead to an incorrect diagnosis for others.
- Encourage the spread of antibiotic-resistant bacteria.
- Introduce allergens or irritants to individuals who haven't been medically evaluated.
Treat this product with the same care as you would a prescription drug; it requires individual assessment and should only be used as directed for your specific condition.
Cleaning Infected Areas Regularly and Maintaining Hygiene
Good skin care routines are crucial for effectively managing fungal skin conditions and reducing fungal growth. Advise patients to gently clean the affected area using mild products and avoid materials that could damage the skin's outer layer.
Here are some key hygiene practices:
- Dry thoroughly: After washing, make sure to completely dry your feet, especially between your toes and in any skin folds.
- Dedicated towels: Use a separate towel for affected areas and wash it after each use to prevent spreading the infection.
- Breathable clothing: Wear clothing that allows your skin to breathe and effectively absorbs moisture. Remember to change socks and underwear daily.
Maintaining good hygiene not only speeds up the healing process but also significantly lowers the risk of secondary bacterial infections.

Preventing Reinfection and Transmission
Dermatophytes, which cause common fungal infections, are highly contagious and can spread easily between people. To prevent transmission:
- Clean surfaces regularly: Remember to disinfect frequently used surfaces like bathroom floors, gym mats, and shared showers.
- Wear footwear in public places: Avoid going barefoot in areas prone to germs and contamination.
- Don't share personal items: Refrain from lending out shoes, socks, razors, or towels.
- Consider preventive measures: In environments where there's a higher risk of infection, using an antifungal powder or preventive cream might be beneficial.
Educating patients about these hygiene measures is crucial for promoting faster recovery and limiting the spread of these illnesses within households and communities.
Tyza Cream, Terbinafine FAQ
- How to tell if Terbinafine is working?
- What are the worst side effects of Terbinafine?
- How long does Terbinafine stay in your system?
- Does Terbinafine cause weight gain?
- How long after taking Terbinafine can I drink alcohol?
- What should you not take with Terbinafine?
- When do Terbinafine side effects start?
- How long does Terbinafine take to work?
- How long does it take for Terbinafine to work?
- Is Terbinafine over the counter?
- How long does it take for Terbinafine to work on toenail fungus?
- How long does it take Terbinafine to work?
- Can I drink alcohol while taking Terbinafine?
- How long do Terbinafine side effects last?
- How does Terbinafine work?
- How long for Terbinafine to work?
- How long does it take for Terbinafine to work on skin?
- Can Terbinafine treat yeast infection?
- Can you drink while taking Terbinafine?
- How to protect your liver while taking Terbinafine?
- What should I avoid while taking Terbinafine?
- Terbinafine how long to work?
- Does Terbinafine cause hair loss?
- How to tell if Terbinafine is working on ringworm?
- Does Terbinafine continue to work after last dose?
- Are Terbinafine tablets effective?
- Are Terbinafine and Lamisil the same thing?
- Are Terbinafine and Fluconazole the same thing?
- Are Terbinafine tablets safe?
- Are Terbinafine tablets antibiotics?
- Are Terbinafine side effects permanent?
- Can Terbinafine cause thrush?
- Can Terbinafine cause weight gain?
- Can Terbinafine cause yeast infection?
- Can Terbinafine cause insomnia?
- Can Terbinafine be crushed?
- Can Terbinafine cause hair loss?
- How Terbinafine works?
- How Terbinafine cream works?
- Terbinafine how long to take?
- Terbinafine how to use?
- What Terbinafine is used for?
- Terbinafine what is the brand name for this?
- Terbinafine what to expect?
- When Terbinafine doesn't work?
- Terbinafine when breastfeeding?
- Where is Terbinafine metabolized?
- Terbinafine which class of drug?
- Terbinafine which group of drug?
- Which is better Terbinafine or Fluconazole?
- Which is better Terbinafine or Clotrimazole?
- Who manufactures Terbinafine?
- Who discovered Terbinafine?
- Why does Terbinafine cause weight gain?
- Why does Terbinafine cause depression?
- Will Terbinafine kill athlete's foot?
- Will Terbinafine treat ringworm?
- Will Terbinafine treat jock itch?
- Will Terbinafine treat yeast infection?
- Will Terbinafine kill Candida?
How to tell if Terbinafine is working?
Seeing progress such, as itching and redness or feeling more comfortable, in the treated area shows that Terbinafine is effective. In cases of nail infections you might notice nail growth starting from the bottom but it may take several months to see complete results.
What are the worst side effects of Terbinafine?
Severe damage, to the liver and skin issues such as Stevens Johnson syndrome are some of the effects to watch out for along with blood disorders and changes, in taste or smell perception; seeking prompt medical care is vital if any of these symptoms manifest.
How long does Terbinafine stay in your system?
Terbinafine stays in the body for quite a while after treatment stops. It can be found in the skin,nails and fatty tissues even though its half life is 36 hours.
