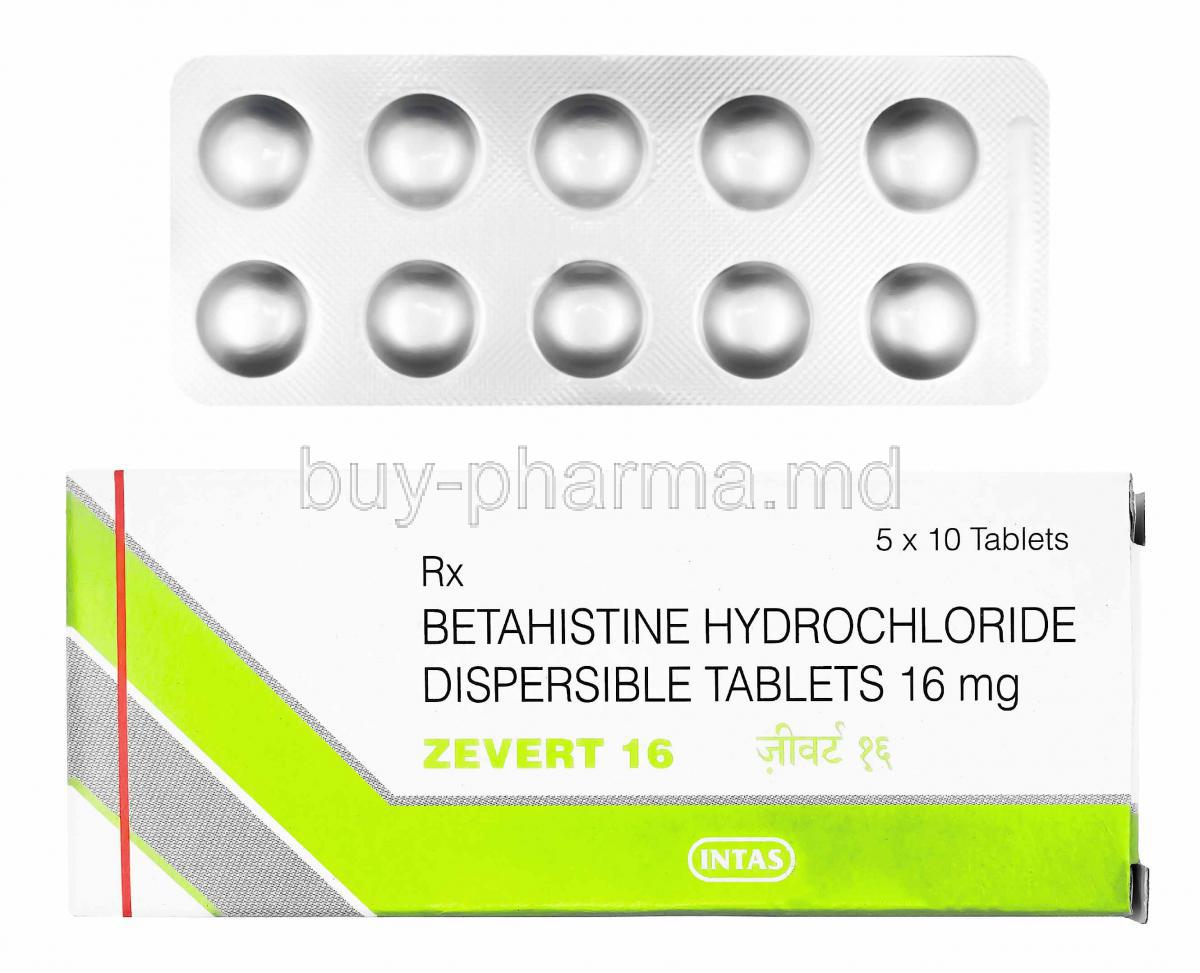
Introduction to Zevert (Betahistine Dihydrochloride)
Zevert, containing the active ingredient Betahistine Dihydrochloride, is a well-established medication used to alleviate symptoms of vertigo and balance disorders. Classified as an antivertigo agent, it operates within the histamine analog category, exerting unique effects on the inner ear and central nervous system. Its pharmacological profile includes modulation of histamine receptors, resulting in improved vestibular function and reduced dizziness episodes.
Zevert is marketed globally under various brand names, making it accessible in numerous healthcare systems. First introduced in Europe in the 1960s, Betahistine rapidly became a mainstay in the management of Ménière’s disease and related vestibular syndromes.