Does Terbinafine cause weight gain?
Weight gain is rarely mentioned as an outcome of using Terbinafine medication according to reports and studies available far; however, if there are noticeable changes, in weight while on the medication it is advisable to explore other potential reasons, for this occurrence.
How long after taking Terbinafine can I drink alcohol?
It's advised to steer clear of alcohol while undergoing Terbinafine treatment and for a days afterward to reduce strain on the liver and minimize the risk of toxicity.
What should you not take with Terbinafine?
Steer clear of medicines that impact liver enzymes such, as rifampin or cimetidine and exercise caution, with antidepressants, blood thinners and beta blockers because of interaction concerns.
When do Terbinafine side effects start?
Side effects may start showing up in the days or weeks of the treatment; however the timing can differ from person to person and depending on the dosage used.
How long does Terbinafine take to work?
Skin infections typically show signs of improvement in about 1 to 3 weeks while nail infections may take from 6 to 12 weeks to get better and could take several months for a full recovery.
How long does it take for Terbinafine to work?
Skin infections typically start improving within one, to two weeks while it may take months to see the effects of toenail fungus because of the slow growth of nails.
Is Terbinafine over the counter?
Terbinafine cream can be bought without a prescription, for use while oral Terbinafine usually needs a prescription because of the side effects that affect the entire system.
How long does it take for Terbinafine to work on toenail fungus?
Visible improvement, in the condition usually becomes noticeable after 6 to 12 weeks of treatment; however it may take months for the nail to show significant growth and recovery.
How long does it take Terbinafine to work?
Most fungal infections show signs of improvement within 1 to 8 days after treatment starts; however the time it takes for recovery varies depending on the type and location of the infection.
Can I drink alcohol while taking Terbinafine?
It's best to steer clear of alcohol while undergoing Terbinafine treatment as it can heighten the chances of liver issues cropping up.
How long do Terbinafine side effects last?
Some mild side effects might go away in a matter of days to weeks while severe issues, like liver or skin reactions could last longer and need attention.
How does Terbinafine work?
How long for Terbinafine to work?
Relief from symptoms usually begins within one to two weeks for skin infections; however, full nail recovery may require months.
How long does it take for Terbinafine to work on skin?
Superficial fungal infections, on the skin typically show improvement within 7 to 14 days after beginning treatment.
Can Terbinafine treat yeast infection?
Terbinafine is usually not prescribed for yeast infections, like those caused by Candida since it works better against skin infections caused by dermatophytes such as Trichophyton species.
Can you drink while taking Terbinafine?
It's recommended to avoid consuming alcohol when taking Terbinafine to lower the chances of harming your liver.
How to protect your liver while taking Terbinafine?
Remember to stay from alcohol consumption and keep an eye on your liver enzyme levels as recommended by your healthcare provider; if you experience any signs such, as yellowing of the skin or eyes (jaundice) persistent tiredness (fatigue) or colored urine (dark urine) make sure to inform your doctor right away.
What should I avoid while taking Terbinafine?
Steer clear of alcohol and specific medications that impact liver enzymes and avoid supplements that could potentially burden the liver.
Terbinafine how long to work?
Response to treatment usually shows up in about 1 to 3 weeks for skin infections. It can take months for nail infections to improve.
Does Terbinafine cause hair loss?
Hair loss is not common. Has been noted as a side effect of using Terbinafine for an extended period of time.
How to tell if Terbinafine is working on ringworm?
Signs that Terbinafine is effective against ringworm can be seen in the form of redness scaling, itching, and shrinking lesion size within the initial week or two of treatment. The skin may start clearing, starting from the center. Spreading outward to create a more consistent look.
Does Terbinafine continue to work after last dose?
Terbinafine builds up in the skin and nails as, in fat tissues and remains effective, against fungi for several days to weeks even after the last dose is taken.
Are Terbinafine tablets effective?
Terbinafine tablets work well in treating infections, like athletes foot and ringworm; they're also great for curing conditions such as nail fungus which makes them stand out compared to antifungal treatments.
Are Terbinafine and Lamisil the same thing?
Lamisil and the generic medication Terbinafine share the ingredient; however they are marketed under different brand names.
Are Terbinafine and Fluconazole the same thing?
Terbinafine and Fluconazole are types of antifungals; Terbinafine focuses on dermatophytes, while Fluconazole is commonly prescribed for yeast and systemic fungal infections.
Are Terbinafine tablets safe?
Terbinafine tablets are usually considered safe when used as directed; however, they may sometimes lead to liver issues, skin problems or changes in taste perception.
Are Terbinafine tablets antibiotics?
Terbinafine is actually not an antibiotic—it's a type of medicine specifically meant for treating infections and not bacterial ones.
Are Terbinafine side effects permanent?