Medical Uses of Zevert
Approved Uses
- Treatment of Ménière’s disease: Reduces the frequency and intensity of vertigo attacks, tinnitus, and hearing loss.
- Vertigo from vestibular disorders: Helps stabilize balance in patients with inner ear dysfunction.
- Reduction of tinnitus: Eases ringing or buzzing sensations linked to labyrinthine fluid imbalance.
- Hearing loss episodes: Minimizes fluctuations in hearing caused by endolymphatic pressure changes.
Off-Label Uses
- Adjunct therapy for vestibular migraine to mitigate dizziness and aura-related symptoms.
- Treatment support for benign paroxysmal positional vertigo (BPPV).
- Balance rehabilitation aid in older adults prone to instability.
- Post-labyrinthectomy recovery to accelerate central vestibular adaptation.
How Zevert Works (Mechanism of Action)
Betahistine functions as both an H1 receptor agonist and an H3 receptor antagonist. This dual action promotes vasodilation in the microvasculature of the inner ear, particularly the stria vascularis, enhancing nutrient and oxygen delivery to delicate auditory structures. It reduces endolymphatic pressure within the labyrinth and cochlea, a key factor in Ménière’s disease pathophysiology.
Additionally, Zevert facilitates central vestibular compensation after injury, aiding in the brain’s ability to recalibrate balance perception following vestibular nerve damage.
Dosage and Administration Guidelines
Standard Adult Dosage
The typical dosage ranges from 24 mg to 48 mg daily, divided into two or three doses. Treatment often starts at a lower dose, gradually increasing to the maintenance level based on patient tolerance and clinical response.
Dosage Adjustments
- Renal impairment: Dose may require adjustment depending on severity.
- Hepatic impairment: Cautious titration is recommended.
- Gastrointestinal sensitivity: Lower starting doses may reduce discomfort.
Method of Administration
Zevert is administered orally, typically as a tablet. For optimal absorption and to minimize stomach upset, it is best taken with or after meals. Consistent dosing at the same times daily enhances therapeutic effect.
Composition and Formulations
- Active ingredient: Betahistine Dihydrochloride, available in various strengths, commonly 8 mg, 16 mg, and 24 mg tablets.
- Excipients: May include microcrystalline cellulose, mannitol, citric acid, and magnesium stearate.
- Pharmaceutical form: Primarily oral tablets; some markets may offer an oral solution.
Potential Side Effects of Zevert
Common Side Effects
- Mild gastrointestinal upset such as nausea or dyspepsia
- Headache
- Minor allergic skin reactions like rash or itching
Less Common and Rare Side Effects
- Palpitations or blood pressure fluctuations
- Severe allergic responses including angioedema or urticaria
- Aggravation of peptic ulcer symptoms
Drug Interactions with Zevert
- Concurrent use with antihistamines may reduce betahistine efficacy.
- Monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOIs) can potentiate betahistine’s effects; caution required.
- Alcohol may exacerbate dizziness symptoms.
- Potential additive effects with sedatives and central nervous system depressants.
Warnings and Safety Information
Prior to initiating Zevert, a comprehensive clinical assessment is essential to exclude other causes of vertigo. Patients with a history of asthma or bronchospasm should use the medication with caution. Those with prior peptic ulcer disease should be monitored for recurrence. Cardiovascular patients should receive risk-benefit evaluation before commencing therapy.
Contraindications to Zevert Use
- Known hypersensitivity to Betahistine Dihydrochloride or any excipient
- Active peptic ulcer disease
- Diagnosed pheochromocytoma
- Severe bronchial asthma
Special Precautions and Careful Administration
Administration to Elderly Patients
In older adults, Zevert (Betahistine Dihydrochloride) has generally demonstrated good efficacy and tolerability, with therapeutic outcomes comparable to those in younger populations. However, the pharmacodynamic response can vary due to age-related physiological changes, including altered receptor sensitivity and slower hepatic metabolism.
Vertigo management in elderly patients requires heightened vigilance, as dizziness can substantially increase the risk of falls and associated injuries. Supportive interventions such as balance training, physiotherapy, and environmental safety modifications should be considered to complement pharmacotherapy.
Administration to Pregnant Women
Betahistine has limited safety data in human pregnancy, and formal classification within recognized pregnancy risk categories may vary by regulatory authority. Animal studies have not consistently indicated teratogenic effects, but the absence of robust controlled trials in pregnant women necessitates caution.
The medication should only be prescribed if the anticipated therapeutic benefit clearly outweighs potential risks to the developing fetus. In all cases, a thorough risk–benefit analysis and shared decision-making between clinician and patient are essential.
Administration to Nursing Mothers
It remains uncertain whether betahistine is excreted into human breast milk in clinically significant quantities. Due to the potential for infant exposure, caution is advised when administering Zevert to lactating mothers. Monitoring for possible gastrointestinal disturbances or allergic reactions in the breastfed infant may be prudent if treatment is deemed necessary.
Administration to Children
The safety and efficacy of betahistine in pediatric patients have not been conclusively established. Clinical data in children are scarce, and age-specific dosing regimens have not been validated in large-scale trials. Consequently, its use in individuals under 18 years of age is generally not recommended unless under specialist supervision in exceptional circumstances.
Overdose Management and Emergency Measures
Documented cases of betahistine overdose are relatively uncommon and typically involve mild to moderate symptoms such as headache, facial flushing, dizziness, tachycardia, and gastrointestinal discomfort. In rare instances, more severe outcomes including seizures or cardiovascular instability have been reported, particularly when ingested with other substances.
Management of overdose is primarily supportive:
- Immediate medical assessment and monitoring of vital signs
- Administration of activated charcoal to reduce systemic absorption, if appropriate
- Gastric lavage in severe or recent ingestions
- Symptomatic treatment for cardiovascular or neurological manifestations
Storage and Handling Precautions
Zevert should be stored at controlled room temperature, typically between 15°C and 30°C, unless otherwise specified on the product labeling. Exposure to excessive heat or direct sunlight should be avoided to preserve chemical stability.
Tablets must be kept in their original blister packaging until administration to protect them from moisture and light. As with all medications, they should be stored securely out of the reach of children to prevent accidental ingestion, which could result in harm.
The shelf life of Zevert is indicated on the packaging and should be strictly observed. Expired medication should be disposed of in accordance with local pharmaceutical waste regulations, avoiding disposal via household drains or general refuse to prevent environmental contamination.
Zevert, Betahistine Dihydrochloride FAQ
- What is betahistine dihydrochloride used for?
- What is the best time of day to take betahistine dihydrochloride?
- Is betahistine dihydrochloride used for anxiety?
- What is the difference between betahistine hydrochloride and betahistine dihydrochloride?
- Is betahistine good for sleep?
- What to avoid when taking betahistine?
- Does betahistine reduce ear pressure?
- Does betahistine affect memory?
- Can betahistine lower blood pressure?
- How long does betahistine stay in your system?
- When is the best time to take betahistine morning or night?
- What are the side effects of betahistine?
- Can I take vitamin D with betahistine?
- Is betahistine bad for your kidneys?
- Is betahistine good for balance?
- Does betahistine increase blood flow to the brain?
- What is a good alternative to betahistine?
- How many days should I take betahistine for vertigo?
- Can I take betahistine with high blood pressure?
- Can betahistine make you tired?
- Does betahistine affect vision?
- Can betahistine affect your mood?
- How long does it take for betahistine to stop dizziness?
What is betahistine dihydrochloride used for?
Betahistine is a medicine used to treat the symptoms of Ménière's disease
What is the best time of day to take betahistine dihydrochloride?
After a meal
Is betahistine dihydrochloride used for anxiety?
Yes
What is the difference between betahistine hydrochloride and betahistine dihydrochloride?
It is just alternate formulations
Is betahistine good for sleep?
Yes
What to avoid when taking betahistine?
Caffeine
Does betahistine reduce ear pressure?
Yes
Does betahistine affect memory?
Yes
Can betahistine lower blood pressure?
Betahistine isn't typically used to treat blood pressure. But at high doses, it can lower blood pressure in some individuals.
How long does betahistine stay in your system?
The half-life of betahistine is 3-4 hours.
When is the best time to take betahistine morning or night?
Night
What are the side effects of betahistine?
Feeling sick (nausea), indigestion, bloating or mild acne, headache
Can I take vitamin D with betahistine?
Yes
Is betahistine bad for your kidneys?
No
Is betahistine good for balance?
Yes
Does betahistine increase blood flow to the brain?
Betahistine in a dose of 16 mg three times daily is an effective antivertigo therapy, which improves blood perfusion to ischaemic areas of the brain
What is a good alternative to betahistine?
Alternatives include Flunarizine, Meclizine, and Promethazine
How many days should I take betahistine for vertigo?
3-8 weeks
Can I take betahistine with high blood pressure?
No
Can betahistine make you tired?
Yes
Does betahistine affect vision?
No
Can betahistine affect your mood?
Yes
How long does it take for betahistine to stop dizziness?
3-8 weeks