Terbinafine side effects are often temporary; however, in some instances there have been reports of loss of taste or smell sensations as well, as liver damage or skin problems.
Can Terbinafine cause thrush?
Terbinafine ever results in thrush; however, disrupting the balance of microorganisms, in certain people could potentially cause an excess growth of yeast afterward.
Can Terbinafine cause weight gain?
Gaining weight is not a frequent outcome of taking Terbinafine. It's probably not directly linked to using it.
Can Terbinafine cause yeast infection?
Terbinafine doesn't typically lead to yeast infections; however,
Can Terbinafine cause insomnia?
It's not very common for people to mention having trouble sleeping when taking this medication; however some individuals have experienced sleep issues while undergoing treatment.
Can Terbinafine be crushed?
It's generally advised not to crush terbinfine tablets because it can lead to a taste and affect how your body absorbs the medication – make sure to talk to a pharmacist before attempting this.
Can Terbinafine cause hair loss?
Hair loss is an occurrence that can potentially happen as an effect of using Terbinafine; however it is typically reversible once you stop taking the medication.
How Terbinafine works?
Terbinafine works by blocking the activity of an enzyme called squalene epoxidase which disrupts the production of ergosterol, in fungi cells causing their cell membranes to malfunction and eventually die off.
How Terbinafine cream works?
Terbinafine cream functions by blocking the enzyme squalene epoxidase which interrupts ergosterol production in the cell membrane resulting in the death of cells and clearance of the infection.
Terbinafine how long to take?
The length of time needed varies based on the situation. Around 1 to 14 days, for skin infections and 6 to 12 weeks or longer, for nail infections when taking oral medications.
Terbinafine how to use?
Apply a layer of the cream once or twice daily on the area and the skin, around it for about 1 to 3 weeks as, per your doctors instructions.
What Terbinafine is used for?
Terbinafine is commonly prescribed for treating infections, like athletes foot and ringworm well as jock itch and onychomycosis which affects the nails.
Terbinafine what is the brand name for this?
Lamisil is the known brand of Terbinafine.
Terbinafine what to expect?
Expect an improvement in symptoms over time, with the chance of experiencing side effects like upset stomach or changes in taste buds along the way, while also understanding that ongoing treatment is necessary, for optimal effectiveness.
When Terbinafine doesn't work?
Terbinafine might not work as expected because of misdiagnosis issues or if there's resistance, from the infection itself or poor adherence to the treatment regimen; it could also be due to not using it for long enough or if the infection is caused by fungal sources such as Candida.
Terbinafine when breastfeeding?
Terbinafine cream is usually seen as safe while nursing a baby; however it's best to consult a healthcare professional before taking it since there isn't safety data available.
Where is Terbinafine metabolized?
The body mostly processes terlinafine in the liver through enzymes such as CYP2C9, CYP1A2 and CYP3A4.
Terbinafine which class of drug?
Terbinafine is part of a group of medications called allylamines.
Terbinafine which group of drug?
Terbinafine belongs to a class of drugs called allylamines. It is different from azoles and polyenes medications.
Which is better Terbinafine or Fluconazole?
Terbinafine is typically more effective, for treating skin and nail infections caused by dermatophytes compared to Fluconazole, which is commonly used for Candida infections and fungal conditions that affect the body.
Which is better Terbinafine or Clotrimazole?
Terbinafine is generally stronger and acts quickly than Clotrimazole in treating dermatophyte infections; however both are effective when used topically.
Who manufactures Terbinafine?
Terbinafine is produced by drug companies with Novartis introducing the product as Lamisil.
Who discovered Terbinafine?
Terbinafine was created by Sandoz in the 1980s as a type of medication belonging to the allylamine class.
Why does Terbinafine cause weight gain?
Putting on weight is not a noted or documented consequence of taking Terbinafine; if it does happen to occur in some cases as reported by individuals it could just be, by chance or influenced by other variables at play.
Why does Terbinafine cause depression?
Terbinafine can sometimes impact a persons mood by changing neurotransmitter levels or, due to effects, like taste changes and feeling unwell. In such instances, seeking advice is advised.
Will Terbinafine kill athlete's foot?
Terbinafine works well in getting rid of the fungus that leads to athletes foot and can show results in 1 1 weeks of treatment.
Will Terbinafine treat ringworm?
Certainly! Terbinafine is mainly used to treat ringworm (known as tinea corporis), offering relief from symptoms and clearing up the infection efficiently.
Will Terbinafine treat jock itch?
Terbinafine is known to work for treating jock itch (also known as tinea cruris) usually showing progress after about a week of applying it topically.
Will Terbinafine treat yeast infection?
Terbinafine is not the preferred medication, for treating yeast infections caused by Candida as it is mainly effective, against dermatophytes.
Will Terbinafine kill Candida?
Terbinafine effectiveness, against Candida species is restricted,. It is usually not employed to treat candidiasis infections.